Serissa serissoides
Serissa serissoides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Serissa serissoides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCC8957
Episyringaresinol 4'-O-β-D-glncopyranoside137038-13-2
Instructions

-
BCN3323
Deacetylasperulosidic acid14259-55-3
Instructions
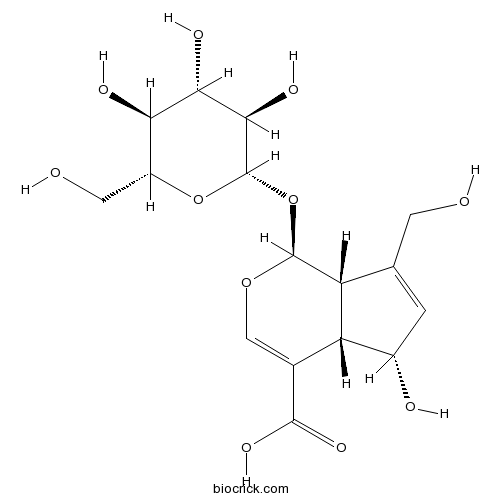
-
BCN3171
3-oxo-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid17990-42-0
Instructions
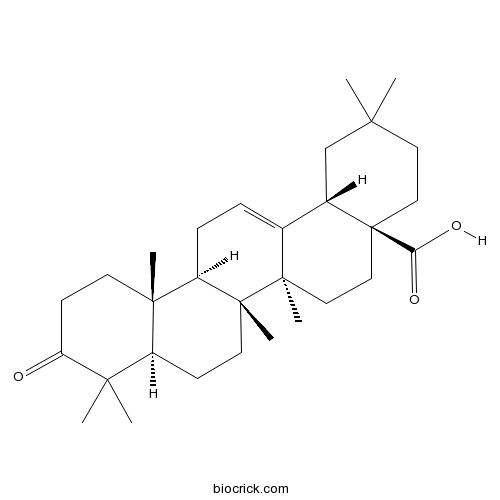
-
BCN3438
Paederosidic acid18842-98-3
Instructions
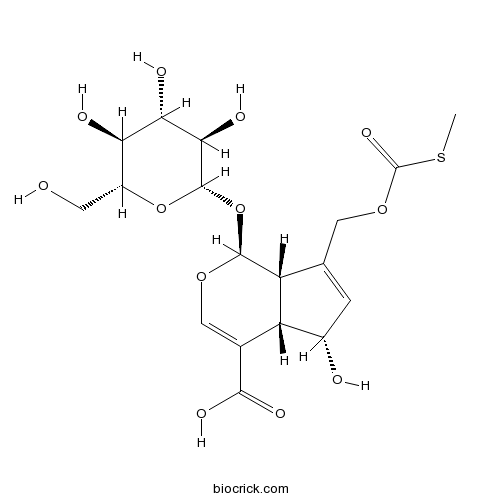
-
BCN5423
Vitexin3681-93-4
Instructions

-
BCN5503
Corosolic acid4547-24-4
Instructions

-
BCN2205
D-Mannitol69-65-8
Instructions

[Studies on chemical constituents from Serissa serissoides].[Pubmed: 17583202]
To study the chemical constituents of Serissa serissoides.
[Studies on chemical constituents of Serissa serissoides roots].[Pubmed: 17076236]
To study the chemical constituents from Serissa serissoides DC. roots.
[Interspecific association between understory species in a southern highland plantation].[Pubmed: 16471332]
Based upon 2 x 2 contingency table, chi2 test and association coefficient were used to determine the interspecific association between understory species in a southern highland plantation, and to analyze the restoration degree and the stability of southern highland vegetations originated from plantation. The Qianyanzhou in Taihe County of Jiangxi Province, a typical sample of southern highland plantation, was chosen to make the study. The results showed that both in shrub layer and in herb layer, species pair with chi2 reaching significant level (P <0.05) was few in number. In shrub layer, 12 species pairs' association was highly significant (P < 0.01), 19 pairs' was significant (P < 0.05), and other 200 pairs' was nonsignificant, while in herb layer, 11 pairs' was highly significant, 11 pairs' was significant and other 83 pairs' was nonsignificant. According to interspecific association and correlation, shrub layer was divided into two species groups: Group I . Adinandra bockiana, Syzygiumn grijsii, Vaccinium bracteatunm, Ilex aculeolata, Smilax ferox, Eurya muricata and Group II . Lespedeza davidii, Serissa serissoides, Vitex negundo var. cannabifolia. Many species in Group I had a significantly negative association with the species in Group II, and dominant species always played a key role in the relationships among species. The three dominant species in herb layer, Wooduardia japonica, Dryopteris atrata and Adiantun flabellulaturn, had a highly significant positive correlation between each other, and moreover, had a significant or highly significant positive association with many other herbaceous species. Similarily, dominant species in shrub layer played a key role on the interspecific association in the two species groups. The ratios of positive and negative association indicating the species compositions of the two layers were fluctuating, which was 125/106 in shrub layer and 42/63 in herb layer. Several shortcomings of interspecific association method were pointed out, with some proposals put forward.
[Contrastive analysis of volatile oil from Serissa serissoides in different seasons].[Pubmed: 15709384]
To provide the foundation for reasonable utilization by analysing the essential oils from Serissa serissoides in different seasons.
[Effects of the water-soluble extracts from the single herb of ganduqing against hepatitis B virus in vitro].[Pubmed: 12571922]
Comparing with Ara-Amp, the effects of the water-soluble extracts from the single herb of the formula for Ganduqing on HBeAg and HBsAg expression in 2.2.15 cells were studied. The results showed that the extracts of Serissa serissoides (DC) Druce, Hibiseus mutabilis Linn, Paedeuia scangens (Lour) Merr var tomentosa (BL) Hand-Mazz, Plumbago zeylanica L, Garcinia oblougifolia Champ and Begpnia edulia Levl had marked inhibition effects on HBeAg and HBsAg which expressed by 2.2.15 cells.


