Lysionotus pauciflorus
Lysionotus pauciflorus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Lysionotus pauciflorus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
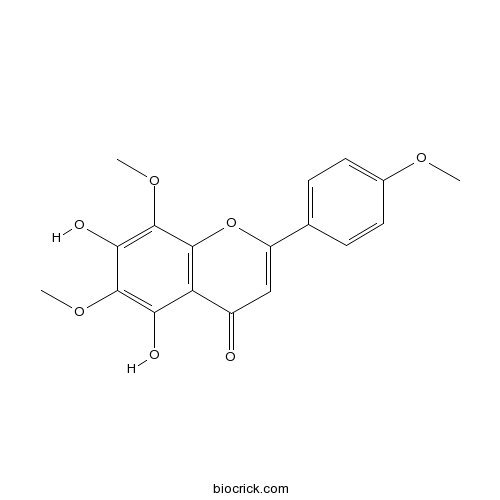
BCN6806
Nevadensin10176-66-6
Instructions
-
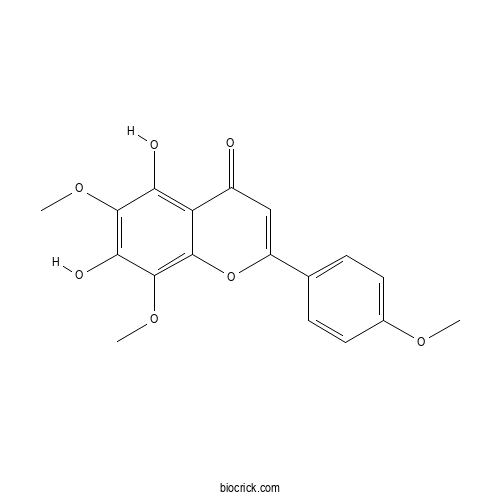
BCX0898
Lysionotin152743-19-6
Instructions
-
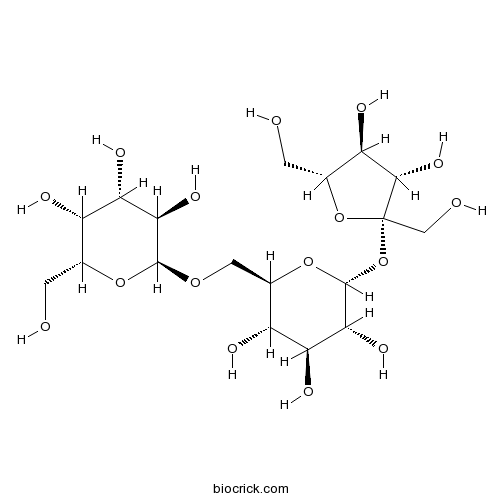
BCN8427
Raffinose512-69-6
Instructions
Metabolism profiling of nevadensin in vitro and in vivo by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS.[Pubmed: 29573625]
Nevadensin is major constituents of Lysionotus pauciflorus Maxim. (Chinese name: Shidiaolan), which has a variety of pharmacological effects such as anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis activities, antitussive, anti-inflammatory and anti-hypertensive. In this paper, we investigated the metabolism of nevadensin in vitro and in vivo. A strategy was firstly developed to identify the metabolites of nevadensin by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS). An on-line data acquisition method a multiple mass defect filter (MMDF) combined with dynamic background subtraction (DBS) was developed to trace all probable metabolites. Furthermore, some assistant tools, such as key fragment ions (KFI), were employed for compound hunting and identification. Based on the proposed method, 23 metabolites were structurally characterized in vivo including 16 phase I and 7 phase II metabolites, and 12 metabolites were detected in vitro containing 10 phase I and 2 phase II metabolites. The results indicated that oxidation, hydrolysis, demethylation, methylation, sulfate conjugation and glucuronide conjugation were main metabolic pathways of nevadensin. In a word, this study maybe can provide reference and valuable evidence for further investigation of the metabolic mechanism of nevadensin.
A New Flavonoid Glycoside from Lysionotus pauciflorus.[Pubmed: 27319133]
Ten flavonoids (1-10), including a new glycoside (nevadensin-7-sambubioside, 7), together with a phenylpropanoid glycoside (11) were isolated from Lysionotus pauciflorus. Their structures were elucidated by a combination of spectroscopic methods and comparing with literature data. Five compounds (1, 3, 4, 8, and 9) were obtained from the family Gesneriaceae for the first time. The new compound was evaluated in vitro for anticholinesterase activities against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), but was found to be inactive.
