Ophiopogon japonicus
Ophiopogon japonicus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
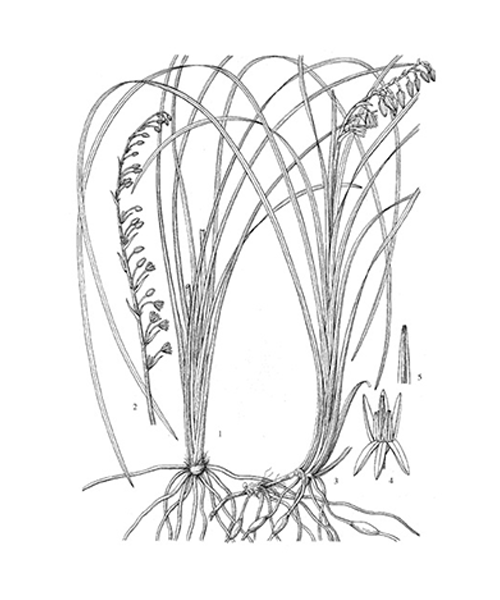
Natural products/compounds from Ophiopogon japonicus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2755
17-Hydroxy sprengerinin C1029017-75-1
Instructions

-
BCN2777
14-Hydroxy sprengerinin C1111088-89-1
Instructions

-
BCN2860
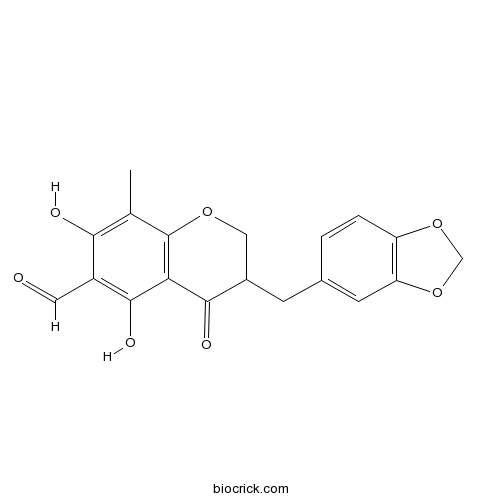
6-Aldehydoisoophiopogonanone A116291-82-8
Instructions
-
BCN1587
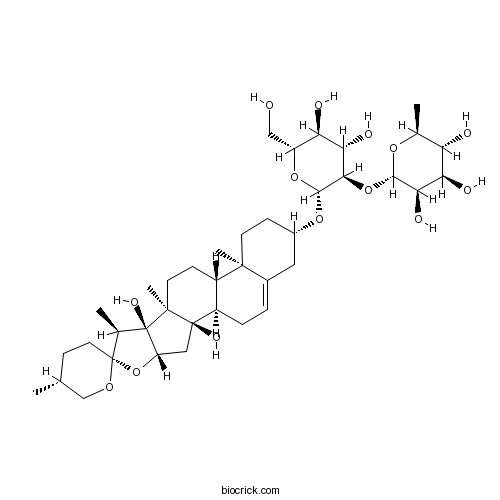
Ophiogenin-3-O-alpha-L-rhaMnopyranosyl-(1→2)-beta-D-glucopyranoside128502-94-3
Instructions
-
BCN6273
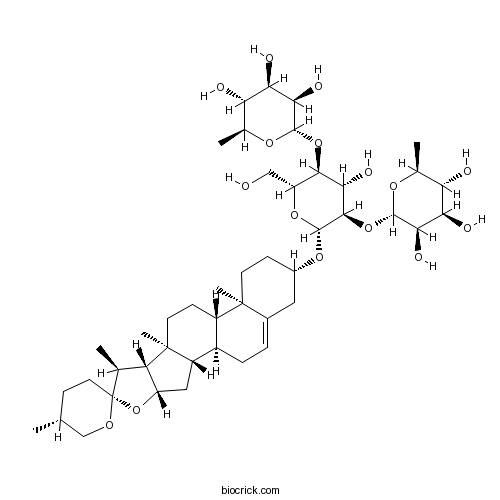
Dioscin19057-60-4
Instructions
-
BCN4865
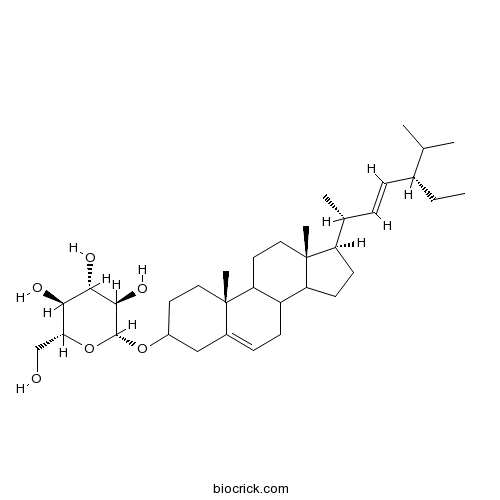
Stigmasterol glucoside19716-26-8
Instructions
-
BCN4916
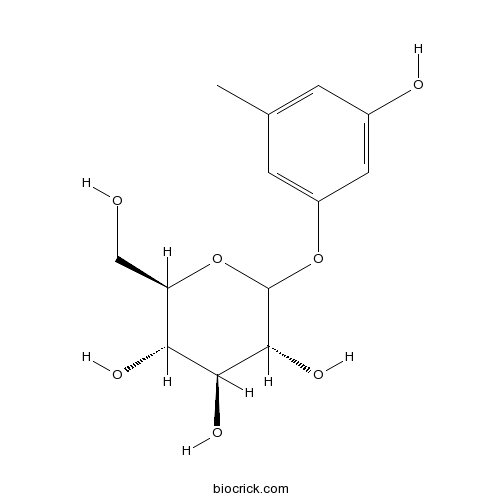
Sakakin21082-33-7
Instructions
-
BCN2778
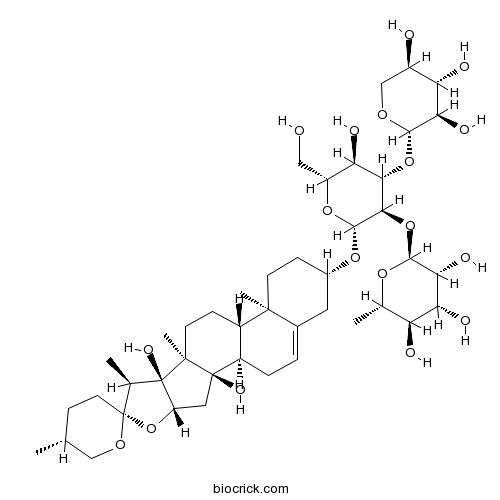
Cixiophiopogon A288143-27-1
Instructions
-
BCN5320
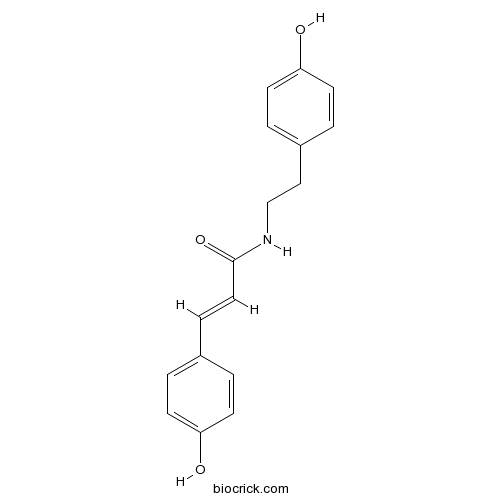
N-p-trans-Coumaroyltyramine36417-86-4
Instructions
-
BCN2645
Ophiopogonin D'65604-80-0
Instructions
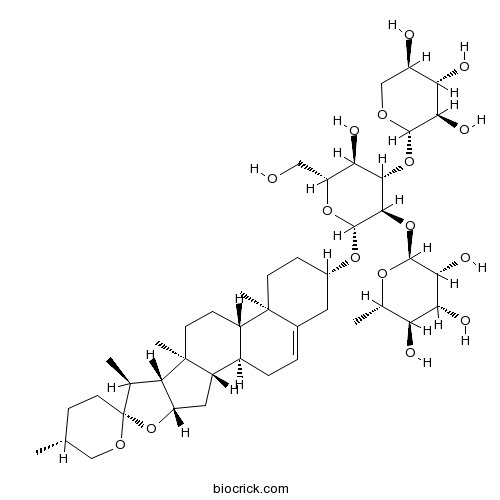
-
BCN4603
N-p-Coumaroyloctopamine66648-45-1
Instructions

-
BCN2841
Methylophiopogonone A74805-90-6
Instructions

-
BCN5418
Methylophiopogonanone B74805-91-7
Instructions

-
BCN5417
Methylophiopogonanone A74805-92-8
Instructions

-
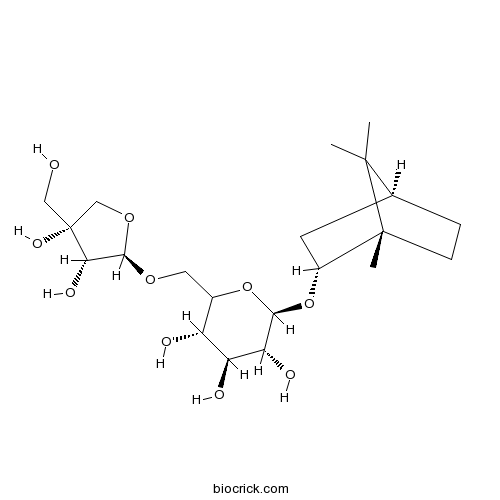
BCN7814
Borneol 7-O-[beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1->6)]-beta-D-glucopyranoside88700-35-0
Instructions
[Complex network analysis of law on Chinese herbal drugs intervention on radiation induced lung injury].[Pubmed: 30111064]
To mainly analyze the prescription rules of Chinese herbal drugs for radiation induced lung injury, optimize the prescriptions, and provide a reference for the clinical treatment of radiation induced lung injury. The major Chinese databases CNKI, CBM and Wanfang data were searched to obtain the literature on Chinese herbal drugs for radiation induced lung injury. BICOMS 2 