D-(-)-SalicinCAS# 138-52-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 138-52-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 439503 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
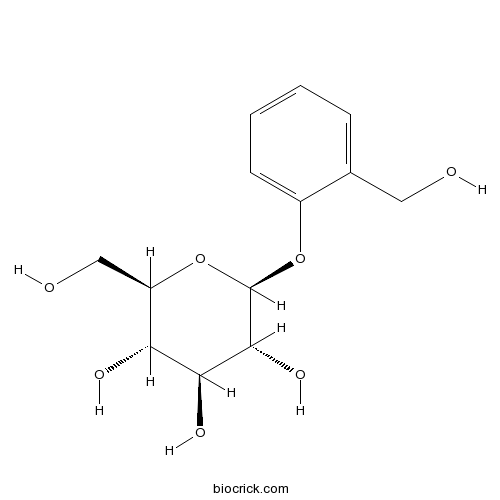
| Formula | C13H18O7 | M.Wt | 286.27 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Salicoside; Salicyl alcohol glucoside; Saligenin β-D-glucoside | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 150 mg/mL (523.96 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[2-(hydroxymethyl)phenoxy]oxane-3,4,5-triol | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)CO)OC2C(C(C(C(O2)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NGFMICBWJRZIBI-UJPOAAIJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H18O7/c14-5-7-3-1-2-4-8(7)19-13-12(18)11(17)10(16)9(6-15)20-13/h1-4,9-18H,5-6H2/t9-,10-,11+,12-,13-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | D(-)-Salicin is a traditional medicine which has been known to exhibit anti-inflammation and other therapeutic activities, it can inhibit the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models. |
| Targets | TNF-α | MAPK | NF-kB | IL Receptor |
| In vitro | D(-)-Salicin inhibits the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models.[Pubmed: 25907238]Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Jun;26(2):286-94.D(-)-Salicin is a traditional medicine which has been known to exhibit anti-inflammation and other therapeutic activities.
|
| In vivo | D(-)-Salicin inhibits the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models.[Pubmed: 25907238]Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Jun;26(2):286-94.D(-)-Salicin is a traditional medicine which has been known to exhibit anti-inflammation and other therapeutic activities.
|
| Structure Identification | Int J Pharm. 2008 Jun 24;358(1-2):192-7.Relaxation behaviour of D(-)-salicin as studied by Thermally Stimulated Depolarisation Currents (TSDC) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC).[Pubmed: 18417303]Thermally Stimulated Depolarisation Currents (TSDC) measurements on D-(-)-Salicin have been carried out in the temperature region from -165 degrees C up to 150 degrees C. The slow molecular mobility was characterised in the crystal and in the glassy state. The value of the steepness index or fragility (T(g)-normalized temperature dependence of the relaxation time) was obtained by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) from the analysis of the scanning rate dependency of T(g). The existence of an unknown polymorph of salicin is also reported. |

D-(-)-Salicin Dilution Calculator

D-(-)-Salicin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4932 mL | 17.466 mL | 34.9321 mL | 69.8641 mL | 87.3301 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6986 mL | 3.4932 mL | 6.9864 mL | 13.9728 mL | 17.466 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3493 mL | 1.7466 mL | 3.4932 mL | 6.9864 mL | 8.733 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0699 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6986 mL | 1.3973 mL | 1.7466 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0349 mL | 0.1747 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6986 mL | 0.8733 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Mafenide
Catalog No.:BCC5237
CAS No.:138-39-6
- Atroscine
Catalog No.:BCN1941
CAS No.:138-12-5
- Mozavaptan
Catalog No.:BCC5095
CAS No.:137975-06-5
- Dehydrotolvaptan
Catalog No.:BCC8932
CAS No.:137973-76-3
- CBB1007
Catalog No.:BCC4272
CAS No.:1379573-92-8
- CBB1003
Catalog No.:BCC5524
CAS No.:1379573-88-2
- Arillatose B
Catalog No.:BCN6196
CAS No.:137941-45-8
- ML 239
Catalog No.:BCC3987
CAS No.:1378872-36-6
- 6-O-Feruloylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN6195
CAS No.:137887-25-3
- Valsartan methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC9189
CAS No.:137863-17-3
- Valsartan
Catalog No.:BCC5017
CAS No.:137862-53-4
- 2,3-Di(3',4'-methylenedioxybenzyl)-2-buten-4-olide
Catalog No.:BCN1576
CAS No.:137809-97-3
- Picrocrocine
Catalog No.:BCC8232
CAS No.:138-55-6
- Shikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6200
CAS No.:138-59-0
- Limonene
Catalog No.:BCN3797
CAS No.:138-86-3
- Decorticasine
Catalog No.:BCN2006
CAS No.:1380-03-6
- BET bromodomain inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC6426
CAS No.:1380087-89-7
- KB SRC 4
Catalog No.:BCC6253
CAS No.:1380088-03-8
- EPZ5676
Catalog No.:BCC2215
CAS No.:1380288-87-8
- EPZ004777 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4550
CAS No.:1380316-03-9
- Valeriandoid B
Catalog No.:BCN6754
CAS No.:1380399-57-4
- KML 29
Catalog No.:BCC6312
CAS No.:1380424-42-9
- EHop-016
Catalog No.:BCC5022
CAS No.:1380432-32-5
- YM 750
Catalog No.:BCC7542
CAS No.:138046-43-2
Relaxation behaviour of D(-)-salicin as studied by Thermally Stimulated Depolarisation Currents (TSDC) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC).[Pubmed:18417303]
Int J Pharm. 2008 Jun 24;358(1-2):192-7.
