AlantolactoneAntiproliferative; induces activin/Smad3 signaling CAS# 546-43-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 546-43-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72724 | Appearance | White powder/needles |
| Formula | C15H20O2 | M.Wt | 232.32 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (+)-Alantolactone; Alant camphor; Elecampane camphor; Eupatal; Inula camphor | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (430.44 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
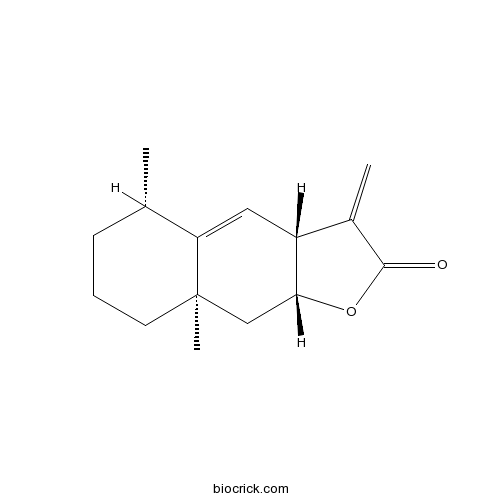
| Chemical Name | (3aR,5S,8aR,9aR)-5,8a-dimethyl-3-methylidene-5,6,7,8,9,9a-hexahydro-3aH-benzo[f][1]benzofuran-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCCC2(C1=CC3C(C2)OC(=O)C3=C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PXOYOCNNSUAQNS-AGNJHWRGSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Alantolactone, an allergenic sesquiterpene lactone, has significant antitumor effects on malignant tumor cells, it can suppress inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by down-regulating NF-κB, MAPK and AP-1 via the MyD88 signaling pathway in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells, and inhibit cell proliferation by interrupting the interaction between Cripto-1 and activin receptor type II A in activin signaling pathway. |
| Targets | Caspase | PARP | NF-kB | TNF-α | IkB | p65 | Bcr-Abl | STAT | IL Receptor | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | CDK | Bcl-2/Bax | IKK | MyD88 | COX |
| In vitro | Alantolactone induces apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia sensitive or resistant to imatinib through NF-κB inhibition and Bcr/Abl protein deletion.[Pubmed: 23613107 ]Apoptosis. 2013 Sep;18(9):1060-70.Alantolactone, an allergenic sesquiterpene lactone, has recently been found to have significant antitumor effects on malignant tumor cells. Here, we investigated the potential effect of Alantolactone on Bcr/Abl+ imatinib-sensitive and -resistant cells.
|
| Kinase Assay | Mechanism-based inhibition of Alantolactone on human cytochrome P450 3A4 in vitro and activity of hepatic cytochrome P450 in mice.[Pubmed: 25858508]J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 7.Alantolactone (AL), one of the main active ingredients in Inula helenium L., has been included in various prescriptions of traditional Chinese medicine. The effects of Alantolactone on cytochrome P450 (CYP450) were still unclear. This study evaluated the inhibitory effect of Alantolactone on cytochrome P450s in vitro and in vivo. |
| Cell Research | Alantolactone Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest on Lung Squamous Cancer SK-MES-1 Cells.[Pubmed: 25597476]Alantolactone from Saussurea lappa Exerts Antiinflammatory Effects by Inhibiting Chemokine Production and STAT1 Phosphorylation in TNF-α and IFN-γ-induced in HaCaT cells.[Pubmed: 25881570]Phytother Res. 2015 Apr 17.Skin inflammation is the most common condition seen in dermatology practice and can be caused by various allergic reactions and certain toxins or chemicals.
In the present study, we investigated the antiinflammatory effects of Saussurea lappa, a medicinal herb, and its marker compounds Alantolactone, caryophyllene, costic acid, costunolide, and dehydrocostuslactone in the HaCaT human keratinocyte cell line.
J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2015 May;29(5):199-206.Alantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone compound, has variety of pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory and antineoplastic effects.
