IsoalantolactoneCAS# 470-17-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 470-17-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73285 | Appearance | White powder/needles |
| Formula | C15H20O2 | M.Wt | 232.32 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (+)-Isoalantolactone; Isohelenin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (215.22 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
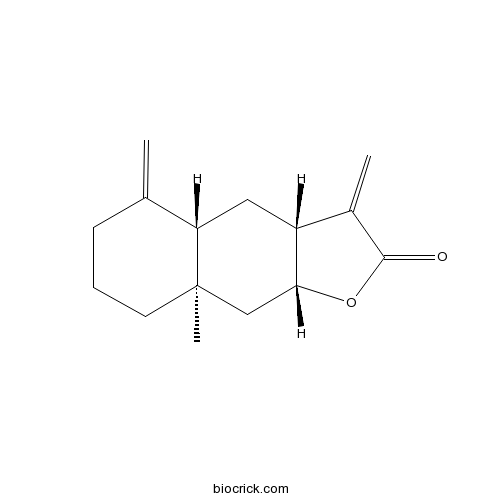
| Chemical Name | (3aR,4aS,8aR,9aR)-8a-methyl-3,5-dimethylidene-3a,4,4a,6,7,8,9,9a-octahydrobenzo[f][1]benzofuran-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC12CCCC(=C)C1CC3C(C2)OC(=O)C3=C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CVUANYCQTOGILD-QVHKTLOISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H20O2/c1-9-5-4-6-15(3)8-13-11(7-12(9)15)10(2)14(16)17-13/h11-13H,1-2,4-8H2,3H3/t11-,12+,13-,15-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Isoalantolactone, an apoptosis inducer, possesses multiple biological activities including antifungal, anthelmintic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antitrypanosomal activities and antiproliferative effects on several cancer cell lines, such as colon, melanoma, ovary, prostate, lung, and leukemia. Isoalantolactone induces apoptosis, may be mediated through caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways, S phase arrest, inhibition of phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt, and downregulation of Bcr/Abl. |
| Targets | Bcr-Abl | PI3K | Akt | PARP | Caspase | ROS | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | NF-kB | p65 | Bcl-2/Bax | p38MAPK |
| In vitro | Growth inhibition effects of isoalantolactone on K562/A02 cells: caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways, S phase arrest, and downregulation of Bcr/Abl.[Pubmed: 24865355]Phytother Res. 2014 Nov;28(11):1679-86.Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, is the active component of Inula helenium (Compositae). It has been reported that Isoalantolactone has the capacity to inhibit tumor cell growth through induction of apoptosis. The purposes of this study were to evaluate the effects of Isoalantolactone on the human erythroleukemia drug-resistant cell line K562/A02 and to provide evidence of its function as a potent therapeutic agent in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia with the Bcr/Abl phenotype.
Repellent, insecticidal and phytotoxic activities of isoalantolactone from Inula racemosa.[Reference: WebLink]Crop Prot., 2006, 25(5):508-11. Isoalantolactone, a natural product isolated from traditional Chinese medicinal herb roots of Inula racemosa Hook. f. (Fam. Compositae), has been shown to possess strong antifungal activities.
|
| In vivo | Isoalantolactone induces reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 cells.[Pubmed: 22532787 ]Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(4):533-47.Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone compound possesses antifungal, antibacteria, antihelminthic and antiproliferative activities.
|
| Cell Research | Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, induces apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells via mitochondrial and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 23881702]Isoalantolactone inhibits constitutive NF-κB activation and induces reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in osteosarcoma U2OS cells through mitochondrial dysfunction.[Pubmed: 25109871]Oncol Rep. 2014 Oct;32(4):1585-93.Human osteosarcoma is an aggressive tumor which frequently resists chemotherapy; therefore, the search for new agents for its treatment is of great importance. Isoalantolactone, isolated from Inula spp., has been reported to inhibit the growth of several types of cancer cells. However, no prior research has been conducted to demonstrate the antiproliferative potential of Isoalantolactone on osteosarcoma. The present study is the first to investigate the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability in human osteosarcoma U2OS, MG-63 and Saos-2 cells, and its mechanism of action in Human osteosarcoma is an aggressive tumor which frequently resists chemotherapy; therefore, the search for new agents for its treatment is of great importance. Isoalantolactone, isolated from Inula spp., has been reported to inhibit the growth of several types of cancer cells. However, no prior research has been conducted to demonstrate the antiproliferative potential of Isoalantolactone on osteosarcoma.
The present study is the first to investigate the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability in human osteosarcoma U2OS, MG-63 and Saos-2 cells, and its mechanism of action in U2OS cells.
Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Oct;36(10):1262-9.Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, possesses anti-fungal as well as cytotoxic properties. In this study, the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability, cell cycle, and apoptosis were investigated in human gastric adenocarcinoma SGC-7901 cells.
|

Isoalantolactone Dilution Calculator

Isoalantolactone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3044 mL | 21.522 mL | 43.0441 mL | 86.0882 mL | 107.6102 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8609 mL | 4.3044 mL | 8.6088 mL | 17.2176 mL | 21.522 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4304 mL | 2.1522 mL | 4.3044 mL | 8.6088 mL | 10.761 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0861 mL | 0.4304 mL | 0.8609 mL | 1.7218 mL | 2.1522 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.043 mL | 0.2152 mL | 0.4304 mL | 0.8609 mL | 1.0761 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Isoalantolactone is an apoptosis inducer, which also acts as an alkylating agent.