A comparative study on Ca content and distribution in two Gesneriaceae species reveals distinctive mechanisms to cope with high rhizospheric soluble calcium.[Pubmed: 25477893]
Excessive Ca is toxic to plants thus significantly affects plant growth and species distribution in Ca-rich karst areas. To understand how plants survive high Ca soil, laboratory experiments were established to compare the physiological responses and internal Ca distribution in organ, tissue, cell, and intracellular levels under different Ca levels for Lysionotus pauciflorus and Boea hygrometrica, two karst habitant Gesneriaceae species in Southwest China. In the controlled condition, L. pauciflorus could survive as high as 200 mM rhizospheric soluble Ca, attributed to a series of physiological responses and preferential storage that limited Ca accumulation in chloroplasts of palisade cells. In contrast, B. hygrometrica could survive only 20 mM rhizospheric soluble Ca, but accumulated a high level of internal Ca in both palisade and spongy cells without disturbance on photosynthetic activity. By phenotype screening of transgenic plants expressing high Ca-inducible genes from B. hygrometrica, the expression of BhDNAJC2 in A. thaliana was found to enhance plant growth and photosynthesis under high soluble Ca stress. BhDNAJC2 encodes a recently reported heat shock protein (HSP) 40 family DnaJ-domain protein. The Ca-resistant phenotype of BhDNAJC2 highlights the important role of chaperone-mediated protein quality control in Ca tolerance in B. hygrometrica. Taken together, our results revealed that distinctive mechanisms were employed in the two Gesneriaceae karst habitants to cope with a high Ca environment.
A new sesquiterpene glucoside from Lysionotus pauciflorus.[Pubmed: 25233587]
A new acorane sesquiterpene glucoside, 1R,3S,4R,5R,10R-3,10-dihydroxyacoronene-3-O-beta-D-gluc-oside (1), was isolated from the EtOAc-soluble partition of the ethanol extract of Lysionotus pauciflorus, together with six known compounds, namely p-hydroxybenzoic acid (2), vanillic acid (3). caffeic acid (4). beta-hydroxypropiosyringone (5), alpha,beta-dihydroxypropiosyringone (6), and lyoniresinol (7). The structure of the new compound was elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods, including 1D and 2D NMR, and high-resolution MS analysis. The absolute configuration of 1 was determined from CD spectra. When evaluated against several bacterial and fungal strains, and human cancer cell lines, compound 1 and its aglycone were inactive.
A new acorane sesquiterpene from Lysionotus pauciflorus.[Pubmed: 23787187]
To study the chemical constituents of the whole plant of Lysionotus pauciflorus
[Anti-bacteria activity of Puraboeo rutescens and Lysionotus pauciflorus].[Pubmed: 22016971]
Antibacteria activity of compounds from Puraboeo ruescens and Lysionotus pauciflorus was assayed.
Study of polyethylene glycol as a green solvent in the microwave-assisted extraction of flavone and coumarin compounds from medicinal plants.[Pubmed: 21531418]
In this paper, the application of polyethylene glycol (PEG) aqueous solution as a green solvent in microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) was firstly developed for the extraction of flavone and coumarin compounds from medicinal plants. The PEG solutions were optimized by a mono-factor test, and the other conditions of MAE including the size of sample, liquid/solid ratio, extraction temperature and extraction time were optimized by means of an orthogonal design L(9) (3(4)). Subsequently, PEG-MAE, organic solvent-MAE, and conventional heating reflux extraction (HRE) were evaluated with nevadensin extraction from Lysionotus pauciflorus, aesculin and aesculetin extraction from Cortex fraxini. Furthermore, the mechanism of PEG-MAE was investigated, including microwave-absorptive property and viscosity of PEG solutions, the kinetic mechanism of PEG-MAE and different microstructures of those samples before and after extraction. Under optimized conditions, the extraction yields of nevadensin from L. pauciflorus, aesculin and aesculetin from C. fraxini were 98.7%, 97.7% and 95.9% in a one-step extraction, respectively. The recoveries of nevadensin, aesculin and aesculetin were in the range of 92.0-103% with relative standard derivation lower than 3.6% by the proposed procedure. Compared with organic solvent-MAE and conventional extraction procedures, the proposed methods were effective and alternative for the extraction of flavone and coumarin compounds from medicinal plants. On the basis of the results, PEG solution as a green solvent in the MAE of active compounds from medicinal plants showed a great promising prospect.
Micropropagation of Lysionotus pauciflorus Maxim. (Gesneriaceae).[Pubmed: 20099097]
Numerous shoots were directly regenerated from the leaf explants of Lysionotus pauciflorus on the MS medium containing 0.5-2 microM NAA with or without 1 microM BA. The calli were induced from the leaves on MS medium supplemented with 2 microM 2, 4-D. The calli proliferated about four times in fresh weight in the liquid medium of the same composition as the callus induction medium after 4 weeks of culture on a rotary shaker at 100 rpm. Shoots were induced from these calli on the regeneration medium amended with 32 microM BA or 0.5 microM zeatin. Regenerated shoots rooted easily on (1/2) MS medium without any plant growth regulators. Most of the regenerants from callus were diploid, whereas eight of 66 acclimatized plantlets were tetraploid determined by flow cytometric analysis. Furthermore, flow cytometric analysis of calli also revealed tetraploidy.
Phenylpropanoids and flavonoid glycosides from Lysionotus pauciflorus.[Pubmed: 9637066]
A new phenylpropanoid glycoside, alpha-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-(2'-O-alpha-L-rhamno-pyranosyl- 3'-O-beta-D-apiofuranosyl-4'-O-E-caffeoyl)-beta-D-glucopyran oside, verbascoside, and two new flavone glucosides, nevadensin 7-O-beta-D-glucoside and nevadensin 7-O-[alpha-L-rhamnosyl(1-->6)]-beta-D-glucoside, have been isolated from the aerial parts of Lysionotus pauciflorus. The structures have been elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data and chemical correlation.


