Nardostachys jatamansi
Nardostachys jatamansi
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Nardostachys jatamansi
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
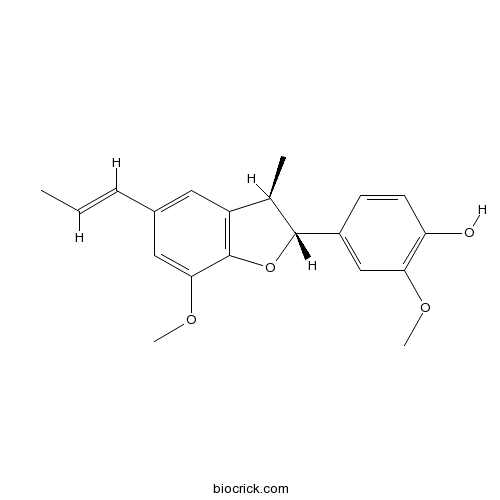
BCN2324
Nardosinone23720-80-1
Instructions

-
BCN5304
Cryptotanshinone35825-57-1
Instructions

-
BCN1193
alpha-Cyperone473-08-5
Instructions

-
BCC9008
(+)-Licarin A51020-86-1
Instructions
-
BCN2973
1-Octacosanol557-61-9
Instructions

-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

Six kanshone C-derived sesquiterpenoid hybrids nardochalaristolones A-D, nardoflavaristolone A and dinardokanshone F from Nardostachys jatamansi DC.[Pubmed: 30092385]
Four sesquiterpenoid-chalcone hybrids (nardochalaristolones A-D, 1-4), a pair of epimeric sesquiterpenoid-flavonone hybrids ((2'S)- and (2'R)-nardoflavaristolone A, 5 and 6), and a sesquiterpenoid dimer (dinardokanshone F, 7), all sharing a kanshone C-derived sesquiterpenoid unit, were isolated from the underground parts of Nardostachys jatamansi (D.Don) DC. Their structures were elucidated by analysis of the extensive spectroscopic data, and the absolute configurations were established by analysis of 2D NMR spectroscopic data including NOESY data, combined with comparisons of experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism spectra. Further, the plausible biosynthetic pathways for these compounds were proposed. And the results of SERT activity assay revealed that nardochalaristolones C-D (3 and 4) and nardoflavaristolone A (5 and 6) significantly enhanced SERT activity, while other compounds didn't show any SERT regulatory activities.
Anxiolytic actions of Nardostachys jatamansi via GABA benzodiazepine channel complex mechanism and its biodistribution studies.[Pubmed: 29934858]
None
Nardostachys jatamansi DC Extract Alleviates Insulin Resistance and Regulates Glucose Metabolism in C57BL/KsJ-db/db Mice Through the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed: 29630449]
This study investigated whether Nardostachys jatamansi DC extract (NJE) improved insulin sensitivity and suppressed hepatic glucose production in an animal model of type 2 diabetes. C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice were divided into three dietary groups: regular diet (control), NJE, and rosiglitazone. After 6 weeks of feeding, blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, and plasma insulin levels were significantly lower in NJE than in diabetic control group mice. The oral glucose tolerance test also revealed a positive effect of NJE on increasing insulin sensitivity. The homeostatic index of insulin resistance was significantly lower in NJE than in diabetic control group mice. NJE markedly lowered the plasma lipid concentration compared to diabetic control group mice. In the skeletal muscle, the expression of phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase, pAkt substrate of 160 kDa, and plasma membrane glucose transporter type 4 increased more in NJE compared to diabetic control group mice. NJE also decreased the expression of glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in the liver. These findings demonstrate that NJE alleviates hyperglycemia by improving insulin sensitivity and inhibiting gluconeogenesis in the liver.
Nardosinone-Type Sesquiterpenes from the Hexane Fraction of Nardostachys jatamansi Attenuate NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells.[Pubmed: 29616391]
None
Dinardokanshones C-E, isonardoeudesmols A-D and nardoeudesmol D from Nardostachys jatamansi DC.[Pubmed: 29544214]
Dinardokanshones C-E, three sesquiterpenoid dimers comprising an unusual nornardosinane-type sesquiterpenoid core and an aristolane-type sesquiterpenoid unit conjugated by an extra pyran or furan ring, together with monomeric sesquiterpenoids isonardoeudesmols A-D and nardoeudesmol D, were isolated from the underground parts of Nardostachys jatamansi DC. Structures of the eight compounds were elucidated by analysis of the extensive spectroscopic data, and their absolute configurations were established by analysis of NOESY and X-ray diffraction data, combined with computational electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculations. The results of SERT activity assay revealed that isonardoeudesmol D and nardoeudesmol D significantly inhibited SERT activity, while dinardokanshones D-E and isonardoeudesmols B-C significantly enhanced SERT activity, among which dinardokanshone D exhibited the strongest effect.
A System Pharmacology Study for Deciphering Anti Depression Activity of Nardostachys jatamansi.[Pubmed: 29512454]
The plant Nardostachys jatamansi from Valerianaceae family is a well known antidepressant plant and has historically been used in traditional medicine. As N. jatamansi contains many different compounds, to identify its mechanisms of action, we need a network-based study. Network-based studies are becoming an increasingly important tool in understanding the mechanisms of actions of drugs. Systems pharmacology (SP) and bioinformatics are two emerging tools that use computation to develop an understanding of drug actions in molecular and cellular levels. SP can provide mechanistic understanding of protein-protein (drug-target) interaction involved in a common biological pathway. The present study was undertaken to identify unknown targets and mechanisms of antidepressant activity of N. jatamansi according to a systems pharmacology approach.
Nardostachys jatamansi Ethanol Extract Ameliorates Aβ42 Cytotoxicity.[Pubmed: 29398668]
The Nardostachys jatamansi DC (NJ) root has been used as a sedative or analgesic to treat neurological symptoms and pain in traditional Korean medicine. Here, we investigate the potential effects of NJ on Alzheimer's disease (AD) and reveal the molecular mechanism through which NJ exerts its effects. The neuroprotective effect of the NJ root ethanol extract against β amyloid (Aβ) toxicity was examined in vitro using a cell culture system and in vivo using a Drosophila AD model. The NJ extract and chlorogenic acid, a major component of NJ, inhibited Aβ-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells. Moreover, the NJ extract rescued the neurological phenotypes of the Aβ42-expressing flies (decreased survival and pupariation rate and a locomotor defect) and suppressed Aβ42-induced cell death in the brain. We also found that NJ extract intake reduced glial cell number, reactive oxygen species level, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation, and nitric oxide level in Aβ42-expressing flies, without affecting Aβ accumulation. These data suggest that the neuroprotective activity of NJ might be associated with its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as its inhibitory action against ERK signaling; thus, NJ is a promising medicinal plant for the development of AD treatment.
Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of sesquiterpenoids isolated from Nardostachys jatamansi.[Pubmed: 29221883]
None
A Simple and Rapid UPLC-PDA Method for Quality Control of Nardostachys jatamansi.[Pubmed: 29202512]
None


