Erigeron breviscapus
Erigeron breviscapus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
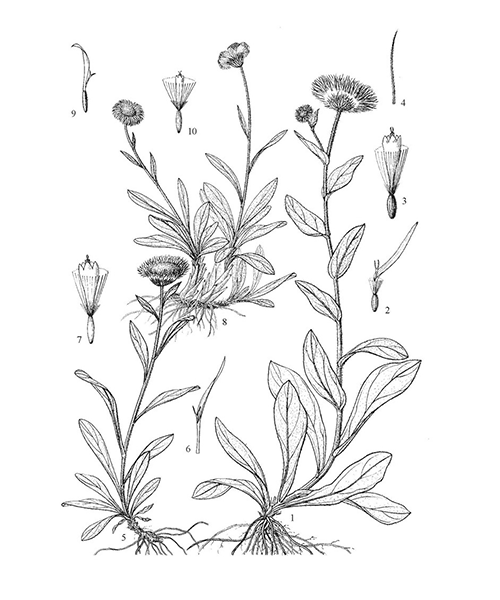

Natural products/compounds from Erigeron breviscapus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1524
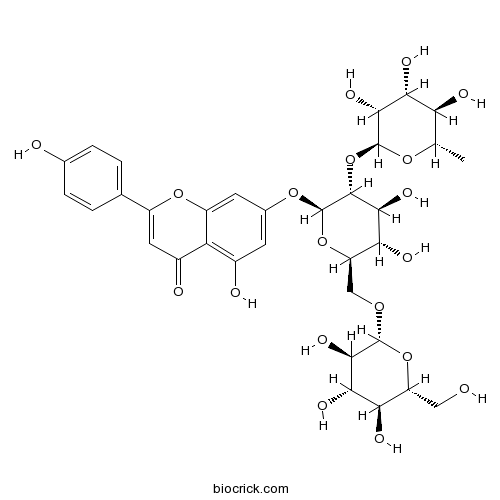
Apigenin 7-O-(2G-rhamnosyl)gentiobioside174284-20-9
Instructions
-
BCN5902
Scutellarin27740-01-8
Instructions

-
BCN5326
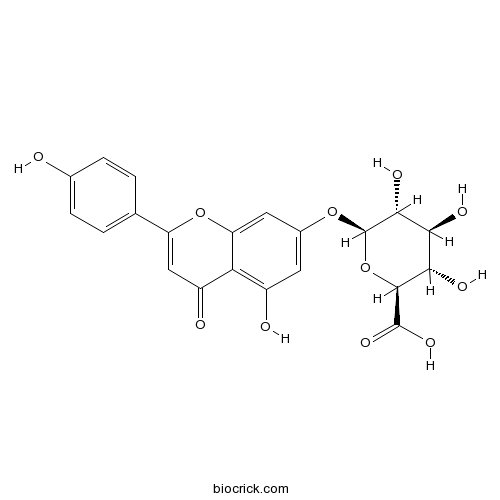
Apigenin-7-glucuronide29741-09-1
Instructions
-
BCN5906
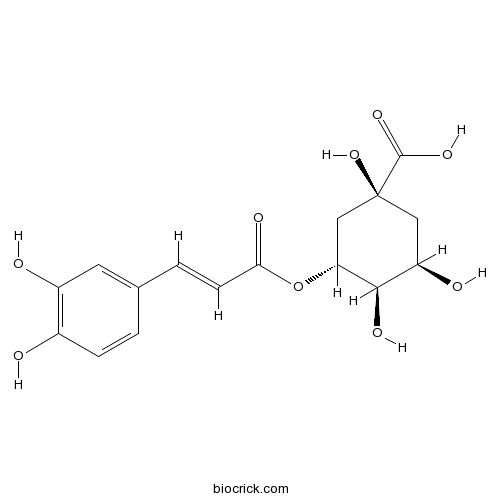
Chlorogenic acid327-97-9
Instructions
-
BCN5979
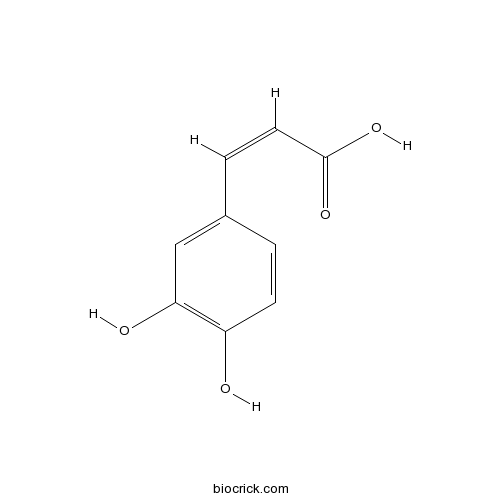
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5599
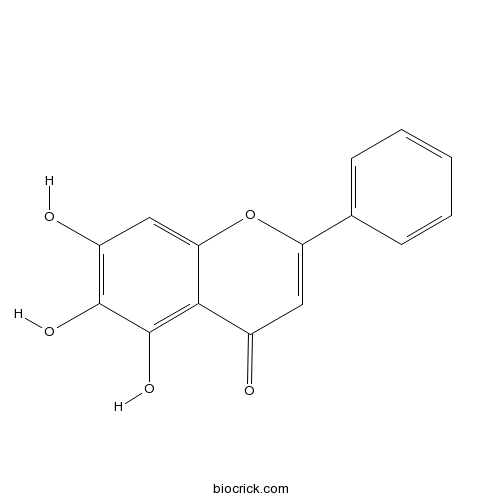
Baicalein491-67-8
Instructions
-
BCN5600
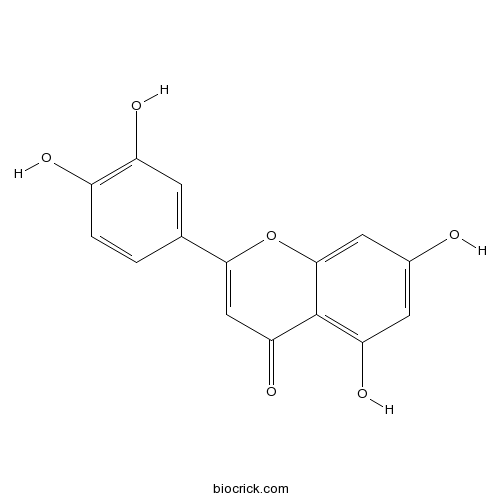
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN5380
Scutellarein529-53-3
Instructions

