Morus australis
Morus australis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Morus australis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
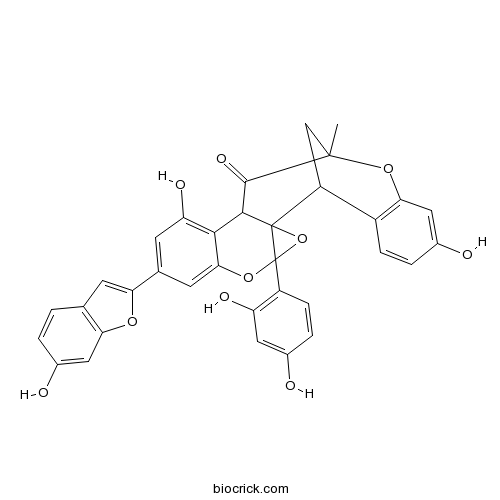
BCN8844
Mulberrofuran Q101383-35-1
Instructions
-
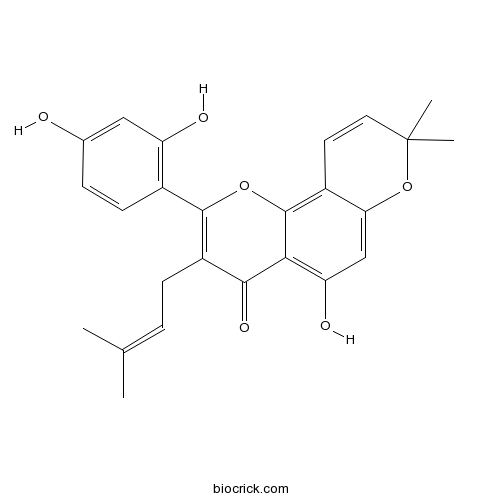
BCN4165
Morusin62596-29-6
Instructions
Several newly discovered Mo-enriched plants with a focus on Macleaya cordata.[Pubmed: 29987470]
Phytoremediation as an alternative strategy has been a widespread attention. The screening of enriched plants and hyperaccumulators is the key of the strategy. So this study examined the status of heavy metal pollution in molybdenum (Mo) mine soils, metal accumulation in plants growing on mine, and their tolerance strategies. The analysis of 14 soils and 27 plant samples in mining area showed that Mo, zinc (Zn), and cadmium (Cd) concentrations exceeded soil safety standards and their levels varied in 27 plant samples. Mo was the heavy pollution with an average total content of 256.1 mg/kg in soils. As Mo-enriched plants, Mo concentrations of Macleaya cordata (Willd.) R. Br. and Morus australis Poir. were 704.4 and 772.4 mg/kg, respectively. M. cordata was selected as the research material, due to its high biomass. Molybdenum significantly decreased the biomass and photosynthesis of M. cordata at high concentration (> 200 μmol/L), but its biomass and photosynthesis reached the maximum after 50 μmol/L Mo treatment, respectively. Analysis of the subcellular distribution and chemical speciation showed that Mo was distributed a certain way in the extracts and that this suggested that it may be present in cell wall and soluble fraction of roots (51.9-63.9%; 26.1-44.7%) or shoots (30.0-44.4%; 47.3-56.0%) and complexed to organic acid, pectate, oxalate, and protein. This might be responsible for the adaptation of M. cordata to Mo stress. Therefore, M. cordata could serve as a potential plant to utilize for the phytoremediation of Mo-contaminated soil.
Intra-specific trends of lumen and wall resistivities of vessels within the stem xylem vary among three woody plants.[Pubmed: 29036681]
Water flow through xylem vessels encounters hydraulic resistance when passing through the vessel lumen and end wall. Comparative studies have reported that lumen and end wall resistivities co-limit water flow through stem xylem in several angiosperm woody species that have vessels of different average diameter and length. This study examined the intra-specific relationship between the lumen and end wall resistivities (Rlumen and Rwall) for vessels within the stem xylem using three deciduous angiosperm woody species found in temperate forest. Morus australis Poir. and Acer rufinerve Siebold et Zucc. are early- and late-successional species, and Vitis coignetiae Pulliat ex Planch is a woody liana. According to the Hagen-Poiseuille equation, Rlumen is proportional to the fourth power of vessel diameter (D), whereas vessel length (L) and inter-vessel pit area (Apit) determine Rwall. To estimate Rlumen and Rwall, the scaling relationships between the L and D and between Apit and D were measured. The scaling exponents between L and D were 1.47, 3.19 and 2.86 for A. rufinerve, M. australis and V. coignetiae, respectively, whereas those between Apit and D were 0.242, 2.11 and 2.68, respectively. Unlike the inter-specific relationships, the wall resistivity fraction (Rwall/(Rlumen + Rwall)) within xylem changed depending on D. In M. australis and V. coignetiae, this fraction decreased with increasing D, while in A. rufinerve, it increased with D. Vessels with a high wall resistivity fraction have high Rwall and total resistivity but are expected to have low susceptibility to xylem cavitation due to a small cumulative Apit. In contrast, vessels with a low wall resistivity fraction have low Rwall and total resistivity but high susceptibility to xylem cavitation. Because the wall resistivity fraction varies with D, the stem xylem contains vessels with different hydraulic efficiencies and safety to xylem cavitation. These features produce differences in the hydraulic properties of plants with different life forms.
