Mentha canadensis
Mentha canadensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
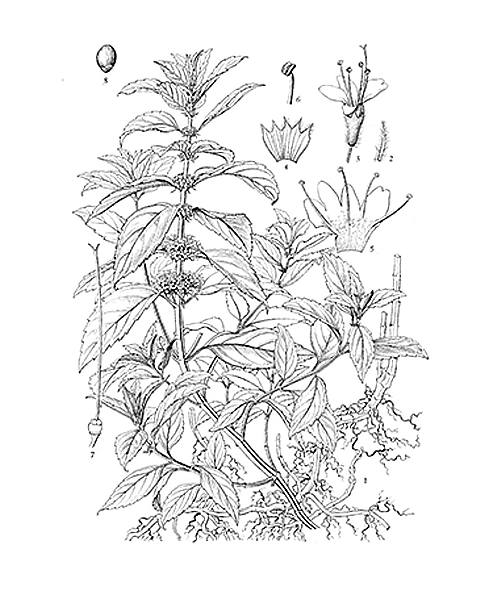
Natural products/compounds from Mentha canadensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
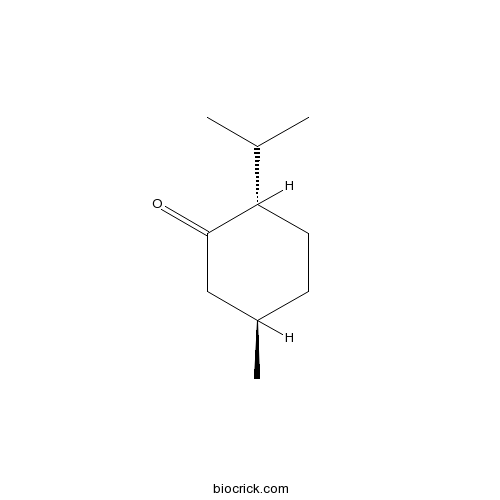
BCN9070
(-)-Menthone14073-97-3
Instructions
-
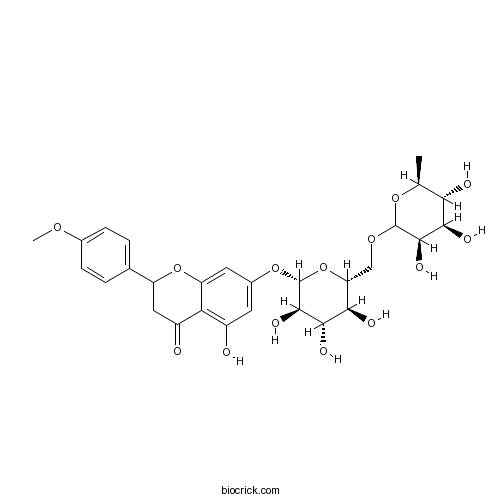
BCN3327
Didymin14259-47-3
Instructions
-
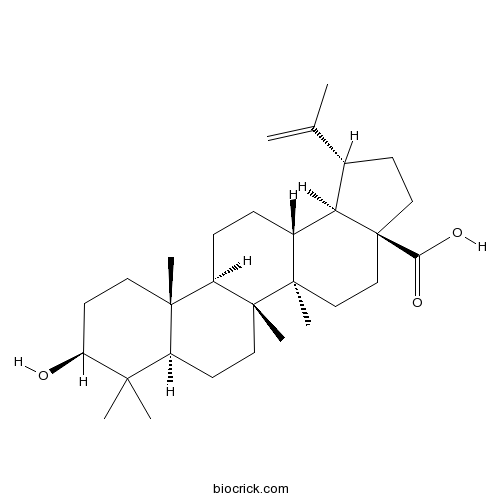
BCN5524
Betulinic acid472-15-1
Instructions
-
BCN5554
Linarin480-36-4
Instructions

-
BCN5560
Acacetin480-44-4
Instructions

-
BCN8949
(-)-Carvone6485-40-1
Instructions
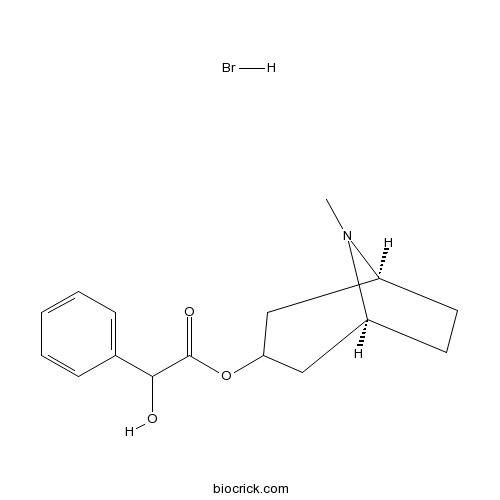
-
BCN2644
trans-Caryophyllene87-44-5
Instructions

-
BCN9045
Menthol89-78-1
Instructions
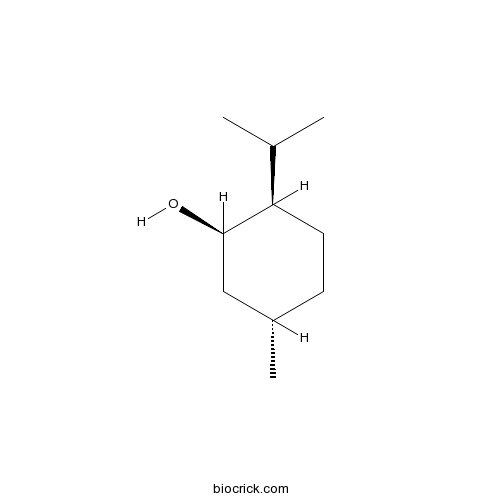
-
BCC9239
(+)-Menthone89-80-5
Instructions

