Corydalis bungeana
Corydalis bungeana
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Corydalis bungeana
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6165
Protopine130-86-9
Instructions
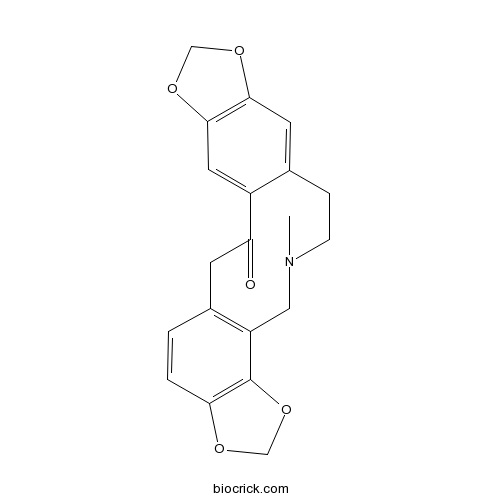
-
BCN1235
(+)-Corynoline18797-79-0
Instructions

-
BCN1239
Acetylcorynoline18797-80-3
Instructions
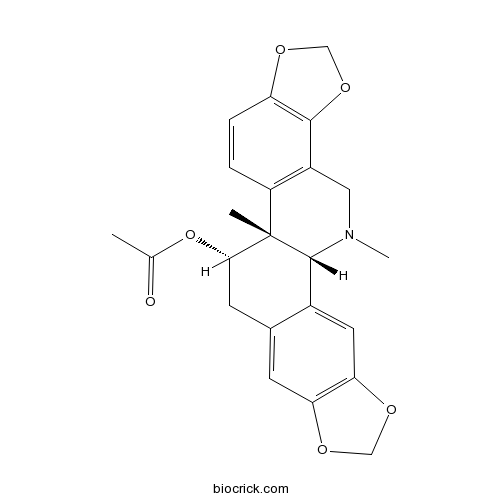
-
BCN7827
Cheilanthifoline483-44-3
Instructions
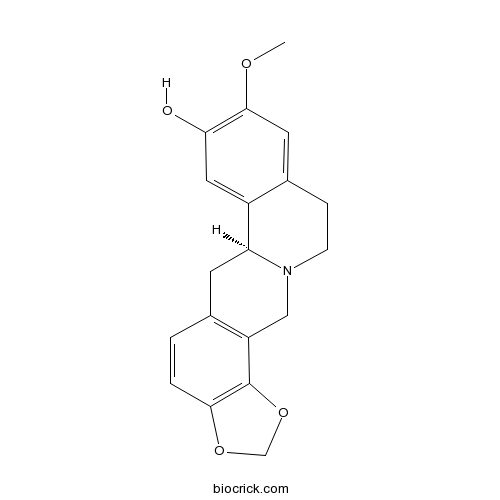
-
BCN4213
N-trans-Feruloyltyramine66648-43-9
Instructions

Hexahydrobenzophenanthridine alkaloids from Corydalis bungeana Turcz. and their anti-inflammatory activity.[Pubmed: 29853329]
None
Corynoline attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by activating Nrf2.[Pubmed: 28486213]
Corynoline, isolated from Corydalis bungeana Turcz, has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory and antibacterial activities. In this study, we aimed to explore the treatment effect of corynoline on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) in mice. In the present study, the signaling pathways were measured by Western blot analysis. The levels of inflammatory cytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Additionally, the effects of corynoline on LPS-induced myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was examined. The results showed that corynoline markedly inhibited LPS-induced neutrophils influx, MPO activity, and inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 release. Corynoline also attenuated lung histopathological changes induced by LPS. Furthermore, corynoline inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB activation. In addition, corynoline up-regulated the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 in a dose-dependent manner. The data suggest that corynoline has a treatment effect on LPS-induced ALI in mice by inhibiting inflammatory response.
Corydalis bungeana Turcz. attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses via the suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 27616027]
Corydalis bungeana Turcz. (C. bungeana) is one of traditionally used medicines in China and possesses various biological effects, such as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial activity and inhibition of the immune function of the host.