software was used to extract and collect all Chinese herbal drugs information and generate the co-occurrence matrix; NetDraw and Gcluto software were then used to make network map and visualization matrix for analysis. A total of 552 articles (19 types and 304 Chinese herbal drugs) were included. Ophiopogon japonicus had the highest frequency (229 times), followed by Astragalus membranaceus(181 times), Glycyrrhiza uralensis (166 times), and Scutellaria baicalensis (150 times). After the classification of efficacy, deficiency-supplementing medicinal (69 kinds of Chinese herbs), heat-clearing medicine (51 kinds of Chinese herbs) and phlegm cough medicine (42 kinds of Chinese herbs) accounted for 53.29% of all the Chinese herbs, acting in the main position. After the prescription analysis for the top 25 herbal prescriptions, six main structures of common prescriptions were found for the treatment of radiation induced lung injury. There are many kinds of Chinese herbal drugs for the treatment of radiation induced lung injury in clinical application. In the future, researchers can mainly focus on Ophiopogon japonicus etc. as the main drugs, combine with other high-frequency Chinese herbal drugs found in this study, or directly refer to the main structures of commonly used prescriptions found in this analysis.
The influence of polysaccharides from Ophiopogon japonicus on 2,3,5,4'-tetrahydroxy-stilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside about biopharmaceutical properties in vitro and pharmacokinetics in vivo.[Pubmed: 30067956]
None
New steroidal glycosides from the fibrous roots of Ophiopogon japonicus.[Pubmed: 30014711]
Two new steroidal glycosides (named fibrophiopogonins A, B), along with one known glycoside, were isolated from the fibrous roots of Ophiopogon japonicus (Liliaceae). Comprehensive spectroscopic analysis, including 2D NMR spectroscopy, and the results of acid hydrolysis allowed the chemical structure of the compounds to be assigned as 26-[(O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 