Gelsemium elegans
Gelsemium elegans
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Gelsemium elegans
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6190
Koumine1358-76-5
Instructions

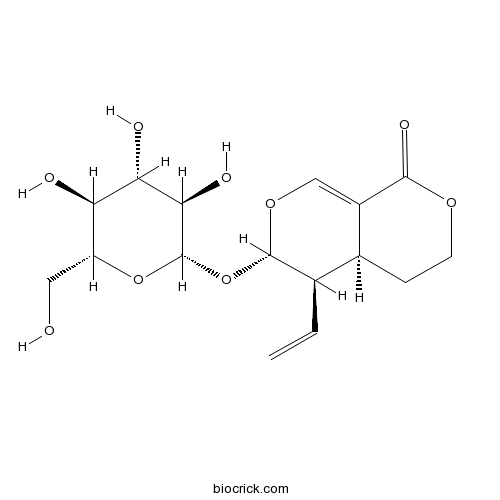
-
BCN6219
Sweroside14215-86-2
Instructions
-
BCN4984
Orientin28608-75-5
Instructions

-
BCN5443
Gelsevirine38990-03-3
Instructions

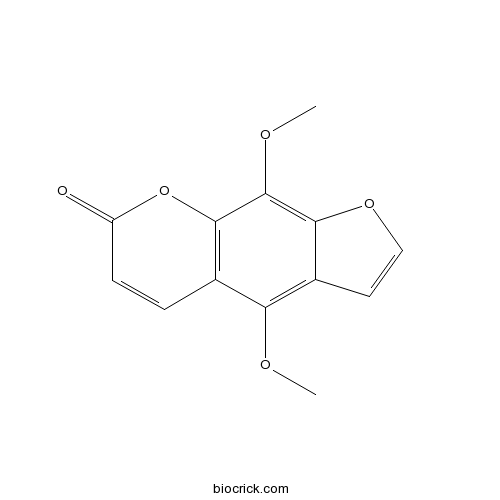
-
BCN5568
Isopimpinellin482-27-9
Instructions
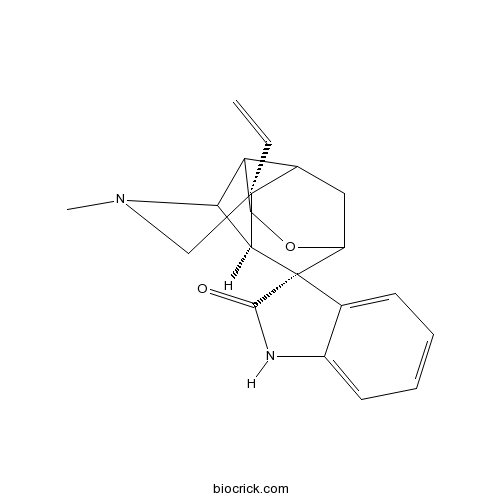
-
BCN5804
Gelsemine509-15-9
Instructions
-
BCN4582
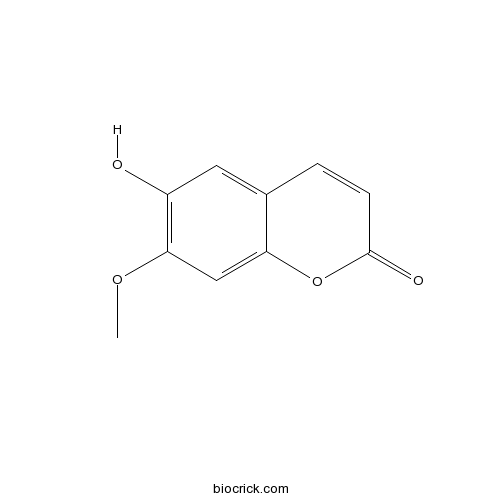
Isoscopoletin776-86-3
Instructions
-
BCN4357
Humantenmine82354-38-9
Instructions

The analgesic effect and possible mechanisms by which koumine alters type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats.[Pubmed: 30054785]
Gelsemium elegans Benth. is a toxic plant that has been used as an ancient Chinese herbal remedy for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and nervous pain, spasticity, skin ulcers, and cancers. Koumine, one of its representative alkaloids, shows numerous promising pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities. Here, we investigated the analgesic effect of koumine on the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rat model of RA and explored the potential pharmacological mechanisms underlying the analgesia. In the CIA rats, repeated koumine treatments significantly reduced pain compared to controls and attenuated the collagen-induced increase in levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β). Cultured astrocytes showed reduced astrocyte reactivation and decreased production of both tested cytokines. Based on our results, koumine exerted both analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects on the CIA rat model that were apparently mediated by inhibiting astrocyte reactivation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
Gelsecorydines A-E, Five Gelsedine-Corynanthe-Type Bisindole Alkaloids from the Fruits of Gelsemium elegans.[Pubmed: 29719959]
Five monoterpenoid bisindole alkaloids with new carbon skeletons, gelsecorydines A-E (1-5), together with their biogenetic precursors were isolated from the fruits of Gelsemium elegans. Compounds 1-5 represent the first examples of heterodimeric frameworks composed of a gelsedine-type alkaloid and a modified corynanthe-type one. Notably, compound 2 featured an unprecedented caged skeleton with a 6/5/7/6/5/6 heterohexacyclic ring system, which possessed a pyridine ring that linked the two monomers. Their structures and absolute configurations were elucidated by spectroscopic analysis, X-ray diffraction, and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculation. A plausible biosynthetic pathway for compounds 1-5 is proposed. Compounds 1, 3, 4, and 5 exhibited a significant inhibitory effect against nitric oxide (NO) production in macrophages.
Simultaneous determination of gelsemine and koumine in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and application to pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Gelsemium elegans Benth extract.[Pubmed: 29388221]
None


