GelsemineCAS# 509-15-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
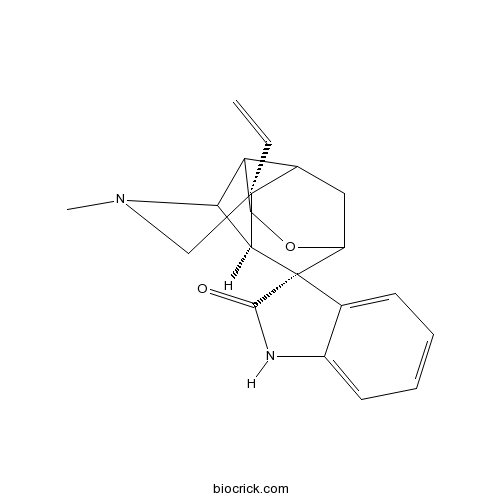
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 509-15-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6713959 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C20H22N2O2 | M.Wt | 322.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 125 mg/mL (387.72 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| SMILES | CN1CC2(C3CC4C5(C2C1C3CO4)C6=CC=CC=C6NC5=O)C=C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NFYYATWFXNPTRM-ZIWPNRSCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H22N2O2/c1-3-19-10-22(2)16-11-9-24-15(8-13(11)19)20(17(16)19)12-6-4-5-7-14(12)21-18(20)23/h3-7,11,13,15-17H,1,8-10H2,2H3,(H,21,23)/t11?,13?,15?,16?,17-,19-,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Gelsemine is a highly toxic compound and may be a glycine receptor agonist. Gelsemine has antitumor, anti-hyperlipidemic,anti-oxidative activities,it also has marked antinociception in inflammatory, neuropathic and bone cancer pains without inducing antinociceptive tolerance. |
| Targets | LDL |
| In vitro | Antitumor activity of two gelsemine metabolites in rat liver microsomes.[Pubmed: 20839118]J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2010 Sep;12(9):731-9.Gelsemine is one of the major alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans Benth., which has been used as an antitumor remedy in clinic. |
| In vivo | Anti-hyperlipidemic and anti-oxidative effects of gelsemine in high-fat-diet-fed rabbits.[Pubmed: 25213292]Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Jan;71(1):337-44.The present study investigated the anti-hyperlipidemic proprieties of a natural alkaloid, Gelsemine, in a high-fat-fed rabbit model. |
| Structure Identification | Org Lett. 2008 Nov 6;10(21):4747-50.A concise approach to a gelsemine core structure using an oxygen to carbon bridge swapping strategy.[Pubmed: 18837555]A tricyclic core structure 2 related to Gelsemine 1 was synthesized from an oxabicyclo[3.2.1]octanone 4 by a three-step bridge swapping strategy involving elimination of the bridging ether oxygen and intramolecular Michael addition of a tethered cyanoacetamide unit. |

Gelsemine Dilution Calculator

Gelsemine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1017 mL | 15.5087 mL | 31.0174 mL | 62.0347 mL | 77.5434 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6203 mL | 3.1017 mL | 6.2035 mL | 12.4069 mL | 15.5087 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3102 mL | 1.5509 mL | 3.1017 mL | 6.2035 mL | 7.7543 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.062 mL | 0.3102 mL | 0.6203 mL | 1.2407 mL | 1.5509 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.031 mL | 0.1551 mL | 0.3102 mL | 0.6203 mL | 0.7754 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 1-Acetyl-beta-carboline
Catalog No.:BCN3101
CAS No.:50892-83-6
- WY-14643 (Pirinixic Acid)
Catalog No.:BCC2265
CAS No.:50892-23-4
- 1,4-Bis(2-benzoxazolyl)naphthalene
Catalog No.:BCC8423
CAS No.:5089-22-5
- Liensinine diperchlorate
Catalog No.:BCN6336
CAS No.:5088-90-4
- Neoliquiritin
Catalog No.:BCN6663
CAS No.:5088-75-5
- 1,5,6-Trihydroxy-3-methoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN8121
CAS No.:50868-52-5
- Tetramisole HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4735
CAS No.:5086-74-8
- Friedelanol
Catalog No.:BCN5620
CAS No.:5085-72-3
- 1,3,5,6-Tetrahydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN3453
CAS No.:5084-31-1
- 14,15-Didehydroisoeburnamine
Catalog No.:BCN5619
CAS No.:50838-11-4
- Vortioxetine
Catalog No.:BCC2046
CAS No.:508233-74-7
- Ganoderic acid LM2
Catalog No.:BCN2442
CAS No.:508182-41-0
