Pyrola calliantha
Pyrola calliantha
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Pyrola calliantha
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6307
Arbutin497-76-7
Instructions

-
BCN1218
2''-O-Galloylhyperin53209-27-1
Instructions
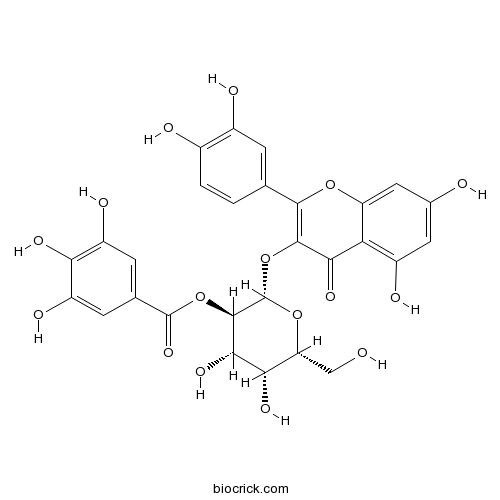
-
BCN6280
Monotropein5945-50-6
Instructions
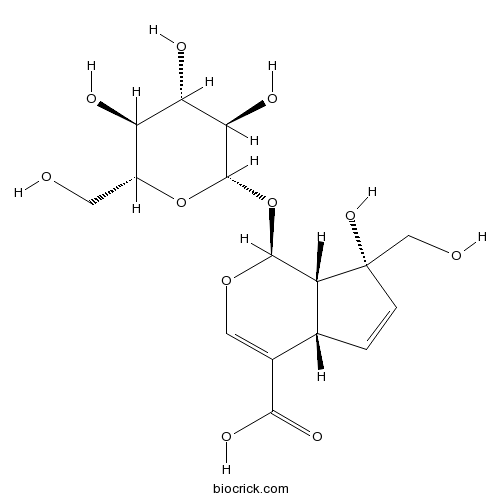
Screening for Neuraminidase Inhibitory Activity in Traditional Chinese Medicines Used to Treat Influenza.[Pubmed: 27618892]
To screen for influenza virus neuraminidase inhibition and to provide a reference for the clinical treatment of influenza using traditional Chinese medicines (TCM). In this study, 421 crude extracts (solubilized with petroleum ether, ethanol, ethyl acetate, and aqueous solvents) were obtained from 113 TCM. The medicine extracts were then reacted with oseltamivir, using 2'-(4-methylumbelliferyl)-α-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid (MUNANA) as the substrate, to determine influenza virus neuraminidase activity using a standard fluorimetric assay. It was found that Chinese medicine extracts from Pyrola calliantha, Cynanchum wilfordii, Balanophora involucrata and Paeonia delavayi significantly inhibited neuraminidase activity at a concentration of 40 μg/mL. Dose-dependent inhibitory assays also revealed significant inhibition. The IC50 range of the TCM extracts for influenza virus neuraminidase was approximately 12.66-34.85 μg/mL, respectively. Some Chinese medicines have clear anti-influenza viral effects that may play an important role in the treatment of influenza through the inhibition of viral neuraminidase. The results of this study demonstrated that plant medicines can serve as a useful source of neuraminidase (NA) inhibitors and further investigation into the pharmacologic activities of these extracts is warranted.
Validated LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of hyperoside and 2''-O-galloylhyperin in rat plasma: application to a pharmacokinetic study in rats.[Pubmed: 24375731]
An LC-MS/MS method was developed for the first time to simultaneously determine hyperoside and 2''-O-galloylhyperin, two major components in Pyrola calliantha extract, in rat plasma. Following extraction by one-step protein precipitation with methanol, the analytes were separated on a Venusil MP-C18 column within 2 min, using methanol-water-formic acid (50:50:0.1, v/v/v) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. Detection was performed on electrospray negative ionization mass spectrometry by multiple-reaction monitoring of the transitions of 2''-O-galloylhyperin at m/z 615.1 → 301.0, of hyperoside at m/z 463.1 → 300.1, and of internal standard at m/z 415.1 → 295.1. The limits of quantification were 2 ng/mL for both hyperoside and 2''-O-galloylhyperin. The precisions were <13.1%, and the accuracies were between -9.1 and 5.5% for both compounds. The method was successfully applied in pharmacokinetic studies following intravenous administration of the total flavonoids of P. calliantha extract in rats.
[A new naphthaquinone derivative from Pyrola calliantha H. Andres].[Pubmed: 21351589]
To investigate the chemical constituents of hemostatic extract of Pyrola calliantha H. Andres, the extract was subjected to chromatographic separation and purification. Along with some known compounds, a new naphthaquinone derivative was isolated and identified as 2-(1, 4-dihydro-2, 6-dimethyl-1, 4-dioxo-3-naphthalenyl)-3, 4, 5-trihydroxylbenzoic acid by physicochemical and spectroscopic analysis.
Two new isomeric alpha-tetralones from Pyrola calliantha.[Pubmed: 18991208]
Callianthones A ( 1) and B ( 2), a pair of new isomeric alpha-tetralones, together with a known alpha-tetralone ( 3) and four known flavonoids ( 4 - 7) were isolated from the 50 % EtOH extract of Pyrola calliantha. The structures and absolute configurations of the two new isomers were established to be (2 S,4 R) - and (2 S,4 S)-2,4-dihydroxy-2,7-dimethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2 H)-one ( 1 and 2, respectively) on the basis of spectral analysis, including 2 D NMR, model studies, and CD spectra.
Tetralones and flavonoids from Pyrola calliantha.[Pubmed: 18081103]
Two new tetralones, pyrolones A (1) and B (2), and a new flavonol glycoside, 2''-O-(4-hydroxybenzoyl)hyperin (3), were isolated from Pyrola calliantha (whole plant), together with six structurally related compounds, including 2''-O-galloylhyperin (4), hyperin (5), formononetin (6), quercetin 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside (7), quercetin 3-O-alpha-L-arabinofuranoside (8), and kaempferol 3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside (9). The structures and absolute configurations of the new compounds were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic (UV, ORD, CD, NMR) and mass-spectrometric (HR-ESI-MS) analyses.
[Pharmacological actions of different species form genus Pyrola].[Pubmed: 12572417]
This paper reporst the pharmacological actions and toxicities of the water extracts from Pyrola calliantha, Pyrola decorta and P. forrestiana. The results show that the actions of P. forrestiana on antiventricular fibrillation, strengthening cardiac musicular contraction and antihypoxia abitity are more stronger, but on antiinflammation and antipyretic, effects of P. decorta and P. calliantha are significantly better than that of P. forrestiana. The effects of the three species on immunization and antisepsis are similar.
[Experimental study and textual research on whether the genus of Pyrola contains arbutin].[Pubmed: 7646801]
Thin layer chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography show that Pyrola calliantha does not contain arbutin. Literature survey shows that to date no one has ever isolated arbutin from this herb.


