Coriaria nepalensis
Coriaria nepalensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Coriaria nepalensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5056
Guaijaverin22255-13-6
Instructions
-
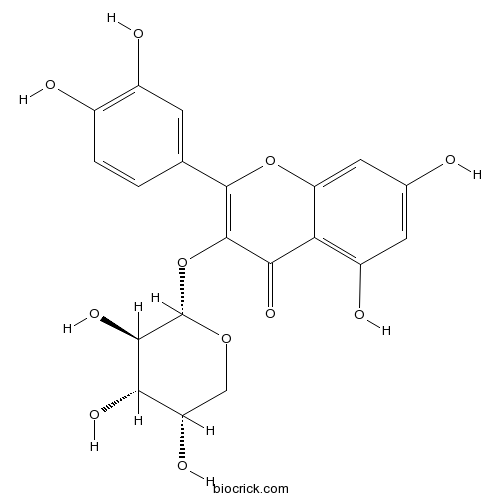
BCN5573
Afzelin482-39-3
Instructions
-
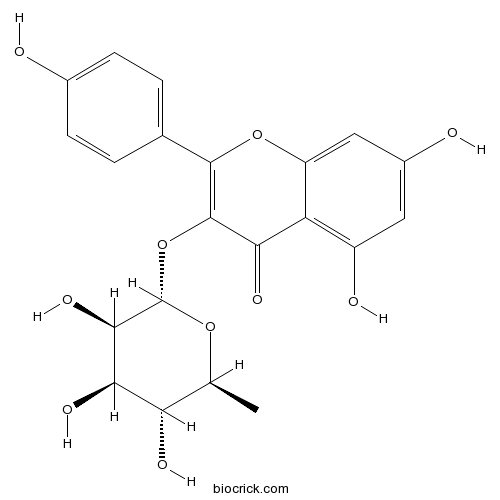
BCN4541
Kaempferol 3-O-arabinoside99882-10-7
Instructions

(P)/(M)-corinepalensin A, a pair of axially chiral prenylated bicoumarin enantiomers with a rare C-5C-5' linkage from the twigs of Coriaria nepalensis.[Pubmed: 29501013]
None
Frankia saprophytica sp. nov., an atypical, non-infective (Nod-) and non-nitrogen fixing (Fix-) actinobacterium isolated from Coriaria nepalensis root nodules.[Pubmed: 29458682]
None
Enhancing the soil heavy metals removal efficiency by adding HPMA and PBTCA along with plant washing agents.[Pubmed: 28609727]
Plant washing agents-water-extracted from Coriaria nepalensis (CN), Clematis brevicaudata (CB), Pistacia weinmannifolia (PW) and Ricinus communis (RC)-are feasible and eco-friendly for soil heavy metal removal, but their single application has limited removal efficiency. To improve their metal removal efficiencies, two biodegradable assistant agents, hydrolytic polymaleic anhydride (HPMA) and 2-phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTCA), were investigated in combination with plant washing agents through batch soil washing experiments. Results showed that the addition of HPMA or PBTCA with plant agents greatly enhanced the removal efficiencies of soil heavy metals (p<0.05). Under acidic conditions, the maximum improvements in soil heavy metal removal reached 18.69% and 18.00% for soil Cd and Zn by PW+HPMA, respectively, and 12.89% for soil Pb by CN+HPMA. Under neutral or alkaline conditions, the largest improvements in soil Cd, Pb and Zn were 24.18%, 54.38% and 25.47% by PW+PBTCA, respectively. When compared with EDTA, the loss rates of soil nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium significantly decreased (p<0.05) and the soil organic carbon significantly increased (p<0.05) after washing with the combinations. Hence, the addition of HPMA or PBTCA with the plant agents could improve the removal of soil heavy metals.