|

Alantolactone Dilution Calculator

Alantolactone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3044 mL | 21.522 mL | 43.0441 mL | 86.0882 mL | 107.6102 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8609 mL | 4.3044 mL | 8.6088 mL | 17.2176 mL | 21.522 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4304 mL | 2.1522 mL | 4.3044 mL | 8.6088 mL | 10.761 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0861 mL | 0.4304 mL | 0.8609 mL | 1.7218 mL | 2.1522 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.043 mL | 0.2152 mL | 0.4304 mL | 0.8609 mL | 1.0761 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Alantolactone(Alant camphor) is a sesquiterpene lactone; has potential activity against triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by suppressing the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway. IC50 value: Target: STAT3 inhibitor in vitro: Alantolactone effectively suppressed both constitutive and inducible STAT3 activation at tyrosine 705. Alantolactone decreased STAT3 translocation to the nucleus, its DNA-binding, and STAT3 target gene expression. Alantolactone significantly inhibits STAT3 activation with a marginal effect on MAPKs and on NF-κB transcription; however, this effect is not mediated by inhibiting STAT3 upstream kinases [1]. 48 h exposure of human erythrocytes to alantolactone (≥20 μM) significantly decreased erythrocyte forward scatter and increased the percentage of annexin-V-binding cells [2]. Alantolactone could efficiently inhibit the promoter activity of TSP50 gene, further results revealed that alantolactone also efficiently inhibited the expression of TSP50 in both mRNA and protein levels [3]. Alantolactone treatment of RKO cells was found to result in dose?dependent inhibition of cell viability and induction of apoptosis, accompanied with the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential [4]. Alantolactone induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. This alantolactone-induced apoptosis was found to be associated with GSH depletion, inhibition of STAT3 activation, ROS generation, mitochondrial transmembrane potential dissipation, and increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activation [5]. in vivo: The in vivo administration of alantolactone inhibited the growth of human breast xenograft tumors [1].
References:
[1]. Chun J, et al. Alantolactone selectively suppresses STAT3 activation and exhibits potent anticancer activity in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cancer Lett. 2015 Feb 1;357(1):393-403.
[2]. Alzoubi K, et al. Triggering of programmed erythrocyte death by alantolactone. Toxins (Basel). 2014 Dec 22;6(12):3596-612.
[3]. Mi XG, et al. Alantolactone induces cell apoptosis partially through down-regulation of testes-specific protease 50 expression. Toxicol Lett. 2014 Jan 30;224(3):349-55.
[4]. Zhang Y, et al. Alantolactone induces apoptosis in RKO cells through the generation of reactive oxygen species and the mitochondrial pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2013 Oct;8(4):967-72.
[5]. Khan M, et al. Alantolactone induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells through GSH depletion, inhibition of STAT3 activation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:719858.
- Conessine
Catalog No.:BCC7352
CAS No.:546-06-5
- Doxercalciferol
Catalog No.:BCC4902
CAS No.:54573-75-0
- Quercetin-3-O-glucose-6'-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6545
CAS No.:54542-51-7
- AMG 9810
Catalog No.:BCC7329
CAS No.:545395-94-6
- QNZ (EVP4593)
Catalog No.:BCC2249
CAS No.:545380-34-5
- Nicardipine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4685
CAS No.:54527-84-3
- Methyl protogracillin
Catalog No.:BCN8177
CAS No.:54522-53-1
- Methyl protodioscin
Catalog No.:BCN6342
CAS No.:54522-52-0
- H-Leu-CMK.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2971
CAS No.:54518-92-2
- 5-Aminolevulinic acid HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4883
CAS No.:5451-09-2
- Erythrodiol
Catalog No.:BCN5726
CAS No.:545-48-2
- Lupeol
Catalog No.:BCN5725
CAS No.:545-47-1
- α-Thujone
Catalog No.:BCC8271
CAS No.:546-80-5
- Columbin
Catalog No.:BCN2622
CAS No.:546-97-4
- Boc-Lys(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3416
CAS No.:54613-99-9
- URB597
Catalog No.:BCC2324
CAS No.:546141-08-6
- Diethyl 2-acetamido-2-phenethylmalonate
Catalog No.:BCC8940
CAS No.:5463-92-3
- Boc-Hyp(Bzl)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3253
CAS No.:54631-81-1
- 2-Amino-4-methoxybenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8532
CAS No.:5464-79-9
- ML 204
Catalog No.:BCC6272
CAS No.:5465-86-1
- 1-O-Methyljatamanin D
Catalog No.:BCN6671
CAS No.:54656-47-2
- 2-(Acetylamino)-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1420
CAS No.:5469-45-4
- 4'-Benzyloxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8698
CAS No.:54696-05-8
- 8-Hydroxy-7-iodo-5-quinolinesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8788
CAS No.:547-91-1
Alantolactone from Saussurea lappa Exerts Antiinflammatory Effects by Inhibiting Chemokine Production and STAT1 Phosphorylation in TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-induced in HaCaT cells.[Pubmed:25881570]
Phytother Res. 2015 Jul;29(7):1088-96.
