Inula helenium
Inula helenium
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Inula helenium
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
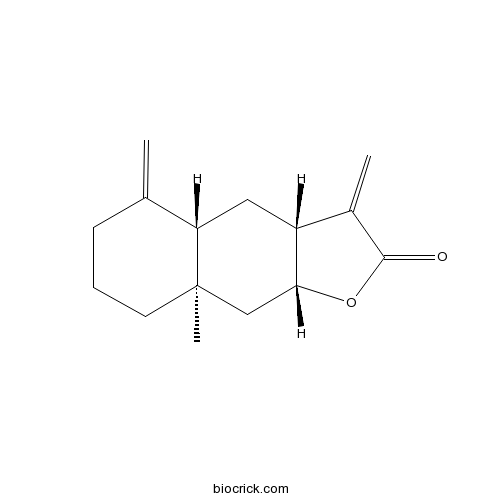
BCN4955
Isoalantolactone470-17-7
Instructions
-
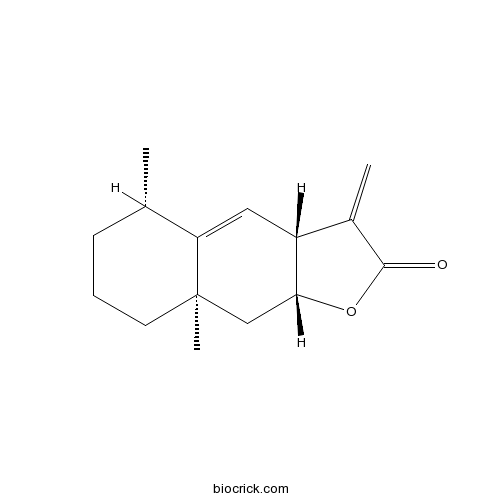
BCN1033
Alantolactone546-43-0
Instructions
Total sesquiterpene lactones isolated from Inula helenium L. attenuates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice.[Pubmed: 30097125]
Inula helenium L. is an herb whose anti-inflammatory properties are attributed to its active components, the sesquiterpene lactones (SLs). Our previous study demonstrated that the total sesquiterpene lactones isolated from Inula helenium L. (TSL-IHL), consisting mainly of alantolactone (AL) and isoalantolactone (IAL), may have potential in the prevention and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the effect of TSL-IHL on atopic dermatitis (AD) has not been studied yet.
Alantolactone induces apoptosis and improves chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells by impairment of autophagy-lysosome pathway via targeting TFEB.[Pubmed: 30086361]
The lysosome is emerging as a central regulator of the autophagic process, which plays a critical role in tumor growth and chemoresistance. Alantolactone, which is a natural compound produced by Inula helenium, has been shown to induce apoptosis in numerous cancer types. However, the mechanism by which alantolactone regulates apoptosis is still poorly understood. In this work, we observed that alantolactone caused the accumulation of autophagosomes due to impaired autophagic degradation and substantially inhibited the activity and expression of CTSB/CTSD proteins that when depleted caused lysosomal dysfunction. Furthermore, we found that alantolactone inhibited the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo and enhanced the chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to oxaliplatin. In addition, a reduction in TFEB levels was a critical event in the apoptosis and cell death caused by alantolactone. Our data demonstrated that alantolactone, which impaired autophagic degradation, was a pharmacological inhibitor of autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells and markedly enhanced the chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to oxaliplatin.
Isoalantolactone suppresses LPS-induced inflammation by inhibiting TRAF6 ubiquitination and alleviates acute lung injury.[Pubmed: 30013035]
Isoalantolactone (IAL) is a sesquiterpene lactone extracted from roots of Inula helenium L and has shown anti-inflammatory effects. In this study we investigated the therapeutic effects of IAL on acute lung injury (ALI) and elucidated the mechanisms underlying its anti-inflammation potential in vitro and in vivo. Treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 ng/mL) drastically stimulated production of inflammatory mediators such as NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs), which was dose-dependently suppressed by pretreatment with IAL (2.5, 5, 10, 20 μM). We further revealed that IAL suppressed LPS-induced NF-κB, ERK, and Akt activation. Moreover, the downregulation of non-degradable K63-linked polyubiquitination of TRAF6, an upstream transcription factor of NF-κB, contributed to the anti-inflammatory effects of IAL. ALI was induced in mice by intratracheal injection of LPS (5 mg/kg). Administration of IAL (20 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly suppressed pulmonary pathological changes, neutrophil infiltration, pulmonary permeability, and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. Our results demonstrate that IAL is a potential therapeutic reagent against inflammation and ALI.
Isoalantolactone protects LPS-induced acute lung injury through Nrf2 activation.[Pubmed: 30009971]
Isoalantolactone (ISO), a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Inula helenium, is known to have anti-inflammatory activity. Here, using a mouse model of acute lung injury, we investigated the effects of ISO on lung inflammation in vivo. ISO (2.5, 5, 10 mg/kg) was administered 1 h before LPS treatment. Histopathological changes suggested that ISO attenuated the injury of lung tissues induced by LPS. ISO also inhibited LPS-induced MPO activity, MDA content, lung W/D ratio, and the production of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β. LPS decreased the activities of the antioxidant enzymes SOD, GPX, and CAT and the decreases were inhibited by ISO. Further studies were performed to detect the Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathway. The results showed that ISO significantly suppressed LPS-induced NF-κB activation, as well as PI3K and AKT phosphorylation. Additionally, the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 were dose-dependently up-regulated by the treatment of ISO. Taken together, the results indicate the protective action of ISO against LPS-induced ALI were through activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway.


