Descurainia sophia
Descurainia sophia
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Descurainia sophia
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
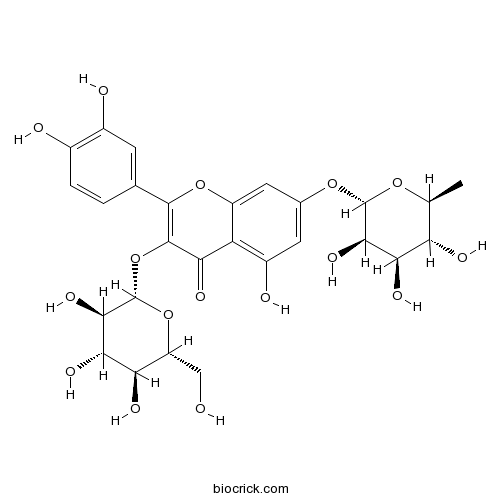
BCN1520
Quercetin 3-O-glucoside-7-O-rhamnoside18016-58-5
Instructions
-
BCN2851
Quercetin 3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside549-32-6
Instructions

-
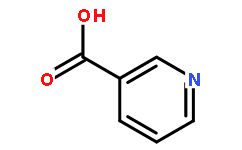
BCN8328
Nicotinic acid59-67-6
Instructions
-
BCN7821
Quercetin 3-O-beta-D-glucose-7-O-beta-D-gentiobioside60778-02-1
Instructions

Effects of resistance mutations of Pro197, Asp376 and Trp574 on the characteristics of acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) isozymes.[Pubmed: 29424952]
Descurainia sophia L., a problematic weed in winter wheat fields in China, has developed high resistance to tribenuron-methyl. Amino acid substitutions at sites Pro197, Asp376 and Trp574 in the target acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) were primarily responsible for D. sophia resistance to tribenuron-methyl. In this study, purified subpopulations of D. sophia plants individually homozygous for a specific resistance mutation (Pro197Leu, Pro197His, Pro197Ser, Pro197Thr, Asp376Glu or Trp574Leu) in AHAS were generated, and the effects of resistance mutations on D. sophia resistance and AHAS characteristics were investigated.
Lead, zinc, and cadmium uptake, accumulation, and phytoremediation by plants growing around Tang-e Douzan lead-zinc mine, Iran.[Pubmed: 29322395]
In the current study, soils of Tang-e Douzan mine, located in Isfahan, Iran, were collected and analyzed for soluble, exchangeable, and total amounts of Pb, Zn, Cd, Ca, and Mg. The maximum Pb, Zn, Cd, Ca, and Mg concentrations in soils were 2500, 1100, 59, 43,800, and 1320 mg/kg for total metals, 86, 83, 6.3, 4650, and 48 mg/kg for their exchangeable fractions, and 59, 3.7, 0.53, 430, and 6.4 mg/kg for their soluble fractions, respectively. All specimens collected, including 69 plant species, were analyzed for Pb, Zn, and Cd. Moreover, their phytoremediation potential was investigated by calculating bioconcentration factors (BCF), translocation factors (TF), and extraction factors (EF) for each heavy metal. Analysis of the leaves for heavy metals showed no metal hyperaccumulation. The highest shoot concentrations of Pb (298 mg/kg) and Zn (740 mg/kg) were found in Roemeria hybrida subsp. dodecandra and Cd (43 mg/kg) in Chenopodium foliosum. Plants having BCFs and TFs > 1 are capable of phytoextraction. Among the analyzed species, four had both TFs and BCFs > 1 for Zn, 13 for Cd, and none for Pb. R. hybrida, Bromus squarrosus, Descurainia sophia, and Poa bulbosa seem to be the best choices for phytoextraction of Zn. Aegilops columnaris, Allium ampeloprasum subsp. iranicum, B. squarrosus, and Cousinia piptocephala are the best choices for phytoextraction of Cd. Plants with BCF > 1 and TF < 1, including Cerastium dichotomum and Muscari neglectum for Pb, Ceratocephala falcata, M. neglectum, Ornithogalum orthophyllum, and Ranunculus arvensis for Zn and C. falcata, M. neglectum, O. orthophyllum, and R. hybrida subsp. dodecandra for Cd, are proposed to be the most efficient species for metal phytostabilization.
Resistance mutations of Pro197, Asp376 and Trp574 in the acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) affect pigments, growths, and competitiveness of Descurainia sophia L.[Pubmed: 29180697]
D. Sophia is one of the most problematic weed species infesting winter wheat in China, and has evolved high resistance to tribenuron-methyl. Amino acid substitutions at site of Pro197, Asp376 and Trp574 in acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) were mainly responsible for D. sophia resistance to tribenuron-methyl. In this study, D. sophia plant individually homozygous for specific AHAS mutation (Pro197Leu, Pro197His, Pro197Ser, Pro197Thr, Asp376Glu and Trp574Leu) were generated. In addition, the effects of resistance mutations on pigments, growths and competitiveness of susceptible (S) and resistant (R) plants of D. sophia were investigated. The results indicated the R plants carrying Pro197Leu or Pro197His or Asp376Glu or Trp574Leu displayed stronger competitiveness than S plants. The adverse effects on R plants aggravated with the increase of R plants proportion, which made the R plants against domination the weed community in absent of herbicide selection. Therefore, these resistance mutation have no obvious adverse effects on the pigments (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoid), relative growth rates (RGR), leaf area ratio (LAR) and net assimilation rate (NAR) of R plants.


