Gynura divaricata
Gynura divaricata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Gynura divaricata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5948
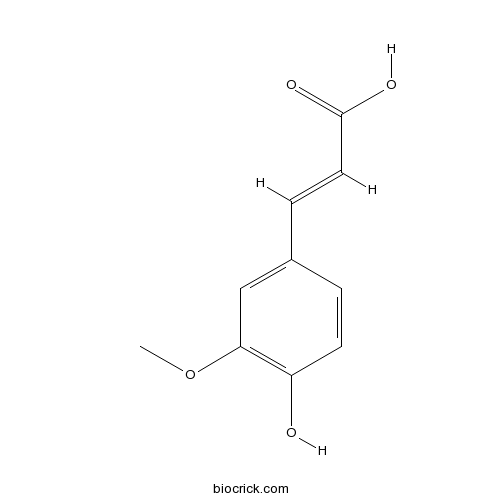
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
BCN1126
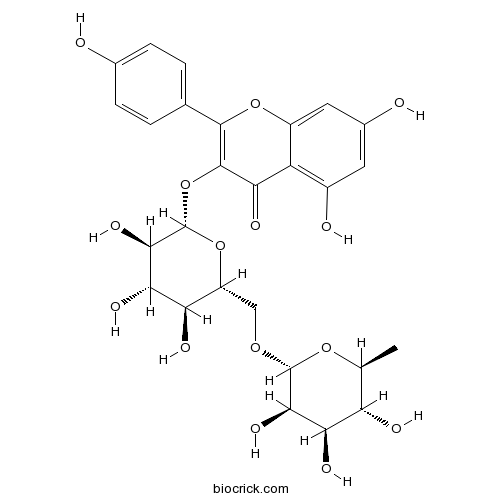
Nicotiflorin17650-84-9
Instructions
-
BCN5747
Friedelin559-74-0
Instructions

-
BCN4376
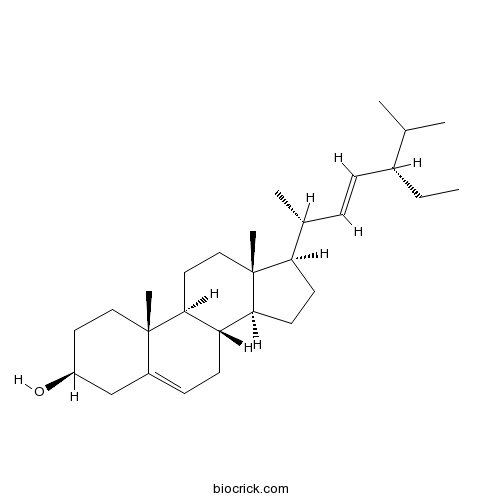
Stigmasterol83-48-7
Instructions
Gynura divaricata attenuates tumor growth and tumor relapse after cisplatin therapy in HCC xenograft model through suppression of cancer stem cell growth and Wnt/β-catenin signalling.[Pubmed: 28729225]
Gynura divaricata subsp. formosana is a widely used traditional herbal medicine for treating liver disorders such as hepatitis and liver cancer in Taiwan.
Detection and Toxicity Evaluation of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Medicinal Plants Gynura bicolor and Gynura divaricata Collected from Different Chinese Locations.[Pubmed: 27623358]
Two edible plants in Southeast Asia, Gynura bicolor and G. divaricata, are not only known to be nutritive but also useful as medicinal herbs. Previous phytochemical investigation of Gynura species showed the presence of hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), indicating the toxic risk of using these two plants. The present study was designed to analyze the distribution of PA components and tried to evaluate the preliminary toxicity of these two Gynura species. Eight samples of G. bicolor and G. divaricata from five different Chinese locations were collected and their specific PAs were qualitatively characterized by applying an UPLC/MS/MS spectrometry method. Using a pre-column derivatization HPLC method, the total retronecine ester-type PAs in their alkaloids extracts were quantitatively estimated as well. Finally, their genotoxicity was investigated with an effective high-throughput screening method referred to as Vitotox™ test and their potential cytotoxicity was tested on HepG2 cells. It was found that different types of PAs were widely present in Gynura species collected from south of China. Among them, no significant genotoxic effects were detected with serial concentrations through the present in vitro assay. However, the cytotoxicity assay of Gynura plants collected from Jiangsu displayed weak activity at the concentration of 100 mg/ml. It is important to note that this research validates in part the indication that the use of Gynura species requires caution.