Extract from Mulberry (Morus australis) leaf decelerate acetaminophen induced hepatic inflammation involving downregulation of myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) signals.[Pubmed: 28987363]
Acetaminophen (APAP) induced inflammation and oxidative stress can cause cell death to induce liver damage. The antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effect of Mulberry (Morus australis) leaf extract (MLE) was shown in previous studies. In this study, we investigated the modulation of MLE on APAP induced inflammation and oxidative stress in rat liver injury or liver cancer cell (HepG2). Wistar rat was fed orally with MLE (0.5% or 1.0 %) for 1 week, and then, 900 mg/kg of APAP was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.). Pretreatment of MLE decreased obvious foci of inflammatory cell infiltration in liver. It also reduced the expression of inflammatory parameters including cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in liver. Treating with MLE increased the antioxidative enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase. Giving APAP to HepG2 hepatocyte was conducted to elucidate the mechanism of MLE or its functional components. The result showed that APAP upregulated hepatic protein expression of (myeloid differentiation factor 88) MyD88, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB), inhibitor of kappa B (IkB), c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), and receptor interacting proteins (RIP1 and RIP3). Pretreatment of MLE, gallic acid (GA), gallocatechin gallate (GCG), or protocatechuic acid (PCA) suppressed the indicated protein expression. These findings confirmed that MLE has the potential to protect liver from APAP-induced inflammation, and the protecting mechanism might involve decreasing oxidative stress and regulating the innate immunity involving MyD88.
Structures of Bordered Pits Potentially Contributing to Isolation of a Refilled Vessel from Negative Xylem Pressure in Stems of Morus australis Poir.: Testing of the Pit Membrane Osmosis and Pit Valve Hypotheses.[Pubmed: 28013275]
Two hypotheses have been proposed to explain the mechanism preventing the refilling vessel water from being drained to the neighboring functional vessels under negative pressure. The pit membrane osmosis hypothesis proposes that the xylem parenchyma cells release polysaccharides that are impermeable to the intervessel pit membranes into the refilling vessel; this osmotically counteracts the negative pressure, thereby allowing the vessel to refill. The pit valve hypothesis proposes that gas trapped within intervessel bordered pits isolates the refilling vessel water from the surrounding functional vessels. Here, using the single-vessel method, we assessed these hypotheses in shoots of mulberry (Morus australis Poir.). First, we confirmed the occurrence of xylem refilling under negative pressure in the potted mulberry saplings. To examine the pit membrane osmosis hypothesis, we estimated the semi-permeability of pit membranes for molecules of various sizes and found that the pit membranes were not semi-permeable to polyethylene glycol of molecular mass <20,000. For the pit valve hypothesis, we formed pit valves in the intervessel pits in the short stem segments and measured the maximum liquid pressure up to which gases in bordered pits were retained. The threshold pressure ranged from 0.025 to 0.10 MPa. These values matched the theoretical value calculated from the geometry of the pit chamber (0.0692-0.101 MPa). Our results suggest that gas in the pits is retained by surface tension, even under substantial positive pressure to resolve gases in the refilling vessel, whereas the molecule size required for the pit membrane osmosis mechanism in mulberry would be unrealistically large.
Bioactive chemical constituents from the root bark of Morus australis.[Pubmed: 27908762]
None
The depigmenting effect of natural resorcinol type polyphenols Kuwanon O and Sanggenon T from the roots of morus australis.[Pubmed: 27851907]
Morus australis, one of the major Morus species growing in East Asia, is rich in phenolic compounds. The extract of M. australis has been used as skin whitening components for a long period. The action mechanisms of its principal constituents are still unclear. This study aims to evaluate the skin lightening effects of phenolic compounds extracted from the root of M. australis in different melanocyte systems and artificial skin models.
Photoprotective effects of oxyresveratrol and Kuwanon O on DNA damage induced by UVA in human epidermal keratinocytes.[Pubmed: 25588103]
Ultraviolet A not only plays a major part in photoaging and skin tanning but also induces genetic damage and mutation in the epidermal basal layer of human skin. The photoprotective effect of oxyresveratrol and kuwanon O, two phenolic compounds from the root extract of Morus australis, in human primary epidermal keratinocytes was investigated in this study. Both of them were nontoxic to cells at a concentration less than 10 and 0.5 μM, respectively. After pretreatment at the concentrations of 5 and 10 μM, oxyresveratrol increased cell viability, exhibited significant suppressions on UVA- or H2O2-induced cellular ROS. UVA-enhanced nitrotyrosine was also reduced by post-treatment with oxyresveratrol at theses concentrations. Kuwanon O presented similar inhibitions on cellular ROS and nitrotyrosine with lower concentrations (0.25 and 0.5 μM), but there is no significant protection on cell survival after UVA irradiation. Their photoprotective effects also involved the enhanced repair of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) as mediated by the augment of p53 expression after UVA radiation.


