Penthorum chinense
Penthorum chinense
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Penthorum chinense
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6769
Pinocembrin 7-O-(3'-galloyl-4',6'-(S)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl)-beta-D-glucose205370-59-8
Instructions

-
BCN2774
Thonningianin A271579-11-4
Instructions

-
BCN5540
Bergenin477-90-7
Instructions

-
BCN5573
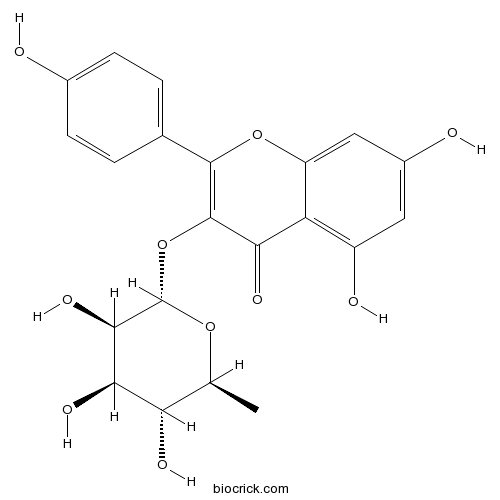
Afzelin482-39-3
Instructions
-
BCN4537
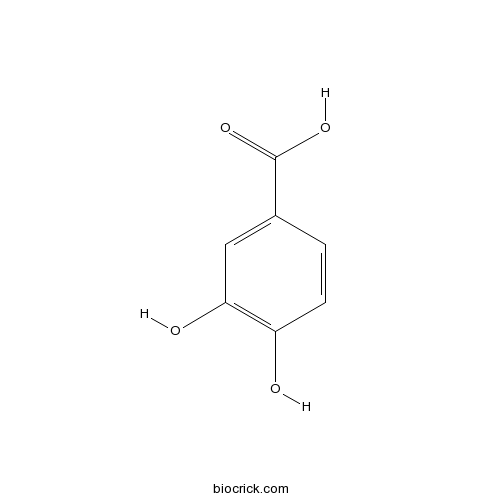
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
Quality assessment of Penthorum chinense Pursh through multicomponent qualification and fingerprint, chemometric, and antihepatocarcinoma analyses.[Pubmed: 29932194]
An efficient method combined with fingerprint and chemometric analyses was developed to evaluate the quality of the traditional Chinese medicine plant Penthorum chinense Pursh. Nine samples were collected from different regions during different harvest periods, and 17 components in the form of extracts were simultaneously examined to assess quality by using high-performance liquid chromatography. The hepatoprotective effects of components were investigated by assessing the inhibition of SMMC-7721 cell growth. The results indicated that the quality control method was accurate, stable, and reliable, and the hierarchical heat-map cluster and the principle component analyses confirmed that the classification of all nine samples was consistent. Quercetin and ellagitannins including pinocembrin-7-O-[3''-O-galloyl-4'',6''-hexahydroxydiphenoyl]-β-glucose (PGHG), thonningianin A, thonningianin B, and other flavonoids were abundant in the extracts, and significantly contributed to the hepatoprotective effects.
Pinocembrin from Penthorum chinense Pursh suppresses hepatic stellate cells activation through a unified SIRT3-TGF-β-Smad signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 29352975]
The inactivation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) has been verified to be an effective therapeutic strategy for treatment of liver fibrosis. Penthorum chinense Pursh has been widely used to protect liver in China; while, the role of P. chinense Pursh in treatment of liver fibrosis is still unexplored. In the current study, the aqueous extract of P. chinense Pursh (PCE) was found to suppress the expressions of fibrotic markers, including collagen I and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), in human HSCs (LX-2); and its major active constituent, pinocembrin (PIN), was discovered to inhibit the expressions of fibrotic markers in LX-2 cells and rat HSCs (HSC-T6). Further study indicated that PIN suppressed the activation of LX-2 and HSC-T6 cells through elevating the expression and activity of silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 3 (SIRT3). Via SIRT3, PIN activated superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), to alleviate the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibit phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-protein kinase B (Akt) signaling, resulting in decreased production of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and nuclear translocation of the transcription factor Sma- and Mad-related proteins (Smad). Furthermore, PIN activated glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) through SIRT3, to enhance Smad protein degradation. Taken together, PCE and PIN were identified as potential anti-fibrotic agents, which might be well developed as a candidate for treatment of liver fibrosis.