Skin inflammation is the most common condition seen in dermatology practice and can be caused by various allergic reactions and certain toxins or chemicals. In the present study, we investigated the antiinflammatory effects of Saussurea lappa, a medicinal herb, and its marker compounds Alantolactone, caryophyllene, costic acid, costunolide, and dehydrocostuslactone in the HaCaT human keratinocyte cell line. HaCaT cells were stimulated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), and treated with S. lappa or each of five marker compounds. Chemokine production and expression were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, respectively. Phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 was determined by immunoblotting. Stimulation with TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma significantly increased the production of the following chemokines: thymus-regulated and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC): regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES): macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC): and interleukin-8 (IL-8). By contrast, S. lappa and the five marker compounds significantly reduced the production of these chemokines by TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-treated cells. S. lappa and Alantolactone suppressed the TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-stimulated increase in the phosphorylation of STAT1. Our results demonstrate that Alantolactone from S. lappa suppresses TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-induced production of RANTES and IL-8 by blocking STAT1 phosphorylation in HaCaT cells.
Alantolactone induces apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia sensitive or resistant to imatinib through NF-kappaB inhibition and Bcr/Abl protein deletion.[Pubmed:23613107]
Apoptosis. 2013 Sep;18(9):1060-70.
Alantolactone, an allergenic sesquiterpene lactone, has recently been found to have significant antitumor effects on malignant tumor cells. Here, we investigated the potential effect of Alantolactone on Bcr/Abl+ imatinib-sensitive and -resistant cells. Alantolactone treatment resulted in obvious apoptosis in both imatinib-sensitive and -resistant K562 cells, as shown by the increase in Annexin V-positive cells, caspase-3 activation, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) cleavage and mitochondrial membrane potential collapse. Alantolactone significantly inhibited NF-kappaB-dependent reporter gene activity, decreased the DNA-binding activity of NF-capital O, CyrillickappaB, and blocked TNF-alpha-induced IkappaBalpha phosphorylation. Of interest, the oncogenic Bcr/Abl fusion protein but not its mRNA levels were quickly reduced upon Alantolactone exposure in imatinib-sensitive and -resistant K562 cells. Bcr/Abl knockdown enhanced the apoptosis driven by Alantolactone. Bcr/Abl protein reduction could not be reversed by the addition of proteasome or caspase-3 inhibitors. The overexpression of p65 inhibited Alantolactone-induced apoptosis, whereas p65 or Bcr/Abl silencing enhanced its apoptotic-inducing effect. Furthermore, Bcr/Abl-transfected 32D cells showed more sensitivity to Alantolactone than vector-transfected control cells, and the Bcr/Abl protein was depleted, as observed in K562 cells. Finally, Alantolactone-induced apoptosis was also observed in primary CD34+ CML leukemic cells. Collectively, these findings suggest that Alantolactone is a promising potent agent to fight against CML cells via the inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and depletion of the Bcr/Abl protein.
Mechanism-based inhibition of Alantolactone on human cytochrome P450 3A4 in vitro and activity of hepatic cytochrome P450 in mice.[Pubmed:25858508]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Jun 20;168:146-9.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Alantolactone (AL), one of the main active ingredients in Inula helenium L., has been included in various prescriptions of traditional Chinese medicine. The effects of AL on cytochrome P450 (CYP450) were still unclear. This study evaluated the inhibitory effect of AL on cytochrome P450s in vitro and in vivo. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The inhibitory effects of AL on the CYPs activity were evaluated in human liver microsomes (HLMs) and recombinant cDNA-expressed enzymes incubation system, and then determined by LC-MS/MS based CYPs probe substrate assay. C57BL/6 mice were treated AL orally (0, 25, 50, 100 mg/kg) for 15 days. The inhibitory effects of AL on major Cyps in mice were examined at both the mRNA and enzyme activity levels. RESULTS: AL showed a potent inhibitory effect on CYP3A4 activity with IC50 values of 3.599 (HLMs) and 3.90 (recombinant CYP3A4) muM, respectively. AL strongly decreased CYP3A4 activity in a dose-dependent but not time-dependent way in HLMs. Results from typical Lineweaver-Burk plots showed that AL could inhibit CYP3A4 activity noncompetitively, with a Ki value of 1.09 muM in HLMs. Moreover, activity of CYP2C19 could also be inhibited by AL with IC50 of 36.82 muM. Other CYP450 isoforms were not markedly affected by AL. The inhibition was also validated by in vivo study of mice. AL significantly decreased mRNA expression of Cyp2c and 3a family. CONCLUSION: The study indicates that herb-drug interaction should be paid more attention between AL and drugs metabolized by CYP3A4.
