Dracaena cochinchinensis
Dracaena cochinchinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
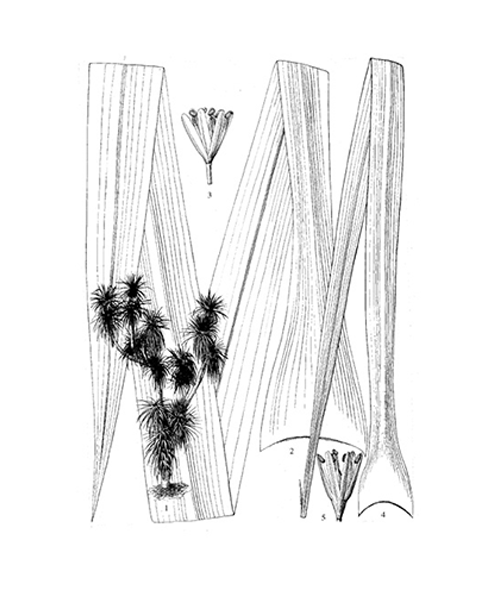
Natural products/compounds from Dracaena cochinchinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN3671
Loureirin A119425-89-7
Instructions

-
BCN5021
Loureirin B119425-90-0
Instructions

-
BCN6277
Echinatin34221-41-5
Instructions
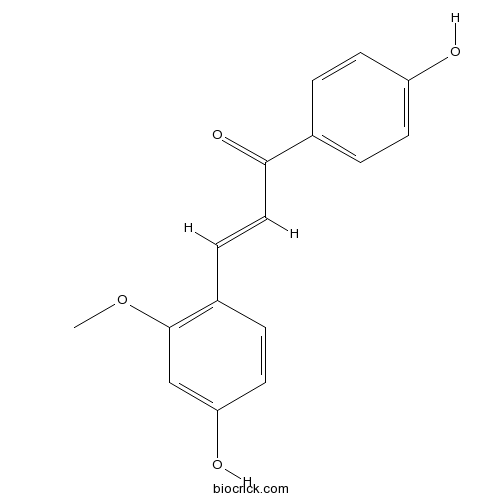
-
BCN5531
Daucosterol474-58-8
Instructions
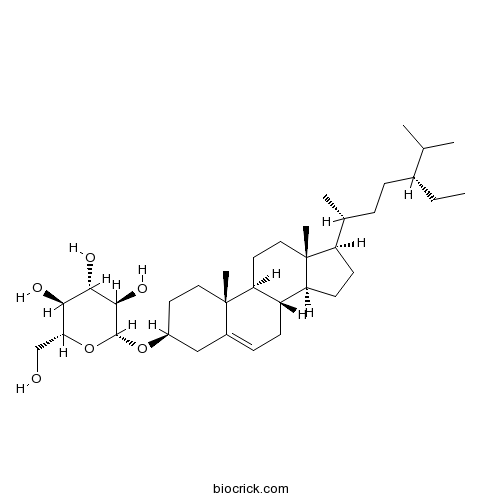
-
BCN5607
Resveratrol501-36-0
Instructions

-
BCN2539
Pterostilbene537-42-8
Instructions

-
BCN5946
Liquiritigenin578-86-9
Instructions

-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Fingerprint analysis of Resina Draconis by ultra-performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed: 29086860]
Resina Draconis, a bright red resin derived from Dracaena cochinchinensis, is a traditional medicine used in China. To improve its quality control approach, an ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) fingerprint method was developed for rapidly evaluating the quality of Resina Draconis.
Flavonoid dimers from the total phenolic extract of Chinese dragon's blood, the red resin of Dracaena cochinchinensis.[Pubmed: 27769819]
None
Isolation and chatacterization of homoisoflavonoids from Dracaena cochinchinensis and their osteogenic activities in mouse mesenchymal stem cells.[Pubmed: 27497307]
Two new homoisoflavonoids, dracaeconolide A (1) and dracaeconolide B (2), together with ten known compounds, namely (3R)-7,4'-dihydroxy-8-methoxyhomoisoflavane (3), (3R)-7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)chromane (4), (3R)-7,4'-dihydroxy-5-methoxy-homoisoflavane (5), (3R)-6,4'-dihydroxy-8-methoxyhomoisoflavan (6), 7,4'-dihydroxy-8-methylflavan (7), (2R)-7,4'-dihydroxy-5-methoxy-8-methylflavan (8), 5,4'-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-6-methylflavane (9), 7,4'-dihydroxy-3'-methoxyflavan (10), 7,4'-dihydroxyflavan (11), 4,4'-dihydroxy-2,6-dimethoxydihydrochlcone (12), were isolated from the red resin of Dracaena cochinchinensis (dragon's blood, DB). All the compounds were then evaluated for their effects on mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) proliferation using CCK8 assay and their abilities in promoting MSCs differentiating into osteoblast through the assay of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in vitro. Compounds 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, and 11, at a concentration of 10μM with no cytotoxicity, significantly promoted MSC osteogenic differentiation by increasing the levels of ALP activity to percents of 159.6±5.9, 167.6±10.9, 162.0±1.4, 151.3±4.0, 171.0±8.2, and 169.9±7.3 in relative to the control, respectively. The results of ALP staining were in accordance to that of ALP activity.
[New study on species of Chinese medicine dragon's blood].[Pubmed: 28879755]
Through comprehensive study on the descriptions of dragon's blood in traditional medical books, we pointed out that before Tang Dynasty, Butea monosperma was used as dragon's blood; during Tang and Song Dynasty, Liquidambar formosana. was used as dragon's blood; in Commentaries on the illustrations of Song Dynasty, the author made a mistake by combined the descriptions of Butea monosperma with the descriptions of the prepared medicine of Dracaena cochinchinensis in dragon's blood, and thus the oversea species D. cochinchinensis became the mainstream of dragon's blood source in homeland. Until the foundation of the Republic of China, Daemonorops draco replaced D. cochinchinensis to the main source of dragon's blood.
Longxuetongluo Capsule Improves Erythrocyte Function against Lipid Peroxidation and Abnormal Hemorheological Parameters in High Fat Diet-Induced ApoE-/- Mice.[Pubmed: 26649134]
Chinese dragon's blood, the red resin of Dracaena cochinchinensis, one of the renowned traditional medicines, has been used to facilitate blood circulation and disperse blood stasis for thousands of years. Phenolic compounds are considered to be responsible for its main biological activities. In this study, total phenolic compounds of Chinese dragon's blood were made into capsule (Longxuetongluo Capsule, LTC) and their effects on the abnormal hemorheological properties were examined by high fat diet (HFD) induced ApoE-/- mice. Compared to the model group, LTC recovered the abnormal hemorheological parameters in HFD-induced ApoE-/- mice by reducing whole blood viscosity (WBV) at high rate and improving erythrocyte function. In conclusion, LTC could ameliorate erythrocyte deformability and osmotic fragility through the reduction of lipid peroxidation on plasma and erythrocyte membranes in HFD-induced ApoE-/- mice, which supported the traditional uses of Chinese dragon's blood as an effective agent for improving blood microcirculation in hypercholesterolemia.
Analgesic effect of total flavonoids from Sanguis draxonis on spared nerve injury rat model of neuropathic pain.[Pubmed: 26547536]
Sanguis draxonis (SD) is a kind of red resin obtained from the wood of Dracaena cochinchinensis (Lour.) S. C. Chen (D. cochinchinensis). The active components of total flavonoids from SD (SDF) have analgesic effect.


