Shikimic acidCAS# 138-59-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 138-59-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1094 | Appearance | Powder |
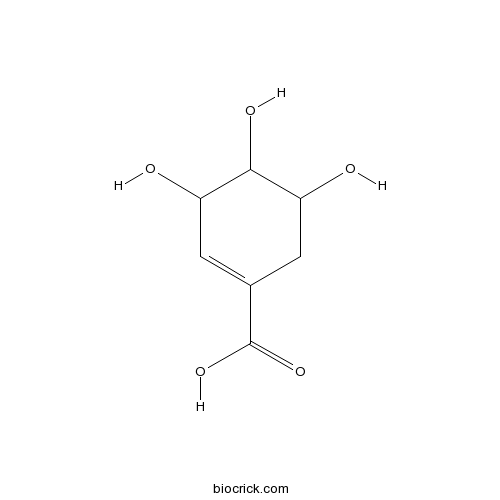
| Formula | C7H10O5 | M.Wt | 174.2 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 130 mg/mL (746.48 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 3,4,5-trihydroxycyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(C(C(C=C1C(=O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JXOHGGNKMLTUBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H10O5/c8-4-1-3(7(11)12)2-5(9)6(4)10/h1,4-6,8-10H,2H2,(H,11,12) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Shikimic acid(Shikimate), more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms, has great potential for the design and synthesis of enzyme inhibitors. It reversed the H2O2 induced oxidative damage in hepatocytes, probably through the inhibition of NF-κB, with the activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway and reduction of apoptosis by interfering the SAPK/JNK/Bax pathway; it also profoundly inhibited pancreatic lipase activity by 66%, thus providing another valuable therapeutic aspect for treating diet induced obesity in humans. |
| Targets | ROS | NF-kB | JNK | Bcl-2/Bax | Nrf2 |
| In vitro | Shikimic acid, a base compound for the formulation of swine/avian flu drug: statistical optimization, fed-batch and scale up studies along with its application as an antibacterial agent.[Pubmed: 25563634]Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2015 Feb;107(2):419-31.The sudden outbreak of swine flu has increased the global demand of Shikimic acid which is an industrially interesting compound, as it is used as a key starting material for the synthesis of a neuraminidase inhibitor Tamiflu(®), for the treatment of antiviral infections such as swine flu.
|
| Kinase Assay | An interactive study of influential parameters for shikimic acid production using statistical approach, scale up and its inhibitory action on different lipases.[Pubmed: 23871288]Bioresour Technol. 2013 Sep;144:675-9.Shikimic acid is the promising candidate as a building block for the industrial synthesis of drug Tamiflu used for the treatment of Swine flu. The fermentative production process using microbes present an excellent and even more sustainable alternative to the traditional plants based extraction methods.
|
| Cell Research | Protective effect of coconut water concentrate and its active component shikimic acid against hydroperoxide mediated oxidative stress through suppression of NF-κB and activation of Nrf2 pathway.[Pubmed: 24835026]J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):132-46.Conventionally coconut water has been used as an 'excellent hydrating' drink that maintain the electrolyte balance and help in treating diverse ailments related to oxidative stress including liver function. The present study was aimed to elucidate whether and how the coconut water concentrate (CWC) and its major active phytoconstituent Shikimic acid (SA) can effectively protect murine hepatocytes from the deleterious effect of hydroperoxide-mediated oxidative stress.
|

Shikimic acid Dilution Calculator

Shikimic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.7405 mL | 28.7026 mL | 57.4053 mL | 114.8106 mL | 143.5132 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1481 mL | 5.7405 mL | 11.4811 mL | 22.9621 mL | 28.7026 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5741 mL | 2.8703 mL | 5.7405 mL | 11.4811 mL | 14.3513 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1148 mL | 0.5741 mL | 1.1481 mL | 2.2962 mL | 2.8703 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0574 mL | 0.287 mL | 0.5741 mL | 1.1481 mL | 1.4351 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Picrocrocine
Catalog No.:BCC8232
CAS No.:138-55-6
- D-(-)-Salicin
Catalog No.:BCN6298
CAS No.:138-52-3
- Mafenide
Catalog No.:BCC5237
CAS No.:138-39-6
- Atroscine
Catalog No.:BCN1941
CAS No.:138-12-5
- Mozavaptan
Catalog No.:BCC5095
CAS No.:137975-06-5
- Dehydrotolvaptan
Catalog No.:BCC8932
CAS No.:137973-76-3
- CBB1007
Catalog No.:BCC4272
CAS No.:1379573-92-8
- CBB1003
Catalog No.:BCC5524
CAS No.:1379573-88-2
- Arillatose B
Catalog No.:BCN6196
CAS No.:137941-45-8
- ML 239
Catalog No.:BCC3987
CAS No.:1378872-36-6
- 6-O-Feruloylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN6195
CAS No.:137887-25-3
- Valsartan methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC9189
CAS No.:137863-17-3
- Limonene
Catalog No.:BCN3797
CAS No.:138-86-3
- Decorticasine
Catalog No.:BCN2006
CAS No.:1380-03-6
- BET bromodomain inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC6426
CAS No.:1380087-89-7
- KB SRC 4
Catalog No.:BCC6253
CAS No.:1380088-03-8
- EPZ5676
Catalog No.:BCC2215
CAS No.:1380288-87-8
- EPZ004777 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4550
CAS No.:1380316-03-9
- Valeriandoid B
Catalog No.:BCN6754
CAS No.:1380399-57-4
- KML 29
Catalog No.:BCC6312
CAS No.:1380424-42-9
- EHop-016
Catalog No.:BCC5022
CAS No.:1380432-32-5
- YM 750
Catalog No.:BCC7542
CAS No.:138046-43-2
- 2-(4-Hydroxy-2-oxoindolin-3-yl)acetonitrile
Catalog No.:BCN1575
CAS No.:1380540-77-1
- LDK378 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1694
CAS No.:1380575-43-8