6)-D-glucopyranosyl)]-barogenin- 3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside and (25R)-26-[(O- β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl)]- 3β,22α,26- trihydroxyfurost- 5-ene-3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside. This is the first isolation of a cholestane glycoside with disaccharide moiety from a Ophiopogon species. The cytotoxic activities of 1~3 against A375 and MCF-7 cells are described.
Anti-inflammatory activities of Ophiopogonis Radix on hydrogen peroxide-induced cellular senescence of normal human dermal fibroblasts.[Pubmed: 29961188]
Ophiopogonis Radix (Ophiopogon root), which nourishes the yin, has been used in clinical practice to promote fluid secretion and to moisturize the lungs and skin in traditional Chinese and Japanese (Kampo) medicine. To evaluate this traditional medicinal effect, we investigated the anti-chronic inflammatory effect of Radix Ophiopogonis on senescent cells. Conversely, although several phenotypes of Ophiopogon japonicus Ker-Gawler (Liliaceae) are prevalent in Japan and China, we used these Ophiopogon roots by considering them as one crude drug, Ophiopogonis Radix. In this study, it was revealed that there are two chemotypes (Types A and B) in the root of the original plant, O. japonicus. Methylophiopogonanone A (compound 1) and methylophiopogonanone B (compound 2) were isolated as index compounds from Type A and compound 1 and ophiopogonanone A (compound 3) from Type B. In addition, ophiopogonin B (compound 4) was isolated as the main steroidal saponin from both Type A and B. The results indicated that two different methanol extracts (from Types A and B) and the main constituents of O. japonicus (compound 1-4), significantly downregulated the expression of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8, which were enhanced by senescent normal human dermal fibroblasts. Moreover, the two different methanol extracts and compounds 1-4 decreased IL-6 production in a strong and concentration-dependent manner by the ELISA method.