Corynoline Isolated from Corydalis bungeana Turcz. Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Effects via Modulation of Nfr2 and MAPKs.[Pubmed: 27472313]
Corydalis bungeana Turcz. is an anti-inflammatory medicinal herb used widely in traditional Chinese medicine for upper respiratory tract infections. It is demonstrated that corynoline is its active anti-inflammatory component. The nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/antioxidant response element (ARE) pathway and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway play important roles in the regulation of inflammation. In this study, we investigated the potential anti-inflammatory mechanism of corynoline through modulation of Nfr2 and MAPKs. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW264.7 cells were used to explore modulatory role of NO production and the activation of signaling proteins and transcription factors using nitrite assay, Western bloting and qPCR. Treatment with corynoline reduced production of nitric oxide (NO) and the protein and mRNA levels of inducible nitric oxide (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Treatment also significantly increased the expression of Nrf2, quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) and hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1) at the mRNA and protein levels, which demonstrated that corynoline may protect cells from inflammation through the Nrf2/ARE pathway In addition, corynoline suppressed the expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), at the mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, molecular data revealed that corynoline inhibited lipopolysaccharide-stimulated phosphorylation of c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38. Taken together, these results suggest that corynoline reduces the levels of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α and IL-1β, by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK) and p38 phosphorylation in RAW264.7 cells, which is regulated by the Nrf2/ARE pathway. These findings reveal part of the molecular basis for the anti-inflammatory properties of corynoline.
[Study on UPLC Fingerprint of Corydalis bungeana].[Pubmed: 26983233]
To establish an Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography fingerprint of Corydalis bungeana from different habitats.
Simultaneous determination of corynoline and acetylcorynoline in human urine by LC-MS/MS and its application to a urinary excretion study.[Pubmed: 26882127]
Corynoline and acetycorynoline, the major active components derived from Corydalis bungeana Herba, showed multiple pharmacological activities. However, quantification of the two compounds in human urine has not been reported. A simple liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of corynoline and acetycorynoline in human urine has been developed and fully validated. The analytes were extracted from urine samples by simple liquid-liquid extraction. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a Hedera ODS-2C18 column with the mobile phase of water (containing 0.5% formic acid) and acetonitrile (28:72, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.4mL/min. A tandem mass spectrometric detection was conducted using multiple reaction monitoring via an electrospray ionization source in positive mode. The monitored ion transitions were m/z 368.1→289.1 for corynoline, m/z 410.2→289.2 for acetycorynoline and m/z 380.2→243.2 for donepezil (internal standard), respectively. The calibration curves were linear (correlation coefficients>0.9970) over the concentration ranges of 3.0-3000pg/mL for corynoline and 3.0-1000pg/mL for acetycorynoline. The established method was highly sensitive with the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of 3.0pg/mL for both analytes. The intra- and inter-day precision was lower than 10% in terms of relative standard deviation for the low, medium, and high quality control samples, and lower than 16% for the LLOQ samples of the analytes. The accuracy was within ±10% in terms of relative error for both analytes. The method was successfully applied to a urinary excretion study after oral administration of the Chinese medicine formula Shuanghua Baihe tablets in healthy volunteers. The urinary excretion profiles of corynoline and acetycorynoline in human were first reported. The results of this study suggest that renal excretion was not the main excretion pathway of corynoline and acetycorynoline in humans.
Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetics of five alkaloids in rat plasma by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry after the oral administration of Corydalis bungeana Turcz extract.[Pubmed: 26805956]
Pharmacokinetic studies were conducted on rats for protopine, corynoline, 7'-(3',4'-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)-ethyl]propenamide, acetylcorynoline, and 8-oxocorynoline, five main active components from Corydalis bungeana Turcz (C. bungeana Turcz). An ultra high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method has been developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of the pharmacokinetic characteristics of these components in rat plasma. Chromatographic separation was achieved on an Agilent SB-C18 column (1.8 μm, 150 × 2.1 mm) using a gradient elution program with a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and water containing 0.1% acetic acid at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. The analytes were detected in the multiple reaction monitoring mode with positive electrospray ionization. Lower limits of quantification were >0.680 ng/mL and matrix effects ranged from 91.26 to 100.38%. The mean extraction recoveries of quality control samples were less than 79.32%, and the precision and accuracy were within the acceptable limits. All analytes were proven to be stable during sample storage and analysis procedures. The validated method was successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic study of five alkaloid components after oral administration of C. bungeana Turcz extract to rats. The obtained results may be helpful to reveal the mechanism of action and to guide the clinical application of C. bungeana Turcz.
Screening for anti-inflammatory components from Corydalis bungeana Turcz. based on macrophage binding combined with HPLC.[Pubmed: 26471417]
Corydalis bungeana Turcz. (CB; family: Corydalis DC.) is an anti-inflammatory medicinal herb used widely in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for upper respiratory tract infection, etc., but its anti-inflammatory active molecules are unknown. This study was designed to screen for the anti-inflammatory components from CB based on macrophage binding combined with HPLC.