In Vitro:Isoalantolactone exhibits good cytotoxic activity against the K562 human leukaemia cell line (IC50=1.2 μM) [1]. The cytotoxic effect of Isoalantolactone on pancreatic carcinoma is evaluated using PANC-1, BxPC3 and HPAC cell lines. Treatment with Isoalantolactone for 24 h inhibits PANC-1 cell growth in a dose-dependent manner. The inhibition rate is above 90% at 80 µM and the concentration to achieve 50% growth inhibition (IC50) is 40 µM. A similar trend in loss of cell viability is observed in BxPC3 and HPAC cells on Isoalantolactone treatment with IC50 values 43 and 48 µM respectively. Pretreatment with 3 mM N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC), a specific ROS scavenger, restores the viability of cells indicating that Isoalantolactone exerts cytotoxic effect on cell viability through ROS generation[2].
In Vivo:The acute and chronic toxic effects of Isoalantolactone in CD1 mice are assessed by measuring the changes in body weight, blood biochemistry and histopathology of liver and kidneys in comparison with control groups. Isoalantolactone is well tolerated by mice and no mortality or any sign of pharmacotoxicity are found at a dose of 100 mg/kg during both experimental periods (7 & 30 days). Body weight gains and food consumption are comparable for control and treated mice during both experimental periods and there were no drug-related changes in histopathological and blood biochemistry parameters. The histopathological changes in liver and kidneys are assessed using hematoxylin and eosin staining and correlated with liver and renal function biomarkers. No obvious morphological changes are observed in liver and kidney structures of control and treatment groups. There is a slight increase in serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level of treatment group at dose day 7 but this increase is not significantly different (P<0.05) from control group. A significant increase in total bilirubin (TBIL) concentration is found in treatment group (1.43±0.26 vs 0.76±0.12 in control, P<0.05) at dose day 7. Similarly the changes in renal function biomarkers are not significantly different (P<0.05) in the serum of control and treatment groups at dose day 7. The concentration of creatinine (Cr) slightly increases whereas concentration of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) slightly decreases in treatment group. The serum level of AST, ALT, TBIL and BUN slightly decreases when mice are injected with Isoalantolactone at a dose of 100 mg/kg for 30 days[2].
References:
[1]. Lawrence NJ, et al. Cytotoxic Michael-type amine adducts of alpha-methylene lactones alantolactone and isoalantolactone. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Feb 12;11(3):429-31.
[2]. Khan M, et al. Isoalantolactone induces reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(4):533-47.
- Uncarine D
Catalog No.:BCC8262
CAS No.:4697-68-1
- Carbenicillin
Catalog No.:BCC5192
CAS No.:4697-36-3
- 5'-IMPdisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCN8175
CAS No.:4691-65-0
- Jervine
Catalog No.:BCN2975
CAS No.:469-59-0
- Cycloeucalenol
Catalog No.:BCN5519
CAS No.:469-39-6
- Hamamelitannin
Catalog No.:BCC8182
CAS No.:469-32-9
- BMS-536924
Catalog No.:BCC1177
CAS No.:468740-43-4
- Cimilactone A
Catalog No.:BCN7948
CAS No.:468733-06-4
- 3-Benzofurancarboxaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8622
CAS No.:4687-25-6
- Dihydrocorynantheine
Catalog No.:BCN3747
CAS No.:4684-43-9
- Picrinine
Catalog No.:BCN5518
CAS No.:4684-32-6
- Norscopolamine
Catalog No.:BCN3983
CAS No.:4684-28-0
- Cinobufagin
Catalog No.:BCN5367
CAS No.:470-37-1
- Marinobufagin
Catalog No.:BCC9238
CAS No.:470-42-8
- Stachyose tetrahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC8252
CAS No.:470-55-3
- 1-Kestose
Catalog No.:BCN8292
CAS No.:470-69-9
- Cineole
Catalog No.:BCN2686
CAS No.:470-82-6
- Benzoyl-DL-methionine
Catalog No.:BCC8863
CAS No.:4703-38-2
- Beta-Lapachone
Catalog No.:BCC5088
CAS No.:4707-32-8
- alpha-Lapachone
Catalog No.:BCN5520
CAS No.:4707-33-9
- Atraric acid
Catalog No.:BCN5521
CAS No.:4707-47-5
- 8-Amino-7-oxononanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1778
CAS No.:4707-58-8
- Glycyrrhetinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5942
CAS No.:471-53-4
- Isocolumbin
Catalog No.:BCN5361
CAS No.:471-54-5
Growth inhibition effects of isoalantolactone on K562/A02 cells: caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways, S phase arrest, and downregulation of Bcr/Abl.[Pubmed:24865355]
Phytother Res. 2014 Nov;28(11):1679-86.
