Dendrobium nobile
Dendrobium nobile
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
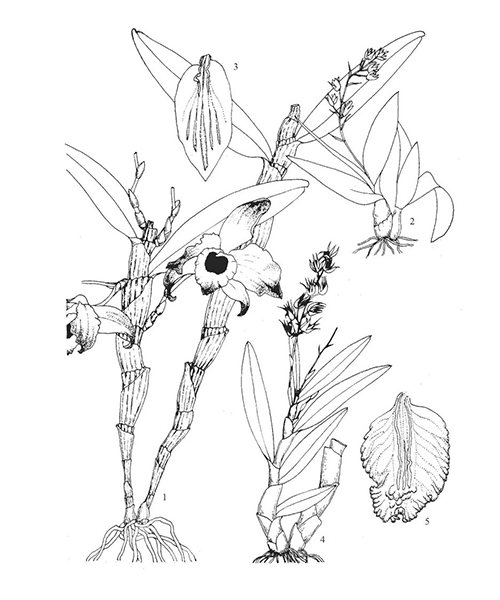
Natural products/compounds from Dendrobium nobile
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
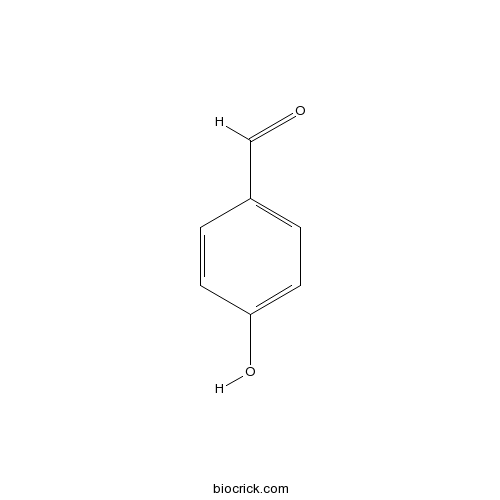
BCN5816
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde123-08-0
Instructions
-
BCN5923
Dendrobine2115-91-5
Instructions

-
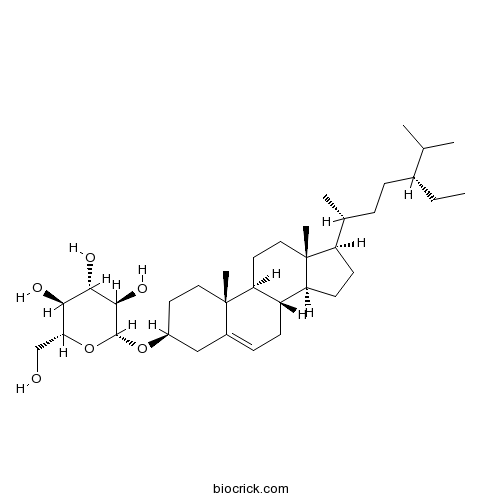
BCN5531
Daucosterol474-58-8
Instructions
-
BCN5567
Chrysophanol481-74-3
Instructions

