Cyclocarya paliurus
Cyclocarya paliurus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Cyclocarya paliurus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCC8952
Docosanoic acid112-85-6
Instructions

-
BCN5911
1-Caffeoylquinic acid1241-87-8
Instructions

-
BCN5569
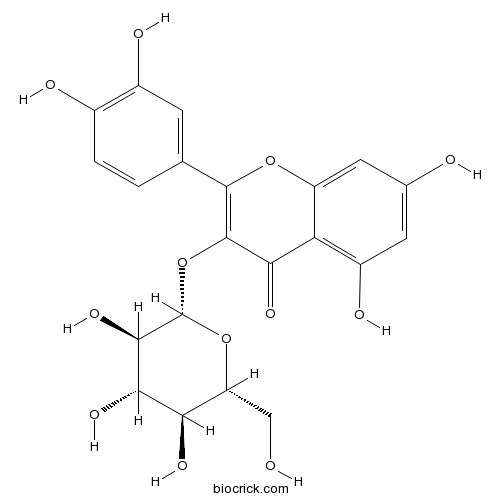
Isoquercitrin482-35-9
Instructions
-
BCN5653
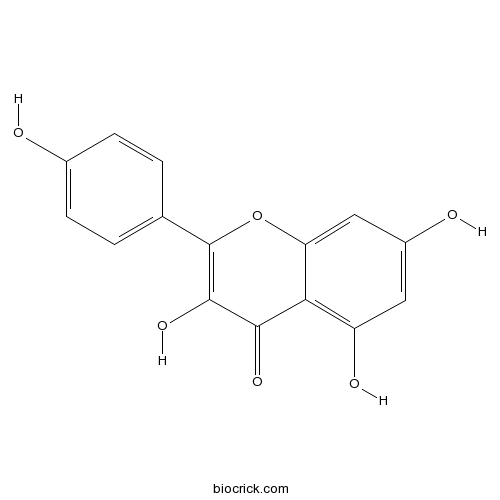
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
-
BCN5656
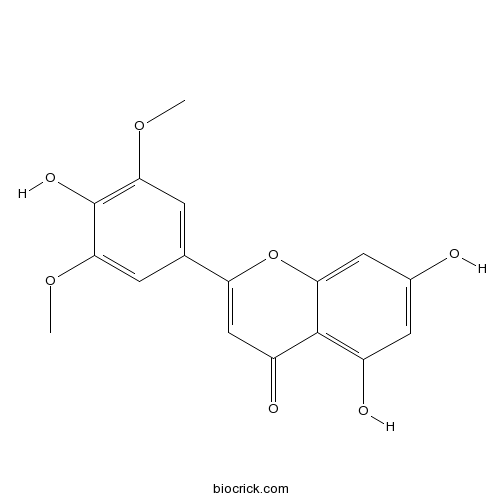
Tricin520-32-1
Instructions
-
BCN3820
Stearic Acid57-11-4
Instructions