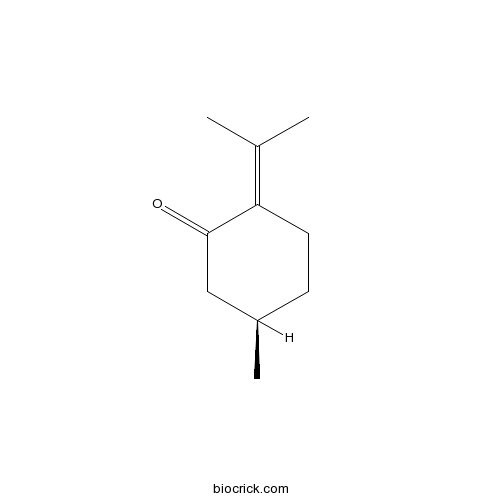
-
BCN3856
Pulegone89-82-7
Instructions
[Sex structure and seed productivity of Mentha canadensis L. from natural flora of primorye of Russia].[Pubmed: 25720285]
The sex structure and seed productivity of Mentha canadensis L. from different climatic regioins of Primorye of Russia was studied. We established that M. canadensis is characterized by a homogeneous population structure due to the formation of vegetative clones. The ratio of female and androgynous individuals was 1:5, and it is possible that this is a species-specific trait. Both sexual forms produced fruits under conditions of isolation from cross-pollination. We discuss the possibility of apomixis and the influence of climatic conditions on seed productivity and morphometric characteristics of plants.