Protective effect of coconut water concentrate and its active component shikimic acid against hydroperoxide mediated oxidative stress through suppression of NF-kappaB and activation of Nrf2 pathway.[Pubmed:24835026]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):132-46.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Conventionally coconut water has been used as an 'excellent hydrating' drink that maintain the electrolyte balance and help in treating diverse ailments related to oxidative stress including liver function. The present study was aimed to elucidate whether and how the coconut water concentrate (CWC) and its major active phytoconstituent Shikimic acid (SA) can effectively protect murine hepatocytes from the deleterious effect of hydroperoxide-mediated oxidative stress. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Bioactivity guided fractionation of CWC resulted in the isolation of a couple of known compounds. Freshly isolated murine hepatocytes were exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (1 and 3mM) in the presence or absence of CWC (200 and 400 mug/ml) and SA (40 muM) for the determination of antioxidative, DNA protective, cellular ROS level by modern methods, including immunoblot and flowcytometry to find out the possible mechanism of action. RESULTS: Pre-treatment of hepatocyte with CWC and SA showed significant prevention of H2O2-induced intracellular ROS generation, nuclear DNA damage along with the formation of hepatic TBARS and cellular nitrite. Further, the H2O2 induced cell death was arrested in the presence of CWC through the inhibition of CDC42 mediated SAPK/JNK pathways and activation of other molecules of apoptotic pathways, including Bax and caspase3. Moreover, CWC and SA help in maintaining the GSH level and endogenous antioxidants like Mn-SOD, to support intracellular defense mechanisms, probably through the transcriptional activation of Nrf2; and inhibition of nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB. CONCLUSION: CWC and its active components SA reversed the H2O2 induced oxidative damage in hepatocytes, probably through the inhibition of NF-kappaB, with the activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway and reduction of apoptosis by interfering the SAPK/JNK/Bax pathway.
Shikimic acid, a base compound for the formulation of swine/avian flu drug: statistical optimization, fed-batch and scale up studies along with its application as an antibacterial agent.[Pubmed:25563634]
Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2015 Feb;107(2):419-31.
The sudden outbreak of swine flu has increased the global demand of Shikimic acid which is an industrially interesting compound, as it is used as a key starting material for the synthesis of a neuraminidase inhibitor Tamiflu((R)), for the treatment of antiviral infections such as swine flu. Statistical optimization and evaluation of medium components for the production of Shikimic acid by Citrobacter freundii is addressed in the present investigation. Plackett-Burman design was applied for the screening of the most significant variables affecting Shikimic acid production, where glucose, asparagine, KH2PO4, CaCO3 and agitation rate were the most significant factors. Response surface methodology was also employed to study the interaction among the most significant variables through which Shikimic acid production increased to 12.76 g/L. Further, fed-batch studies resulted in the production of 22.32 g/L of Shikimic acid. The scalability of the process was also confirmed by running 14 L bioreactor (7.5 L production medium) where 20.12 g/L of Shikimic acid was produced. In addition the antibacterial activity of the Shikimic acid produced was analysed against four Gram positive and four Gram negative bacteria and it was found to have a greater inhibition effect against the Gram negative bacteria.
An interactive study of influential parameters for shikimic acid production using statistical approach, scale up and its inhibitory action on different lipases.[Pubmed:23871288]
Bioresour Technol. 2013 Sep;144:675-9.
Shikimic acid is the promising candidate as a building block for the industrial synthesis of drug Tamiflu used for the treatment of Swine flu. The fermentative production process using microbes present an excellent and even more sustainable alternative to the traditional plants based extraction methods. In the present study, the fermentative production of Shikimic acid by Citrobacter freundii GR-21 (KC466031) was optimized by process engineering using a statistical modeling approach and a maximum amount of 16.78 g L(-1) was achieved. The process was also scaled up to 14L bioreactor to validate the production of Shikimic acid. Further, the potential of anti-enzymatic nature of purified Shikimic acid was evaluated for different lipases wherein, Shikimic acid inhibited the hydrolysis of triglycerides by 55-60%. Shikimic acid also profoundly inhibited pancreatic lipase activity by 66%, thus providing another valuable therapeutic aspect for treating diet induced obesity in humans.
Fermentative production of shikimic acid: a paradigm shift of production concept from plant route to microbial route.[Pubmed:23543261]
Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2013 Nov;36(11):1665-73.
Different physiological and nutritional parameters affect the fermentative production of Shikimic acid. In our study, Citrobacter freundii initially produced 0.62 g/L of Shikimic acid in 72 h. However, when process optimization was employed, 5.11 g/L of Shikimic acid was produced in the production medium consisting of glucose (5.0 %), asparagine (4.5 %), CaCO3 (2.0 %), at pH 6.0, when inoculated with 6 % inoculum and incubated at 30 +/- 1 degrees C, 200 rpm for 60 h. Preliminary fed-batch studies have resulted in the production of 9.11 g/L of Shikimic acid on feeding the production medium by 20 g/L of glucose at 24 h of the fermentation run. Production of similar amount of Shikimic acid was observed when the optimized conditions were employed in a 10-L bioreactor as obtained in shake flask conditions. A total of 9.11 g/L of Shikimic acid was produced in 60 h. This is approximately 14.69-fold increase in Shikimic acid production when compared to the initial un-optimized production conditions. This has also resulted in the reduction of the production time. The present study provides useful information to the industrialists seeking environmentally benign technology for the production of bulk biomolecules through manipulation of various chemical parameters.