Migration and transformation of different phosphorus forms in rainfall runoff in bioretention system.[Pubmed: 29869209]
Artificial bioretention system consisting of Ophiopogon japonicus infiltration medium was used to simulate an infiltration experiment of rainfall runoff. Continuous extraction method was used to detect contents of inorganic phosphorus (P) under exchangeable state (Ex-P) and aluminium phosphate (Al-P) and iron phosphate (Fe-P) at different depths (0, 5, 15 and 35 cm) of soil infiltration medium in bioretention system. Effluent total P (TP) concentration of the system was also monitored. Results indicated that the adsorption of inorganic P, Al-P and Fe-P by soil infiltration medium was implemented layer by layer from top to bottom and gradually weakened. Moreover, Ex-P was gradually transformed into Al-P and Fe-P, whereas Al-P was gradually transformed into Fe-P; thus, Ex-P content reduced layer by layer, whereas Al-P and Fe-P gradually accumulated. The TP removal rate in runoff rainwater by the system was more than 90%, where the TP that was not used by plants was under dynamic equilibrium in water-soil-root system/biological system.
A simple multi-residue method for determination of plant growth retardants in Ophiopogon japonicus and soil using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 29803882]
None
Ophiopogonin D improves osteointegration of titanium alloy implants under diabetic conditions by inhibition of ROS overproduction via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 29705132]
A high failure rate of titanium implants in diabetic patients has been indicated in clinical evidences. Excessive oxidative stress at the bone-implant interface plays an important role in the impaired osteointegration under diabetic conditions. While the underlying mechanisms remain unknown and the targeted treatments are urgently needed. Ophiopogonin D (OP-D), isolated from Chinese herbal Radix Ophiopogon japonicus, is generally reported to be a potent antioxidant agent. In the present study, we hypothesized that OP-D exerted promotive effects on osteointegration against oxidative stress, and investigated the underlying mechanisms associated with alteration of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Rabbit osteoblasts incubated on titanium alloy implant were co-cultured with normal serum (NS), diabetic serum (DS), DS + OP-D, DS + NAC (a potent ROS inhibitor) and DS + OP-D + Dkk1 (a Wnt inhibitor) for examinations of osteoblast behaviors. For in vivo study, titanium alloy implants were implanted into the femoral condyle defects on diabetic rabbits. Results demonstrated that diabetes-induced oxidative stress resulted in osteoblast dysfunctions and apoptotic injury at the bone-implant interface, concomitant with the inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Importantly, OP-D administration attenuated oxidative stress, directly reactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Osteoblast dysfunctions were thus reversed as evidenced by improved osteoblast adhesion, proliferation and differentiation, and ameliorated apoptotic injury, exerting similar effects to NAC treatment. In addition, the positive effects afforded by OP-D were confirmed by improved osteointegration and oetogenesis within the titanium alloy implants in vivo by Micro-CT and histological analyses. Furthermore, the pro-osteogenic effects of OP-D were almost completely abolished by the Wnt inhibitor Dkk1. These results demonstrated, for the first time, OP-D administration alleviated the damaged osteointegration of titanium alloy implants under diabetic conditions by means of inhibiting oxidative stress via a Wnt/β-catenin-dependent mechanism. The OP-D administration would become a reliable treatment strategy for implant failure therapy in diabetics due to the optimal anti-oxidative and pro-osteogenic properties.
Recent advances in polysaccharides from Ophiopogon japonicus and Liriope spicata var. prolifera.[Pubmed: 29634971]
O. japonicus and L. spicata var. prolifera are distinguished as sources of highly promising yin-tonifying medicinals, namely Ophiopogonis Radix and Liriopes Radix. Liriopes Radix is generally medicinally used as a substitute for Ophiopogonis Radix in various prescriptions due to their extremely similar nature. Ophiopogonis Radix and Liriopes Radix are both very rich in bioactive polysaccharides, especially β‑fructans. Over the past twelve years, except for work on physical entrapment and chemical modification of obtained β‑fructans, the vast majority of studies are carried out to investigate the bioactivities of O. japonicus polysaccharides (OJP) and L. spicata var. prolifera polysaccharides (LSP), mainly including anti-diabetes, immunomodulation, anti-inflammation, antioxidation, anti-obesity, cardiovascular protection, etc. In addition, OJP and LSP are considered to have the potential to regulate intestinal flora. The main purpose of this review is to provide systematically reorganized information on structural characteristics and bioactivities of OJP and LSP to support their further therapeutic potentials and sanitarian functions.