Picrotoxane Sesquiterpene Glycosides and a Coumarin Derivative from Coriaria nepalensis and Their Neurotrophic Activity.[Pubmed: 27754343]
None
Functional diversity of genes for the biosynthesis of paeoniflorin and its derivatives in Paeonia.[Pubmed: 24022687]
The Paeonia root, with or without bark, are considered vital traditional Chinese medicine materials; the examples are those of Bai Shao, Chi Shao, and Dan Pi. In this study, we examine 24 genes and their expressions involved in the biosynthesis of paeoniflorin and its derivatives, which are active compounds of the Paeonia root, in Paeonia lactiflora and P. suffruticosa, as well as other related plants, Punica granatum, Rhus radicans, and Coriaria nepalensis. Our phylogenetic analyses suggest that these genes have functional diversity, and analysis of the transcriptional level shows paeoniflorin and gallic acid biosynthesis-related genes exhibit different transcription profiles in flowers, carpels, bark-free roots, and bark of P. lactiflora. The correlation analysis of gene expression and active compound contents support the idea that hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase and phosphomevalonate kinase in the mevalonate pathway and 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase/shikimate dehydrogenase in shikimate biosynthesis are potentially closely related to the accumulation of paeoniflorin and benzoylpaeoniflorin. Coupling gene diversity with chemical analysis, we show that paeoniflorin and its derived aromatic amino acids are predominant in bark.
Draft genome sequence of Frankia sp. strain CN3, an atypical, noninfective (Nod-) ineffective (Fix-) isolate from Coriaria nepalensis.[Pubmed: 23516212]
We report here the genome sequence of Frankia sp. strain CN3, which was isolated from Coriaria nepalensis. This genome sequence is the first from the fourth lineage of Frankia, strains of which are unable to reinfect actinorhizal plants. At 10 Mb, it represents the largest Frankia genome sequenced to date.
Antifungal activity of Coriaria nepalensis essential oil by disrupting ergosterol biosynthesis and membrane integrity against Candida.[Pubmed: 21755533]
Fungal diseases in humans have increased significantly with the advent of an expanding population of immunosuppressed patients and with the introduction of sophisticated life-saving medical procedures. Plant extracts and products have been used in traditional medicine for centuries. Coriaria nepalensis essential oil (CNEO) is known to possess antimicrobial activity. This study was an attempt to examine CNEO against various fluconazole-sensitive and -resistant Candida isolates. Insight into the mechanism of action was elucidated by flow cytometric analysis and ergosterol biosynthesis studies. The susceptibility tests for CNEO were carried out in terms of MIC and by disc diffusion assays against all Candida isolates, employing standard protocols. Insight into the mechanism of action was elucidated by propidium iodide cell sorting (FACS) and by assessing ergosterol content in treated and untreated isolates with the test entity. CNEO was found effective against all Candida isolates, including the resistant strains. While CNEO inflicts fungal cell death by disrupting membrane integrity, significant impairment of ergosterol biosynthesis was induced by the test entity. CNEO showed a strong antifungal effect against all the Candida isolates. Mechanisms of action appear to originate from the inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis and the disruption of membrane integrity. It can be concluded that the observed antimicrobial characteristics of C. nepalensis indicate that it might be a promising antimicrobial agent.
Antimicrobial activities of essential oil and methanol extract of Coriaria nepalensis.[Pubmed: 21726130]
Plant extracts and products have been used for centuries in traditional medicine; for most of them, in addition to the scant scientific credibility, the chemical composition and spectrum of activity are yet to be explored. To put forward this effort and to identify novel antimicrobial agents, the inhibitory activities of methanolic extract and essential oil from Coriaria nepalensis against various microorganisms including pathogenic yeast, and Gram-positive and negative bacteria were evaluated. Chemical compositions of C. nepalensis methanolic extract and essential oil were analysed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. In vitro susceptibility tests against all the tested isolates were performed in terms of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), and well diffusion assay using standard protocols. All microorganisms tested were profoundly found susceptible to both the C. nepalensis extract and oil with MIC values of 1.3-2.1 mg mL⁻¹ (Gram-positive bacteria), 1.4-2.2 mg mL⁻¹ (Gram-negative bacteria) and 0.9-1.6 mg mL⁻¹ (yeasts). The extent of inhibition was shown more by methanolic extract than by essential oil. This study is the first to report the antimicrobial activity of extracts obtained from the C. nepalensis. It can be concluded that the observed antimicrobial characteristics of C. nepalensis indicate that it might be a promising antimicrobial agent.