- Delsoline
Catalog No.:BCN5405
CAS No.:509-18-2
- Aconine
Catalog No.:BCN2394
CAS No.:509-20-6
- Napellonine
Catalog No.:BCN2536
CAS No.:509-24-0
- Strychnine phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC8257
CAS No.:509-42-2
- Mitraphylline
Catalog No.:BCC8213
CAS No.:509-80-8
- Arteannuin B
Catalog No.:BCN5623
CAS No.:50906-56-4
- Toxyloxanthone D
Catalog No.:BCN3070
CAS No.:50906-62-2
- Nemorensine
Catalog No.:BCN2099
CAS No.:50906-96-2
- Taiwanhomoflavone B
Catalog No.:BCN5624
CAS No.:509077-91-2
- 1beta-Hydroxytorilin
Catalog No.:BCN7095
CAS No.:509078-16-4
- IRAK-1-4 Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC1659
CAS No.:509093-47-4
- 2-Amino-3,5-dibromobenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8523
CAS No.:50910-55-9
Antitumor activity of two gelsemine metabolites in rat liver microsomes.[Pubmed:20839118]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2010 Sep;12(9):731-9.
Gelsemine is one of the major alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans Benth., which has been used as an antitumor remedy in clinic. In this paper, metabolism of Gelsemine has been investigated in vitro in phenobarbital-treated rat liver microsomes. The metabolites of Gelsemine were separated and evaluated using the flash silica gel column, preparative HPLC, using NMR and MS methods. According to the spectral data, two metabolites, M1 and M2, were identified as 4-N-demethylGelsemine and 21-oxoGelsemine, respectively. By the MTT method in vitro, the antitumor activities between Gelsemine and its metabolites were compared in the HepG2 and HeLa cell lines. Moreover, the main metabolic pathway was further proposed.
A concise approach to a gelsemine core structure using an oxygen to carbon bridge swapping strategy.[Pubmed:18837555]
Org Lett. 2008 Nov 6;10(21):4747-50.
A tricyclic core structure 2 related to Gelsemine 1 was synthesized from an oxabicyclo[3.2.1]octanone 4 by a three-step bridge swapping strategy involving elimination of the bridging ether oxygen and intramolecular Michael addition of a tethered cyanoacetamide unit.
Anti-hyperlipidemic and anti-oxidative effects of gelsemine in high-fat-diet-fed rabbits.[Pubmed:25213292]
Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Jan;71(1):337-44.
The present study investigated the anti-hyperlipidemic proprieties of a natural alkaloid, Gelsemine, in a high-fat-fed rabbit model. Animals were randomly divided into five groups and fed normal diet, hypercholesterolemic diet (1% cholesterol), or hypercholesterolemic diet (1% cholesterol) supplemented with Gelsemine (1, 5, or 25 mg/kg). After 60 days, serum concentrations of total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides, apolipoproteins A and B, SGOT, SGPT, glucose, and insulin were measured in all experimental groups. Hypercholesterolemic diet resulted in significantly elevated levels of TC, TG, LDL-C, SGOT, and SGPT, and reduced HDL-C compared to the normocholesterolemic diet group. Gelsemine treatment significantly improved lipid profile parameters, affected by hyperlipidemia, while having no effect on the levels of apolipoproteins, glucose, and insulin. Furthermore, Gelsemine treatment decreased hyperlipidemia-induced oxidative stress in a dose-dependent manner, as indicated by the increased activity of superoxide dismutase and catalase, and reduction in serum nitric oxide, and malondialdehyde concentrations in hyperlipidemic animals that received Gelsemine supplementation. Dietary supplementation with Gelsemine may, therefore, reverse the effect of the lipogenic diet on lipid profile and hepatic enzymes in hyperlipidemic rabbits, and protect tissues from oxidative stress, caused by high-fat diet.