Alantolactone Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest on Lung Squamous Cancer SK-MES-1 Cells.[Pubmed:25597476]
J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2015 May;29(5):199-206.
Alantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone compound, has variety of pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory and antineoplastic effects. In our study, Alantolactone inhibited cancer cell proliferation. To explore the mechanisms underlying its antitumor action, we further examined apoptotic cells and cell cycle distribution using flow cytometry analysis. Alantolactone triggered apoptosis and induced cell cycle G1/G0 phase arrest. Furthermore, the expressions of caspases-8, -9, -3, PARP, and Bax were significantly upregulated, while antiapoptotic factor Bcl-2 expression was inhibited. In addition, the expressions of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), CDK6, cyclin D3, and cyclin D1 were downregulated by Alantolactone. Therefore, our findings indicated that Alantolactone has an antiproliferative role on lung squamous cancer cells, and it may be a promising chemotherapeutic agent for squamous lung cancer SK-MES-1 cells.
Alantolactone inhibits cell proliferation by interrupting the interaction between Cripto-1 and activin receptor type II A in activin signaling pathway.[Pubmed:21378277]
J Biomol Screen. 2011 Jun;16(5):525-35.
It has been suggested that deregulation of activin signaling contributes to tumor formation. Activin signaling is blocked in cancer cells due to the complex formed by Cripto-1, activin, and activin receptor type II (ActRII). In this study, the authors used a mammalian two-hybrid system to construct a drug screening model to obtain a small molecular inhibitor capable of interrupting the interaction between Cripto-1 and ActRII. They screened 300 natural components and identified Alantolactone. Data suggested that Alantolactone induced activin/SMAD3 signaling in human colon adenocarcinoma HCT-8 cells. The authors also found that Alantolactone exhibited antiproliferative function specific to tumor cells, with almost no toxicity to normal cells at a concentration of 5 microg/mL. Furthermore, they proved that the antiproliferative function of Alantolactone was activin/SMAD3 dependent. These results suggest that Alantolactone performs its antitumor effect by interrupting the interaction between Cripto-1 and the activin receptor type IIA in the activin signaling pathway. Moreover, screening for inhibitors of Cripto-1/ActRII is a potentially beneficial approach to aid in discovering novel cancer treatment.
Activation of caspases and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage to induce apoptosis in leukemia HL-60 cells by Inula racemosa.[Pubmed:20600805]
Toxicol In Vitro. 2010 Sep;24(6):1599-609.
Inula racemosa Hook.f. commonly known as Pushkarmula (Compositae) has been used as a traditional drug in India, China and Europe. In the present study, 95% ethanolic extract of roots and its fractions (n-hexane, chloroform, n-butanol and aqueous) were evaluated for in vitro cytotoxicity against cancer cell lines of colon, ovary, prostate, lung, CNS and leukemia. The n-hexane fraction containing Alantolactone and isoAlantolactone as its major constituents was further studied for its mode of action in HL-60 cells. The lowest IC(50) value of n-hexane fraction was 10.25 microg/ml for Colo-205, a colon cancer cell line whereas, 17.86 microg/ml was the highest IC(50) value observed against CNS cancer cell line SF-295. Further studies on HL-60 cells treated with n-hexane fraction at 10, 25 and 50 microg/ml for 6h, revealed that it induces apoptosis through intrinsic as well as extrinsic pathways by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) intermediates. Mitochondrial dysfunction prompted the release of cytochrome c, translocation of pro-apoptotic protein (Bax), activation of caspase cascade, resulting in the cleavage of some specific substrates for caspase-3 such as poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), which eventually leads to apoptosis. The results of present study strongly support further research and development of bioactive constituents from Inula racemosa as potential anticancer agent with possible therapeutic implication.
Toxic effect of alantolactone and dihydroalantolactone in in vitro cultures of leukocytes.[Pubmed:1000726]
Chem Biol Interact. 1976 Nov;15(3):205-17.
Alantolactone, an allergenic sesquiterpene lactone, is toxic to leukocytes in in vitro cultures. Cell (1 X 10(6) cells/ml of culture) stimulation by pokeweed mitogen (PWM) decreases with increasing amounts of terpene. A concentration of 1 mug/ml of culture decreases stimulation by 50%. The reduced terpene, dihydro-11,13-Alantolactone (DHA) is also toxic. A concentration of 1.7 mug/ml of culture of DHA brings about a 50% decrease in stimulation. Both compounds affect cell viability as measured by dye exclusion. It is suggested that the toxicity of Alantolactone is not due to the presence of the alpha-methylene group conjugated to the carbonyl function of the gamma-lactone system.


