Hypericum monogynum
Hypericum monogynum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Hypericum monogynum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
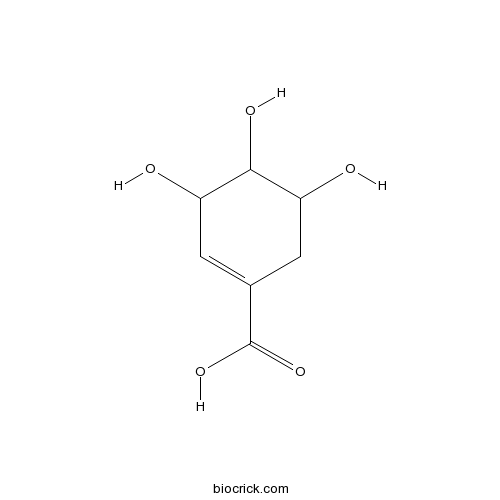
BCN6200
Shikimic acid138-59-0
Instructions
-
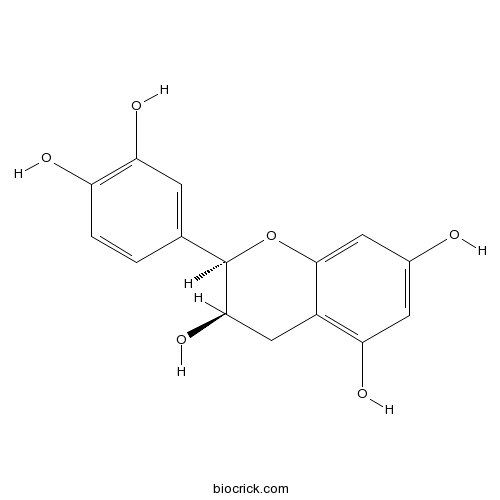
BCN5597
Epicatechin490-46-0
Instructions
-
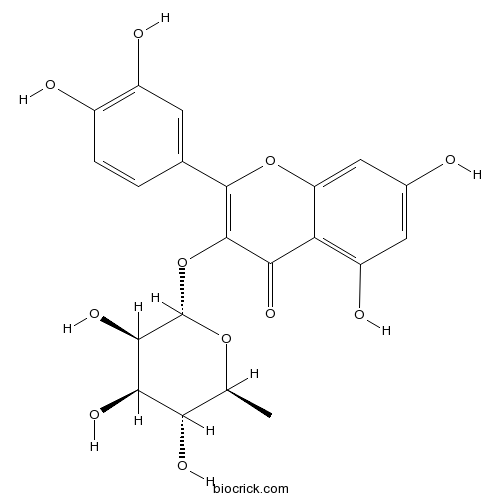
BCN5665
Quercitrin522-12-3
Instructions
Hypermonins A and B, two 6-norpolyprenylated acylphloroglucinols with unprecedented skeletons from Hypericum monogynum.[Pubmed: 29796533]
Two new 6-norpolycyclic polyprenylated acylphloroglucinols (PPAPs), hypermonins A (1) and B (2), featuring an undescribed decahydroindeno[1,7-bc]furan ring system, were isolated from the leaves and twigs of Hypericum monogynum. These compounds are a pair of epimers with opposite configurations at the C-5 position. Their structures, including their absolute configurations, were determined by extensive spectroscopic analysis and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculations. A plausible biosynthetic pathway of 1 and 2 was also proposed. Compound 1 exhibited a significant protective effect against corticosterone-induced injury in PC12 cells.
Chromanopyrones and a flavone from Hypericum monogynum.[Pubmed: 29269232]
None
Polyprenylated Tetraoxygenated Xanthones from the Roots of Hypericum monogynum and Their Neuroprotective Activities.[Pubmed: 27525351]
Ten new polyprenylated tetraoxygenated xanthones, monogxanthones A-J (1-10), together with eight known analogues (4b, 11-17) were identified from the roots of Hypericum monogynum. The structures of these new polyprenylated xanthones (1-10), a class of compounds rarely found in plants of the genus Hypericum, were elucidated by the interpretation of their HRESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR, and electronic circular dichroism data. Compounds 1 and 2 exhibited neuroprotective effects against corticosterone (Cort)-induced lesions of PC12 cells at concentrations of 6.25, 12.50, and 25.00 μM, with cell viability greater than 75%, as well as inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglia cells, with IC50 values of 7.47 ± 0.65 and 9.60 ± 0.12 μM, respectively. Collectively, these results shed new light on the potential of polyprenylated xanthones from the genus Hypericum in the development of antidepression therapies.
Hypermongones A-J, Rare Methylated Polycyclic Polyprenylated Acylphloroglucinols from the Flowers of Hypericum monogynum.[Pubmed: 25924023]
Hypermongones A-J (1-10), rare methylated polycyclic polyprenylated acylphloroglucinol derivatives, together with three known simple acylphloroglucinols (11-13) as their plausible biogenetic precursors, were identified from the flowers of Hypericum monogynum. The structures of 1-10 were elucidated by analysis of their 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic data; the absolute configuration of their polycyclic skeleton was determined by the electronic circular dichroism exciton chirality method and was subsequently confirmed by an X-ray diffraction study of 1. The evaluation of their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells revealed that compound 7 exhibited significant NO inhibition activity, with an IC50 value of 9.5 μM.


