Eurycorymbus cavaleriei
Eurycorymbus cavaleriei
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Eurycorymbus cavaleriei
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
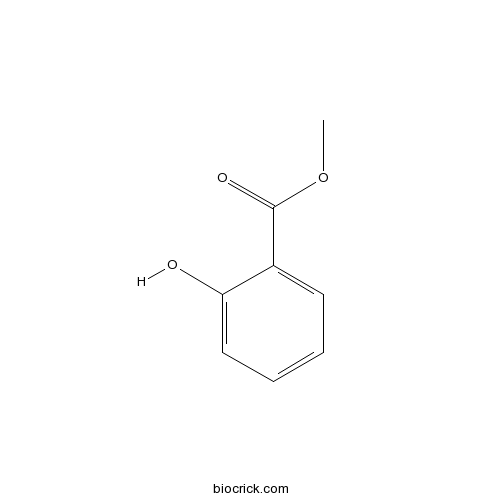
BCN5372
Methyl salicylate119-36-8
Instructions
-
BCN5572
Kaempferitrin482-38-2
Instructions

-
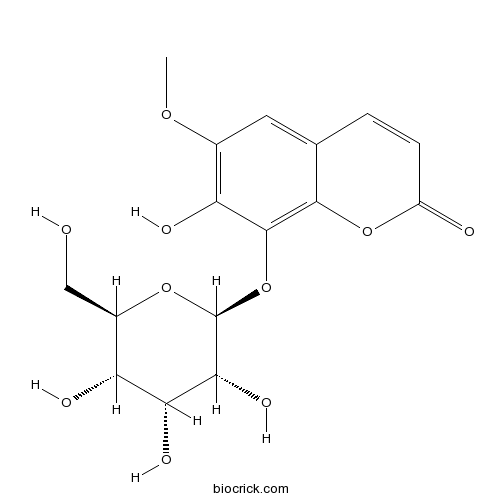
BCN1237
Fraxin524-30-1
Instructions
-
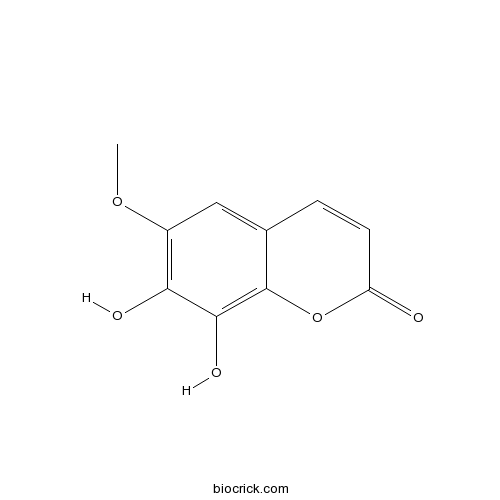
BCN5903
Fraxetin574-84-5
Instructions
Phenolic compounds from Eurycorymbus cavaleriei.[Pubmed: 21623524]
Three new phenolic compounds, eurycorymboside A (1), eurycorymboside B (6), and eurycorymbic acid (8), were isolated from the stem part of Eurycorymbus cavaleriei (Sapindaceae) along with five known phenolic compounds, glucosyringic acid (2), vanillic acid 4-O-β-d-glucoside (3), koaburaside (4), tachioside (5), and 4-hydroxy-3,5-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)benzaldehyde (7). The structures were established on the basis of spectral analysis. The antioxidant activities of compounds 1-6 were evaluated by the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl-free radical scavenging assay. Compound 4 exhibited antioxidant activity with an IC(50) value of 9.0 μM. Compound 4 also showed weak inhibitory activity against influenza A neuraminidase.
Neither biased sex ratio nor spatial segregation of the sexes in the subtropical dioecious tree Eurycorymbus cavaleriei (Sapindaceae).[Pubmed: 19522819]
Knowledge of sex ratio and spatial distribution of males and females of dioecious species is both of evolutionary interest and of crucial importance for biological conservation. Eurycorymbus cavaleriei, the only species in the genus Eurycorymbus (Sapindaceae), is a dioecious tree endemic to subtropical montane forest in South China. Sex ratios were investigated in 15 natural populations for the two defined ages (young and old). Spatial distribution of males and females was further studied in six large populations occurring in different habitats (fragmented and continuous). The study revealed a slight trend of male-biased sex ratio in both ages of E. cavaleriei, but sex ratio of most populations (13 out of 15) did not display statistically significant deviation from equality. All of the four significantly male-biased populations in the young class shifted to equality or even female-biased. The Ripley's K analysis of the distribution of males with respect to females suggested that individuals of the opposite sexes were more randomly distributed rather than spatially structured. These results suggest that the male-biased sex ratio in E. cavaleriei may result from the precocity of males and habitat heterogeneity. The sex ratio and the sex spatial distribution pattern are unlikely to constitute a serious threat to the survival of the species.
Characterization of chemopreventive agents from the dichloromethane extract of Eurycorymbus cavaleriei by liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 19439309]
In the present study, we examined the potential chemopreventive activity of dichloromethane extract of Eurycorymbus cavaleriei by investigating the change of constitutions after incubation with glutathione (GSH). The major constitutions in the dichloromethane extract of E. cavaleriei were cumarin compounds and their cleavage pattern was examined by LC-MS-MS and the characteristic product ions at m/z 206 and 207 were helpful to determine the substitutions of coumarinolignoid compounds. The mechanism of conjugations of 5'-demethylaquillochin and its isomer with GSH was discussed and validated through analysis of the conjugations of reference compound 6-hydroxy-7-methoxycoumarin with GSH by LC-MS-MS and NMR spectrum. The relative ability to induce the detoxification enzyme, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) of nine coumarin compounds was tested which also showed 5'-demethylaquillochin exhibited the most potential chemopreventive ability. These observations suggest that 5'-demethylaquillochin and its isomer from the dichloromethane extract of E. cavaleriei have potential as chemopreventive agents through induction of detoxification enzymes.
Three lignans and one coumarinolignoid with quinone reductase activity from Eurycorymbus cavaleriei.[Pubmed: 19376206]
Four compounds, including one new lignan cavaol H (1), one new coumarinolignoid 5'-hydroxycleomiscosin B (4) and two known lignans (2-3) were isolated from the 95% ethanol extract of the twigs of Eurycorymbus cavaleriei. Their structures were established on the basis of various spectroscopic analyses including 1D-(1H, 13C, and DEPT) and 2D-NMR (COSY, HMQC, and HMBC). The absolute stereochemistry of the two known lignans was firstly reported in this article by 1H NMR studies on Mosher's ester derivatives. In the present study, quinone reductase induction activities of compounds 1-4 were assayed, compound 4 showed moderate quinone reductase induction with concentration to double the enzyme activity (CD) of 10.5 +/- 0.8 microg/mL. Then we established LC-MS-MS analysis of glutathione (GSH) incubation with compound 4 to explain whether compound 4 induced quinone reductase through alkylating of the sulfhydryl groups of Keap1. Reconstructed selected ion chromatogram (SIC) of m/z 706 after compound 4 incubation with GSH was different from that with Tris-HCl buffer solution, which meant the quinone reductase induction activity of compound 4 attributed to alkylating the sulfhydryl groups of Keap1.