In-vivo absorption of pinocembrin-7-O-β-D-glucoside in rats and its in-vitro biotransformation.[Pubmed: 27378517]
Pinocembrin-7-O-β-D-glucoside (PCBG), a flavonoid isolated from Penthorum chinense Pursh., has significant liver-protecting effects. The pharmacokinetics of PCBG and its major metabolite pinocembrin (PCB) in rats were investigated in this study. A sensitive and accurate UPLC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the simultaneous quantitative determination of PCBG and PCB in rat plasma after oral and intravenous administration of PCBG. After intravenous administration, PCBG was the main form in plasma. In contrast, after oral administration, the concentration of PCB was about 4-fold higher than that of PCBG, indicating that PCBG was metabolized to PCB. We also investigated the biotransformation of PCBG in vitro in order to understand whether the pH and the intestinal flora of gastrointestinal tract could affect the metabolism of PCBG. PCBG was incubated in rat plasma, liver homogenization, gastrointestial contents, liver microsomes (RLM) and hepatocytes in vitro. The data showed that PCB was quickly formed in the gastrointestinal incubation but PCBG was converted to PCB gradually in other incubations. The results indicated that the majority of PCBG was converted to its aglycone PCB in digestive system after oral administration, and PCB could be the active ingredient in the body.
Bio-assay guided identification of hepatoprotective polyphenols from Penthorum chinense Pursh on t-BHP induced oxidative stress injured L02 cells.[Pubmed: 27050144]
Penthorum chinense Pursh (Ganhuangcao in Chinese) is traditionally used for liver protection and treatment of liver diseases, including hepatitis B, hepatitis C and alcoholic liver damage. We and others have disclosed the hepatoprotective effect of different extracts from P. chinense. To further explore the chemical principles responsible for its liver protective effect, a bioactivity guided isolation was carried out on the water extract of P. chinense, which led to the identification of an effective fraction (E50M60). Further isolation of the E50M60 fraction produced ten polyphenols. Among them, quercetin showed the most significant protective effect on tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) induced hepatocyte damage. Further study demonstrated that both the E50M60 fraction and quercetin attenuated t-BHP induced hepatocyte apoptosis through up-regulating the expression of B-cell lymphoma-2 protein (BCL-2) and BCL-xL, and down-regulating the cleaved products of caspase-7, -9 and nuclear poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Moreover, the E50M60 fraction and quercetin promoted nuclear factor-like 2 (NRF2), superoxide dismutase-2 (SOD-2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expressions and suppressed Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP-1) expression, resulting in resistance to the reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced mitochondrial oxidative stress. Altogether, both the active fraction and quercetin from P. chinense might be well developed as a novel functional food for liver protection.
Diastereomeric Ellagitannin Isomers from Penthorum chinense.[Pubmed: 26218585]
From the dried stem of Penthorum chinense (Penthoraceae), 1-O-galloyl-4,6-(R)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP)-β-D-glucose and 2',4',6'-trihydroxyacetophenone 4'-O-[4,6-(R)-HHDP]-β-D-glucoside were isolated together with their (S)-HHDP isomers. Ellagitannins with a 4,6-(S)-HHDP-glucose moiety are widely distributed in the plant kingdom; however, 4,6-(R)-HHDP glucoses are extremely rare. Lowest-energy conformers of 1-O-galloyl-(S)- and (R)-HHDP-glucopyranoses were derived by density functional theory calculations, and the calculated (1)H and (13)C NMR chemical shifts and the (1)H-(1)H coupling constants were in agreement with the experimental values. The results revealed a conformational difference of the diastereomeric macrocyclic ester rings. In addition, a new compound, 1',3',5'-trihydroxybenzene 1'-O-[4,6-(S)-HHDP]-β-D-glucoside, was also isolated.
Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine Penthorum chinense Pursh: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review.[Pubmed: 26119956]
Penthorum chinense Pursh (ganhuangcao), a traditional Chinese medicine, is used for the prevention and treatment of liver diseases, including hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and alcoholic liver damage. A wide range of investigations have been carried out on this herbal medicine from pharmacognosy to pharmaceuticals, as well as pharmacology. The extract of P. chinense was reported to have significant liver protective effects through anti-oxidation, reduction of key enzyme levels, inhibition of hepatitis B virus DNA replication, and promotion of bile secretion. Based on the current knowledge, flavonoids and phenols are considered to be responsible for P. chinense's bioactivities. The main purpose of this review is to provide comprehensive and up-to-date knowledge of the phytochemical and pharmacological studies performed on P. chinense during the past few decades. Moreover, it intends to provide new insights into the research and development of this herbal medicine.
Identification and quantitation of major phenolic compounds from Penthorum chinense Pursh. by HPLC with tandem mass spectrometry and HPLC with diode array detection.[Pubmed: 26037645]
Penthorum chinense Pursh. is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine used for the treatment of various ailments specially related to liver. Gansu Granule, the medicine made from the extract of P. chinense, has been widely used in the clinical setting. But the information about its active ingredients is lacking. In this paper, the extract of P. chinense was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Among the 27 compounds that were identified based on their mass spectrometry data, ten were reported for the first time from P. chinense. Chromatographic fingerprints generated by high-performance liquid chromatography by analyzing 21 batches of P. chinense, displayed six common peaks. Finally, four major compounds were identified namely; gallic acid, brevifolin carboxylic acid, 2,6-dihydroxyacetophenone-4-O-β-D-glucoside, and pinocembrin-7-O-β-D-glucoside. The average content of each compound was 24.58, 109.6, 15.52, and 18.81 mg/g, respectively. In addition, this study also suggests that the qualitative liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and the quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography analytical methods using monolithic columns are simple, rapid, accurate, and reproducible and have the potential to be used for the comprehensive quality control of P. chinense.
Improved chromatographic fingerprinting combined with multi-components quantitative analysis for quality evaluation of Penthorum chinense by UHPLC-DAD.[Pubmed: 25920223]
A high performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) fingerprint is commonly used for quality consistency evaluation of herbal medicines. Recently, an improved chromatographic technique resulted in ultra high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), which could provide higher resolution in less time under higher pressure using finer particles (less than 2μm) of stationary phase. A simple and sensitive method was developed and validated for fingerprint analysis of Penthorum chinense Pursh (PC), with the simultaneous determination of seven components using UPLC coupled with a diode-array detector (DAD). It took less than 20 min for analysis of one sample. Both similarity analysis and principle components analysis (PCA) were employed to evaluate the quality consistency of 17 sample batches. The analysis was performed on a Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 (2.1 x 150 mm, 1.7 μm) column, which was maintained at 45°C and the eluents were monitored with DAD at 270 nm. A gradient elution with acetonitrile and water containing 0.075% phosphoric acid was used. The solvent flow rate was 0.4 mL/min. Standard calibration curves showed good linear behavior (R2 > 0.9994) in the range of 0.20-337.05 μg/mL. Acceptable repeatability (RSD < 0.61%), reproducibility (RSD < 2.72%), stability (RSD < 1.59%) and recovery in the range of 94.7%-102.9% were obtained (precision and accuracy). The validated method was successfully applied to evaluate the quality of 21 samples of PC.