-
BCN9061
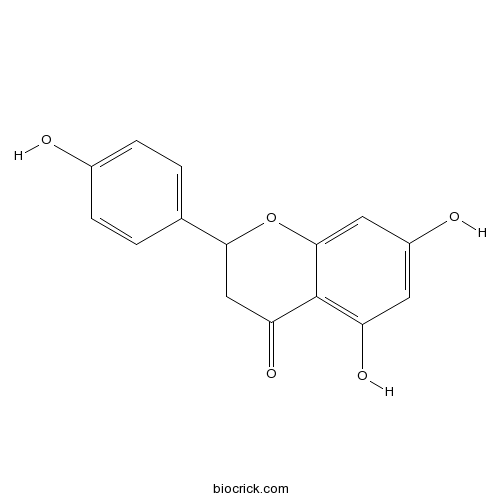
(±)-Naringenin67604-48-2
Instructions
[Establishment of a genetic transformation system for hairy root culture of Erigeron breviscapus].[Pubmed: 29933669]
The electroporation method was performed to transfer plasmid DNA of PBI-1300 carrying GFP gene into Agrobacterium rhizogenes C₅₈C₁ strains. Mediated by A. rhizogenes C₅₈C₁, the GFP gene were transformed into Erigeron breviscapus aseptic leaves by leaf disc method, then the hairy roots were induced and the infected hairy roots were screened by hygromycin resistance. The chromosomal DNA of the hairy root was used as the templates for the PCR amplification with the GFP-specific primers and then the expected amplified DNA bands appeared, the green fluorescent of GFP in the cut hairy roots was observed by two-photon microscope. These results indicated that GFP gene was integrated into the genome of E. breviscapus and was expressed stably. This study laid the groundwork for foreign gene high-efficiency expression inthe genetic transformation system for hairy root culture of E. breviscapus.
Systematic investigation of the Erigeron breviscapus mechanism for treating cerebrovascular disease.[Pubmed: 29783016]
Cerebrovascular diseases (CBVDs), characterized by striking morbidity and mortality, have become the most common life-threatening diseases. The existing drugs of CBVDs target one or a few of pathogenic factors, the efficacy of which is limited because of the complexity of CBVDs. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), featured by multi-component and multi-target endows the great effectiveness in CBVDs treatment. For instance, Erigeron breviscapus (vant.) Hand. Mazz. (Erigeron breviscapus) has been used to treat CBVDs for a long time and the efficacy has been verified through years' of practice. Nevertheless, the mechanisms of Erigeron breviscapus for treating CBVDs are still unclear.
Scutellarin protects against vascular endothelial dysfunction and prevents atherosclerosis via antioxidation.[Pubmed: 29655699]
Scutellarin is the major constituent responsible for the clinical benefits of Erigeron breviscapus (Vant.) Hand.-Mazz which finds a long history of ethnopharmacological use in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Scutellarin as a pure compound is now under investigation for its protections against various tissue injuries.
Pharmacological Effects of Scutellarin, An Active Component of Genus Scutellaria and Erigeron: A Systematic Review.[Pubmed: 29433387]
Flavonoid compound scutellarin (Scu) is quite frequently met in the plant kingdom, particularly in the genus Scutellaria (Lamiaceae) and Erigeron (Asteraceae). The extract of the herb of Erigeron breviscapus, containing this component in high amount, has been used for many years in traditional Chinese medicine. In recent years, studies have made great progress on the usefulness of Scu for treating various diseases by testing its mechanism of action. They support the traditional use of Scu rich plant in heart and cerebral ischemia. Scu can potentially be applied in Alzheimer's disease, Helicobacter pylori infection, vascular complications of diabetes and as an inhibitor of certain carcinomas. Various methods were designed to improve its isolation from plant material, solubility, absorption and bioavailability. On the basis of recent studies, it is suggested that Scu could be a promising candidate for new natural drug and deserves particular attention in further research and development.