Hypoglycemic activities of lyophilized powder of Gynura divaricata by improving antioxidant potential and insulin signaling in type 2 diabetic mice.[Pubmed: 26715102]
Diabetes mellitus is a serious disease affecting about 5% of people worldwide. Although several studies have indicated hypoglycemic activities of Gynura divaricata (GD), the mechanisms by which GD improves the symptoms of diabetes remain unclear.
[Isolation, purification and identification of polysaccharides from Gynura divaricata].[Pubmed: 26281587]
The purpose of this study was to isolate and purify polysaccharide from Gynura divaricata and analyze its monosaccharide composition. A water-soluble crude polysaccharide was obtained by hot water extraction, ethanol precipitation and deproteinization after degreasing. The crude polysaccharide then purified with DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow column chromatography and dialysis. The monosaccharide composition and structure were analyzed by HPLC, UV spectrophotometer and 1H-NMR. The results showed that the purity and molecular weight of GDPS-2 and GDPS-3 were 87.3%, 2.03 x 10(4) Da and 90.9%, 4.29 x 10(4) Da, respectively. The UV spectrophotometer and 1H-NMR data suggested that glycosidic bond of GDPS-2 and GDPS-3 were a type. Both GDPs-2 and GDPs-3 were homogeneous polysaccharides, and GDPs-2 was mainly composed of glucuronic acid and xylose at a molar ratio of 1.1:0.63. GDPs-3 was mainly composed of rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galactose, xylose and galacturonic acid at a molar ratio of 0.32:6.0:0.21:1.75:4.3.
Caffeoylquinic acid derivatives isolated from the aerial parts of Gynura divaricata and their yeast α-glucosidase and PTP1B inhibitory activity.[Pubmed: 25172103]
The phytochemical investigation of natural products of Gynura divaricata led to the isolation of eleven caffeoylquinic acid derivatives. They were characterized by spectrometric methods as 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (1), 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid (2), 5-O-feruloylquinic acid (3), methyl 5-O-caffeoylquinate (4), 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (5), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (6), 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7), methyl 3,4-dicaffeoylquinate (8), methyl 3,5-dicaffeoylquinate (9), methyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (10) and ethyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (11). The individual compounds were screened for the inhibition of yeast α-glucosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) using in vitro assays. Among the isolated compounds, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (5), 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7), methyl 3,4-dicaffeoylquinate (8) and methyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (10) exhibited significant inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase. In addition, 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid (2), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (6) and 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7) had considerable inhibitory effect against PTP1B. Based on these findings, the caffeoylquinic acid derivatives were deduced to be potentially responsible for the anti-diabetic activity of G. divaricata. The preliminary structure-activity relationship study suggests that the number and positioning of caffeoyl groups in the quinic acid derivatives are important for both α-glucosidase and PTP1B inhibitory potency. Moreover, the corresponding methyl esters of some dicaffeoylquinic acids have enhanced inhibitory activity against yeast α-glucosidase.
Quantitative analysis of fructo-oligosaccharides in Gynura divaricata subsp. formosana by high performance anion exchange chromatography-pulsed amperometric detection.[Pubmed: 22978229]
High performance anion exchange chromatography-pulsed amperometric detection was employed in this study to conduct quantitative analysis of the inulin-related fructo-oligosaccharides present in Gynura divaricata subsp. formosana. Result obtained for the 1-kestose (GF2), nystose (GF3) and 1F-beta-fructofuranosyl-nystose (GF4) contents were 146.60 +/- 0.04, 24.70 +/- 0.75 and 16.60 +/- 0.91 microg/g, fresh weight, and 68.90 +/- 0.02, 7.60 +/- 1.34 and 149.30 +/- 0.06 microg/g (mean +/- RSD), dry weight, respectively. Using this method, the limit of quantitation was 20 microg/mL and the linear detectability between 0-250 microg/mL. The developed method provides a practical analysis for these low caloric value, prebiotic and non-digestible carbohydrates in the genus Gynura.