Menthol: a simple monoterpene with remarkable biological properties.[Pubmed: 24054028]
Menthol is a cyclic monoterpene alcohol which possesses well-known cooling characteristics and a residual minty smell of the oil remnants from which it was obtained. Because of these attributes it is one of the most important flavouring additives besides vanilla and citrus. Due to this reason it is used in a variety of consumer products ranging from confections such as chocolate and chewing gum to oral-care products such as toothpaste as well as in over-the-counter medicinal products for its cooling and biological effects. Its cooling effects are not exclusive to medicinal use. Approximately one quarter of the cigarettes on the market contain menthol and small amounts of menthol are even included in non-mentholated cigarettes. Natural menthol is isolated exclusively from Mentha canadensis, but can also be synthesised on industrial scale through various processes. Although menthol exists in eight stereoisomeric forms, (-)-menthol from the natural source and synthesised menthol with the same structure is the most preferred isomer. The demand for menthol is high and it was previously estimated that the worldwide use of menthol was 30-32,000 metric tonnes per annum. Menthol is not a predominant compound of the essential oils as it can only be found as a constituent of a limited number of aromatic plants. These plants are known to exhibit biological activity in vitro and in vivo such as antibacterial, antifungal, antipruritic, anticancer and analgesic effects, and are also an effective fumigant. In addition, menthol is one of the most effective terpenes used to enhance the dermal penetration of pharmaceuticals. This review summarises the chemical and biological properties of menthol and highlights its cooling effects and toxicity.
Yield, content, and composition of peppermint and spearmints as a function of harvesting time and drying.[Pubmed: 20942459]
Peppermint ( Mentha × piperita L.) and spearmints ('Scotch' spearmint, M. × gracilis Sole, and 'Native' spearmint, Mentha spicata L.) are widely grown essential oil crops in more northern latitudes; however, there is limited information on how harvest time and drying influence peppermint and spearmint yield, oil composition, and bioactivity, when grown south of the 41st parallel. In this 2-year study, the effects of harvest time and drying on the yield, oil composition, and bioactivity of peppermint ('Black Mitcham' and 'B90-9'), 'Scotch' spearmint, and 'Native' spearmint were evaluated. Peppermint oil from the dried material had higher menthol and eucalyptol concentrations. Menthone in both peppermint cultivars decreased from harvest 1 (late June) to harvest 5 (late August) or 6 (early September), whereas menthol increased. (-)-Carvone in spearmints accumulated early, before flowering, allowing for early harvest. Oil yields from the dried spearmint biomass reached the maximum at harvest 3 (mid-July). The essential oil compositions of the four mint genotypes were similar to that of 11 commercially available oils, suggesting that these genotypes can be grown in the hot, humid environment of the southeastern United States. The antioxidant activities (ORAC(oil) values) of the essential oils were 4372, 1713, 1107, and 471 μmol of TE L(-1) for 'Scotch' spearmint, 'Native' spearmint, peppermint, and Japanese cornmint ( Mentha canadensis ), respectively. The oils of the four mint genotypes did not affect ruminal fermentation in vivo, and did not exhibit antimicrobial, antileishmanial, or antimalarial activity at levels that would warrant bioassay-directed fractionation in a drug-discovery screening program. Specifically, the oils did not show greater than 50% growth inhibition against Leishmania donovani , Plasmodium falciparum clones D6 and W2, Candida albicans , Escherichia coli , Pseudomonas aeruginosa , Cryptococcus neoformans , Mycobacterium intracellulare , or Aspergillus fumigates at 50 μg mL(-1).
Chemical composition, olfactory evaluation and antioxidant effects of essential oil from Mentha canadensis.[Pubmed: 19731614]
The chemical composition of the essential oil from cornmint (Mentha canadensis L.) was analyzed by GC/FID and GC-MS. The main constituents were menthol (41.2%) and menthone (20.4%). It was established that cornmint oil had antiradical activity with respect to the DPPH and hydroxyl (OH*) radicals. The concentrations necessary for 50% neutralization of the respective radicals (IC50) were 365.0 microg/mL for DPPH and 0.3 microg/mL for OH*, which was indicative that the antioxidant activity in terms of OH* was higher than that of quercetin. Cornmint oil chelated the Fe3+ ions present in the solution. The oil demonstrated antioxidant activity in a linoleic acid emulsion model system, where at 0.1% concentration it inhibited the formation of conjugated dienes by 57.1% and the generation of secondary oxidized products of linoleic acid by 76.1%.


