Crotalaria sessiliflora
Crotalaria sessiliflora
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Crotalaria sessiliflora
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
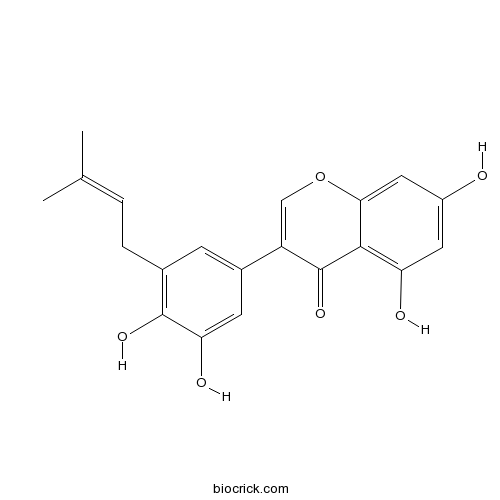
BCN2930
Glycyrrhisoflavone116709-70-7
Instructions
-
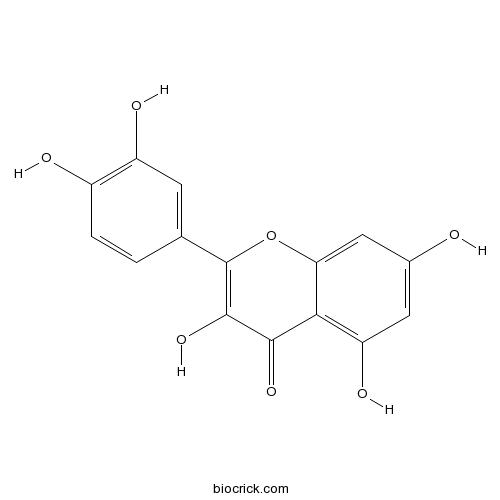
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
-
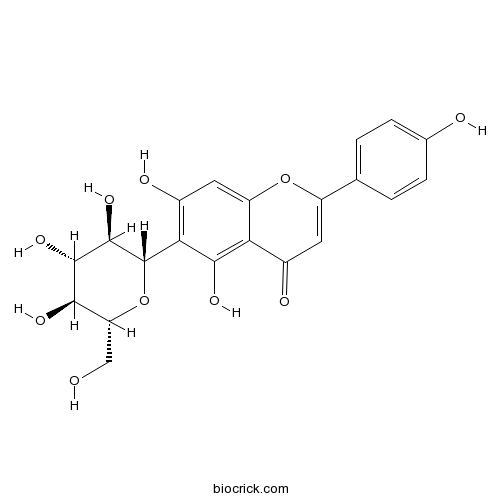
BCN5441
Isovitexin38953-85-4
Instructions
-
BCN5499
Genistein446-72-0
Instructions

-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions

-
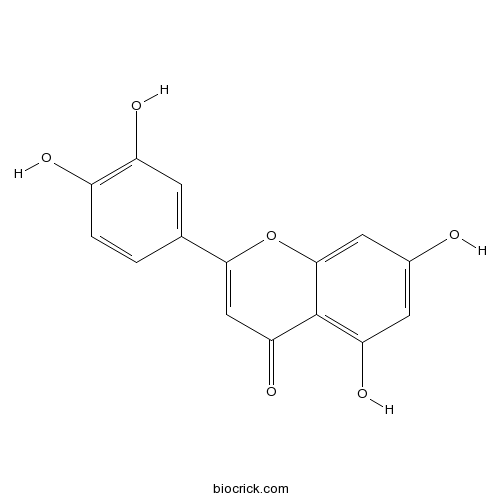
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN5653
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
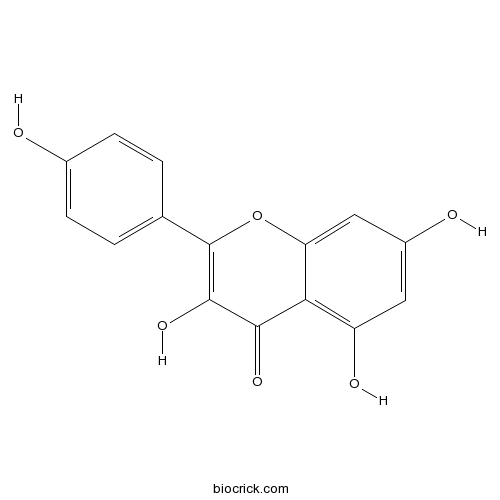
-
BCN5665
Quercitrin522-12-3
Instructions
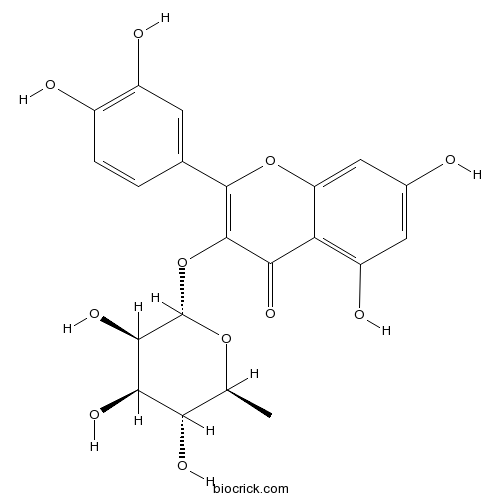
-
BCN2929
Licoisoflavone A66056-19-7
Instructions

Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Hyphenated with Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for Simultaneous Determination of Necine-Core-Structure Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Crotalaria sessiliflora L. without all Corresponding Standards.[Pubmed: 28332747]
Crotalaria sessiliflora L. is a Chinese traditional herb for treatment of cutaneum carcinoma and cervical carcinoma. In addition to monocrotaline, coexisting pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) also require further quantification for quality control and pharmaceutical uses of the herb.
[Chemical constituents from Crotalaria sessiliflora L.].[Pubmed: 29877686]
In this study, we isolated and purified the extracts of the whole plant of Crotalaria sessiliflora L. by column chromatographic.Twelve compounds were isolated and identified as followings: sessiliflorin B(1), quercetin (2), kaempferol (3), soyasapogenol B(4), fernenol (5), neoechinulin A(6), ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate (7), ethyl caffeate (8), 5,7-dihydroxychromone(9), crotadihydrofuran A(10), butesuperin B(11) and aurantiamide acetate(12).Compound 1 is a new compound, compound 3-12 were isolated from the plant for the first time.
Estrogenic and Acetylcholinesterase-Enhancement Activity of a New Isoflavone, 7,2',4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone-4'-O-beta-D-Glucopyranoside from Crotalaria Sessililflora.[Pubmed: 19003217]
A new isoflavone, 7,2',4'-trihydroxyisoflavone-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside has been isolated from the aerial part of Crotalaria sessiliflora. The isoflavone glucoside enhanced the proliferation of the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line, which possesses estrogen receptor (ER) and responds to estrogen in culture. The estrogenic property of the isoflavone glucoside was blocked by the known ER antagonist tamoxifen, indicating the involvement of the ER. Furthermore, the isoflavone glucoside was found to enhance the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity of the rat neuronal cell line PC12 at low concentrations of nerve growth factor (NGF).
Endothelium-dependent vasodilatory and hypotensive effects of Crotalaria sessiliflora L. in rats.[Pubmed: 17202658]
The aim of the present study was to investigate the vasoactive effect of Crotalaria sessiliflora L. extract (CSE) on rats and its mechanism when combining in vivo and in vitro approaches. CSE (0.5-5 mg/ml) induced concentration-dependent relaxation on endothelium-intact thoracic aortic rings precontracted with phenylephrine (PE, 10(-5) M). This effect disappeared with the removal of functional endothelium. Pretreatment of the aortic strips with either N(G)-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA, 10(-5) M) or methylene blue (10(-5) M) significantly reduced the relaxation induced by CSE. The endothelium-dependent relaxation caused by CSE was associated with production of cGMP. CSE (5 mg/ml) increased the production of cGMP in endothelium-intact aortic rings and this effect was significantly attenuated by L-NNA (10(-5) M) and methylene blue (10(-5) M). Relaxation in response to CSE in strips precontracted with PGF2alpha (3x10(-5) M) was eliminated by removing extracellular Ca2+ and significantly reduced by pretreatment with ruthenium red (10(-5) M). In in vivo tests, injection of 40 mg/kg of CSE induced an increase in plasma NO production, and this effect was blocked by L-NNA. Furthermore, CSE produced dose-dependent and transient decrease in blood pressure in normotensive rats and this effect was blocked by atropine as well as L-NNA. These findings suggest that CSE induces endothelium-dependent relaxation via NO/cGMP signaling by promoting extracellular Ca2+ influx and the release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores of endothelium, probably due to endothelial muscarinic receptor activation.
Flavonoids of Crotalaria sessiliflora.[Pubmed: 15202561]
Phytochemical investigation of the whole plants of Crotalaria sessiliflora L. led to the isolation of four flavonoids. The structures of these compounds were identified as 2',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyisoflavone (1), 2',4',7-trihydroxyisoflavone (2), 4',7-dihydroxyflavone (3), and isovitexin (4) using spectroscopic analysis. Among these, compounds 2, and 3 have not been reported from Crotalaria species, whereas compounds 1, and 4 were reported from this plant for the first time.
Antioxidative compounds from Crotalaria sessiliflora.[Pubmed: 12729010]
Seven antioxidative compounds were isolated from the EtOAc extract of the aerial part of C. sessiliflora (Japanese name, tanukimame) by activity-guided fractionation with 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH). Among the isolated compounds, hydroxyeucomic acid showed the strongest free radical-scavenging activity, which was almost identical to that of epigallocatechin gallate, against DPPH. Orientin and isoorientin showed strong anti-peroxidative activities toward linoleic acid and protective effects against the bactericidal action of the tert-butyl peroxyl radical. Their activities were nearly equal to that of epigallocatechin gallate.