-
BCN5807
Caffeine58-08-2
Instructions

Triterpenic acids-enriched fraction from Cyclocarya paliurus attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via improving oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.[Pubmed: 29775890]
The effects of triterpenic acids-enriched fraction from Cyclocarya paliurus (CPT) on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) were investigated using in vivo and in vitro models. In high fat diet-induced Wister rats, CPT significantly increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and glutathione/oxidized glutathione (GSH/GSSG) ratio, reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl (PCO) levels. Moreover, CPT restored mitochondrial membrane potential dysfunction, decreased cytochrome P450 enzyme 2E1 (CYP2E1) activity, improved nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase1 (HO-1) expression. In free fatty acids-induced HepG2 cells, CPT dramatically decreased ROS content, increased mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) and mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase (Complex IV) levels. Furthermore, CPT could upregulate HO-1, quinine oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) expression, and increase Nrf2 translocation from cytoplasm-to-nucleus. The results indicated CPT could protect mitochondria function and improve oxidative stress by activating Nrf2. Therefore, it can be inferred that CPT may be a potential agent against NAFLD.
Pentacyclic triterpenoids from Cyclocarya paliurus and their antioxidant activities in FFA-induced HepG2 steatosis cells.[Pubmed: 29679877]
None
New dammarane triterpenoid saponins from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus.[Pubmed: 29614867]
Three new dammarane triterpenoid saponins, cyclocariosides O-Q (1-3), were isolated from the ethanolic extracts of the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus. The structures of these compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic methods.
Antihyperlipidemic and hepatoprotective activities of polysaccharide fraction from Cyclocarya paliurus in high-fat emulsion-induced hyperlipidaemic mice.[Pubmed: 29352865]
The objective of this study was to analyse the structure of CPP-2, and to observe the pharmacological effects of CPP-2 on lipid metabolism and oxidative stress. CPP-2, eluted as two main fractions comprised of two polysaccharides with Mw of 307 and 3.7kDa, was mainly consisted of rhamnose, mannose, glucose and galactose in a molar ratio of 1.00:0.78:3.22:0.45. The results showed that treatment with CPP-2 could improve blood lipid levels (TC, TG, HDL-C and LDL-C), liver lipid levels (TC and TG) and antioxidant status (SOD, T-AOC, GSH-PX, MDA and LPO). In addition, the histopathological observations of mice livers and the GPT activities indicated that CPP-2 could attenuate liver cell injury. The present findings demonstrated that CPP-2 might be effective in lowering lipid and protecting against HFE-induced hyperlipidemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver.
Protective effect of flavonoids from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice.[Pubmed: 29337229]
None
Light quality affects flavonoid production and related gene expression in Cyclocarya paliurus.[Pubmed: 29334625]
Understanding the responses of plant growth and secondary metabolites to differential light conditions is very important to optimize cultivation conditions of medicinal woody plants. As a highly valued and multiple function tree species, Cyclocarya paliurus is planted and managed for timber production and medical use. In this study, LED-based light including white light (WL), blue light (BL), red light (RL), and green light (GL) were used to affect leaf biomass production, flavonoid accumulation and related gene expression of one-year C. paliurus seedlings in controlled environments. After the treatments of 60 days, the highest leaf biomass appeared in the treatment of WL, while the lowest leaf biomass was found under GL. Compared to WL, the total flavonoid contents of C. paliurus leaves were significantly higher in BL, RL, and GL, but the highest values of selected flavonoids (kaempferol, isoquercitrin and quercetin) were observed under BL. Furthermore, the greatest yields of total and selected flavonoids in C. paliurus leaves per seedling were also achieved under BL, indicating that blue light was effective for inducing the production of flavonoids in C. paliurus leaves. Pearson's correlation analysis showed that there were significantly positive correlations between leaf flavonoid content and relative gene expression of key enzymes (phenylalanine ammonia lyase, PAL; 4-coumaroyl CoA-ligase, 4CL; and chalcone synthase, CHS) in the upstream, which converting phenylalanine into the flavonoid skeleton of tetrahydroxy chalcone. It is concluded that manipulating light quality may be potential mean to achieve the highest yields of flavonoids in C. paliurus cultivation, however this needs to be further verified by more field trials.
New tetralone derivatives from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus.[Pubmed: 29210285]
None
Chemical Fingerprint and Multicomponent Quantitative Analysis for the Quality Evaluation of Cyclocarya paliurus Leaves by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS.[Pubmed: 29112173]
Cyclocarya paliurus is an edible and medicinal plant containing various bioactive components with significant health benefits. A combinative method using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) fingerprint and quantitative analysis was developed and successfully applied for characterization and quality evaluation of C. paliurus leaves collected from 18 geographical locations of China. For the fingerprint analysis, 21 common peaks were observed among the 18 samples, and these peaks were identified by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF-MS), while a simultaneous quantification of 16 markers was conducted to interpret the variations of contents of these bioactive compounds among the C. paliurus leaves from different geographical locations. Quantification results showed that the contents of these sixteen investigated compounds varied greatly among the leaves from different locations. The developed new method would be a valuable reference for further study and development of this bioactive plant.