-
BCN5699
Syringic acid530-57-4
Instructions

-
BCN1263
Narcissoside604-80-8
Instructions

Characterization and antifungal activity against Pestalotiopsis of a fusaricidin-type compound produced by Paenibacillus polymyxa Y-1.[Pubmed: 29933995]
Dendrobium nobile (D. nobile) is a valuable Chinese herbal medicine. The discovery of microbial resources from has provided a wealth of raw materials. Stalk rot, which is caused by Pestalotiopsis, is one of the most serious diseases of D nobile and has resulted in serious losses in production. However, an effective method for the prevention and control of stalk rot remains lacking. In this study, we aimed to identify a biocontrol strain against Pestalotiopsis. We isolated Paenibacillus polymyxa Y-1, an endophytic bacterium, from the stem of D. nobile. Three pairs of active metabolites isolated from this bacterium were identified as fusaricidin compounds. We then investigated the mechanism of fusaricidin compounds on Pestalotiopsis via proteomics. Proteomics data showed that the compounds mainly inhibit energy generation in the respiratory chain and amino acid biosynthesis of Pestalotiopsis.
Dendrobium nobile Lindley and its bibenzyl component moscatilin are able to protect retinal cells from ischemia/hypoxia by dowregulating placental growth factor and upregulating Norrie disease protein.[Pubmed: 29933759]
Presumably, progression of developmental retinal vascular disorders is mainly driven by persistent ischemia/hypoxia. An investigation into vision-threatening retinal ischemia remains important. Our aim was to evaluate, in relation to retinal ischemia, protective effects and mechanisms of Dendrobium nobile Lindley (DNL) and its bibenzyl component moscatilin. The therapeutic mechanisms included evaluations of levels of placental growth factor (PLGF) and Norrie disease protein (NDP).
Study on the Polar Extracts of Dendrobium nobile, D. officinale, D. loddigesii, and Flickingeria fimbriata: Metabolite Identification, Content Evaluation, and Bioactivity Assay.[Pubmed: 29762539]
None
Dendrocoumarin: a new benzocoumarin derivative from the stem of Dendrobium nobile.[Pubmed: 29308678]
A new benzocoumarin derivative, dendrocoumarin (1), along with itolide A were isolated from the stems of Dendrobium nobile. The structure of the new compound 1 elucidated on the basis of NMR and mass spectroscopic data. Compounds 1 and 2 showed broad spectrum antibacterial activity against five terrestrial pathogenic bacteria.
Influence of light intensity and water content of medium on total dendrobine of Dendrobium nobile Lindl.[Pubmed: 29203109]
To ascertain the influence of light intensity and water content of medium on the total dendrobine of Dendrobium nobile (D. nobile).
[DNA marker-assisted selection of medicinal plants (Ⅰ) .Breeding research of disease-resistant cultivars of Panax notoginseng].[Pubmed: 28945026]
SSR is one of the most important molecular markers used in molecular identification and genetic diversity research of Dendrobium nobile. In order to enrich the library of SSR and establish a method for rapid identification of D. nobile, the SSR information was analyzed in the transcriptome of D. nobile. A total of 32 709 SSRs were obtained from the transcriptome of D. nobile, distributed in 26 742 unigenes with the distribution frequency of 12.90%. SSR loci occurred every 3 748 bp. Mono-nucleotide repeat was the main type, account for as much as 72.18% of all SSRs, followed by di-nucleotide (15.97%) and tri-nucleotide (11.19%). Among all repeat types, A/T was the predominant one followed by AG/CT. Finally a total of 62 157 primer pairs were designed for marker development. Randomly 20 pairs of primers were selected for PCR amplification, 17 amplified on clear and reproducible bands, the amplification rate was 85.0%.Thirteen pairs were polymorphic among the 3 Dendrobium plants. The results indicated that the unigenes generated from transcriptome sequencing in D. nobile can be used as effective source to develop SSR markers. The SSR loci in the transcriptome of D. nobile have the characteristics of type riches, high density and high potential of polymorphism, and these characteristics might applied in the study of molecular identification, genetic diversity and marker-assisted breeding of D. nobile and its closely related species.
Protective effects of polysaccharide from Dendrobium nobile against ethanol-induced gastric damage in rats.[Pubmed: 28867231]
Dendrobium nobile is a medicinal herb in traditional China and Southeast Asian countries. Employing a rat model of ethanol-induced gastric ulcer, we examined the protective effect of polysaccharide (JCP) extracted from Dendrobium nobile and explored the related mechanisms. Oral administration with 100mg/kg and 300mg/kg body weight JCP for days can significant prevent the formation of gastric ulcer. Moreover, JCP pretreatment could alleviate ethanol-induced histological damage, antioxidant activities, the level of epidermal growth factor, gastric concentration of prostaglandin E, and regulate the signaling pathways of mitogen-activated protein kinases and matrix metalloproteinases. This study investigated the ethanol-induced gastric ulcer protective effect of JCP for the first time, and elucidated that the protective mechanisms.
Exogenous Catalase and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Improve Survival and Regeneration and Affect Oxidative Stress in Cryopreserved Dendrobium nobile Protocorm-like Bodies.[Pubmed: 28767746]
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced oxidative damage is responsible for viability loss in plant tissues following cryopreservation. Antioxidants may improve viability by preventing or repairing the injury.