Thermally Stimulated Depolarisation Currents (TSDC) measurements on D(-)-salicin have been carried out in the temperature region from -165 degrees C up to 150 degrees C. The slow molecular mobility was characterised in the crystal and in the glassy state. The value of the steepness index or fragility (T(g)-normalized temperature dependence of the relaxation time) was obtained by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) from the analysis of the scanning rate dependency of T(g). The existence of an unknown polymorph of salicin is also reported.
Calorimetric studies on the phenolic glycoside D(-)-salicin.[Pubmed:18484613]
J Pharm Sci. 2008 Dec;97(12):5354-62.
A pure orthorhombic phase sample of D(-)-salicin was purified and characterized for calorimetric measurements. From differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurements it was found that the onset and maximum temperatures of the fusion peak were T(on) = (473.30 +/- 0.05) K and T(max) = (474.74 +/- 0.05) K, respectively, and that the corresponding standard enthalpy of fusion was Delta(cr)(l) H(m)(o) = (55.5 +/- 0.4) kJ mol(-1). From the last two values the standard entropy of fusion is calculated as Delta(cr)(l) S(m)(o) = (116.9 +/- 0.4) J mol(-1) K(-1). The standard molar enthalpy of formation of orthorhombic D(-)-salicin at T = 298.15 K, was determined as Delta(f) H(m)(o) (C(13)H(18)O(7), cr, orthorhombic) = -(1366.9 +/- 3.2) kJ mol(-1), by combustion calorimetry. From the results of solution calorimetry obtained in this work and some auxiliary values taken from the literature the enthalpy of reaction of hydrolysis of D(-)-salicin to produce beta-glucose and o-hydroxybenzyl alcohol was found marginally thermoneutral, if the uncertainty interval was considered. Additionally, specific heat capacity measurements on the orthorhombic phase, glass and liquid-quenched glass obtained by DSC was reported.
D(-)-Salicin inhibits the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models.[Pubmed:25907238]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Jun;26(2):286-94.
D(-)-Salicin is a traditional medicine which has been known to exhibit anti-inflammation and other therapeutic activities. The present study aimed to investigate whether D(-)-Salicin inhibited the LPS-induced inflammation in vivo and in vitro. We evaluated the effect of D(-)-Salicin on cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6 and IL-10) in vivo and in vitro by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and signaling pathways (MAPKs and NF-kappaB) in vivo by Western blot. The results showed that D(-)-Salicin markedly decreased TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 concentrations and increased IL-10 concentration. In addition, western blot analysis indicated that D(-)-Salicin suppressed the activation of MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathways stimulated by LPS. To examine whether D(-)-Salicin ameliorated LPS-induced lung inflammation, inhibitors of MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathways were administrated intraperitoneally to mice. Interference with specific inhibitors revealed that D(-)-Salicin-mediated cytokine suppression was through MAPKs and NF-kappaB pathways. In the mouse model of acute lung injury, histopathologic examination indicted that D(-)-Salicin suppressed edema induced by LPS. So it is suggest that D(-)-Salicin might be a potential therapeutic agent against inflammatory diseases.