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, is the active component of Inula helenium (Compositae). It has been reported that Isoalantolactone has the capacity to inhibit tumor cell growth through induction of apoptosis. The purposes of this study were to evaluate the effects of Isoalantolactone on the human erythroleukemia drug-resistant cell line K562/A02 and to provide evidence of its function as a potent therapeutic agent in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia with the Bcr/Abl phenotype. Our results showed that Isoalantolactone significantly inhibited K562/A02 cell growth by downregulating Bcr/Abl expression. Isoalantolactone also induced apoptosis via increase generation of reactive oxygen species, modulation of the protein levels of Bcl-2 family members, caspase activation, poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage, and release of cytochrome c. We also observed that Isoalantolactone inhibited proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest in the S phase. Taken together, all these findings support that growth inhibition effects of Isoalantolactone on K562/A02 cells may be mediated through caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways, S phase arrest, and downregulation of Bcr/Abl.
Isoalantolactone induces reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 cells.[Pubmed:22532787]
Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(4):533-47.
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone compound possesses antifungal, antibacteria, antihelminthic and antiproliferative activities. In the present study, we found that Isoalantolactone inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Further mechanistic studies revealed that induction of apoptosis is associated with increased generation of reactive oxygen species, cardiolipin oxidation, reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c and cell cycle arrest at S phase. N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC), a specific ROS inhibitor restored cell viability and completely blocked Isoalantolactone-mediated apoptosis in PANC-1 cells indicating that ROS are involved in Isoalantolactone-mediated apoptosis. Western blot study showed that Isoalantolactone increased the expression of phosphorylated p38 MAPK, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 and decreased the expression of Bcl-2 in a dose-dependent manner. No change in expression of phosphorylated p38 MAPK and Bax was found when cells were treated with Isoalantolactone in the presence of NAC, indicating that activation of these proteins is directly dependent on ROS generation. The present study provides evidence for the first time that Isoalantolactone induces ROS-dependent apoptosis through intrinsic pathway. Furthermore, our in vivo toxicity study demonstrated that Isoalantolactone did not induce any acute or chronic toxicity in liver and kidneys of CD1 mice at dose of 100 mg/kg body weight. Therefore, Isoalantolactone may be a safe chemotherapeutic candidate for the treatment of human pancreatic carcinoma.
Isoalantolactone inhibits constitutive NF-kappaB activation and induces reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in osteosarcoma U2OS cells through mitochondrial dysfunction.[Pubmed:25109871]
Oncol Rep. 2014 Oct;32(4):1585-93.
Human osteosarcoma is an aggressive tumor which frequently resists chemotherapy; therefore, the search for new agents for its treatment is of great importance. Isoalantolactone, isolated from Inula spp., has been reported to inhibit the growth of several types of cancer cells. However, no prior research has been conducted to demonstrate the antiproliferative potential of Isoalantolactone on osteosarcoma. The present study is the first to investigate the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability in human osteosarcoma U2OS, MG-63 and Saos-2 cells, and its mechanism of action in U2OS cells. Our results demonstrated that Isoalantolactone triggered S and mainly G2/M cell cycle phase arrest, accompanied by the downregulation of the expression of cyclin B1 at the protein and mRNA levels. Moreover, Isoalantolactone induced apoptosis that was associated with reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). Furthermore, our results indicated that this compound upregulated DR5, FADD and cleaved caspase-8, increased the interation between DR5 and FADD, and inhibited the expression of nuclear NF-kappaBp65. We also found that Isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis was associated with the downregulation of Bcl-2 and upregulation of Bax, which finally led to the activation of caspase-3 and its downstream substrate, PARP, in osteosarcoma U2OS cells. Isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis was markedly abrogated when the cells were pretreated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a specific ROS inhibitor, suggesting that the apoptosis-inducing effect of Isoalantolactone in osteosarcoma cells was mediated by reactive oxygen species. Taken together, our data demonstrated that Isoalantolactone induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in U2OS cells via a novel mechanism involving inhibition of NF-kappaBp65 and provide the rationale for further in vivo and preclinical investigation of Isoalantolactone against osteosarcoma.
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, induces apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells via mitochondrial and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways.[Pubmed:23881702]
Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Oct;36(10):1262-9.
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, possesses anti-fungal as well as cytotoxic properties. In this study, the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability, cell cycle, and apoptosis were investigated in human gastric adenocarcinoma SGC-7901 cells. The results demonstrated that Isoalantolactone induced morphological changes and decreased cell viability. Subsequently, we found that Isoalantolactone induced G2/M and S phase arrest, which was associated with a decrease in the expression level of cyclin B1. Apoptosis triggered by Isoalantolactone was visualized using propidium iodide (PI) and Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. Isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells was associated with the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi m) that was due to the down-regulation of Bcl-2 and up-regulation of Bax that led to the cleavage of caspase-3. Additionally, it was found that Isoalantolactone was involved in the inhibition of phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt. Isoalantolactone-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells involve mitochondria-caspase and PI3K/Akt dependent pathways, which gives the rationale for in vivo studies on the utilization of Isoalantolactone as a potential cancer therapeutic compound.


