Urtica fissa
Urtica fissa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Urtica fissa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
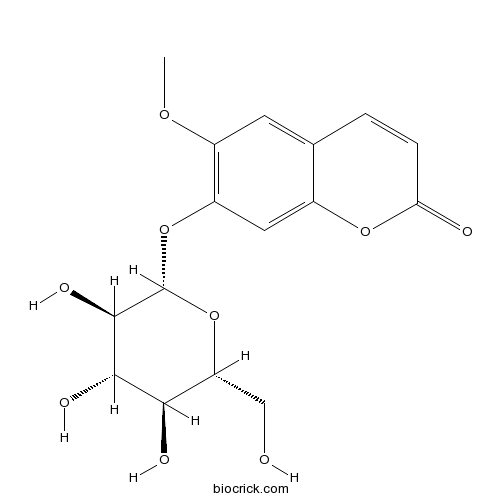
BCN5701
Scopolin531-44-2
Instructions
-
BCN2454
Anemosapogenin85999-40-2
Instructions

The active glycosides from Urtica fissa rhizome decoction.[Pubmed: 29332194]
Using bioassay guided fractionation, 16 glycosides, including two new compounds (1 and 2), were isolated from the anticomplement and anti-inflammatory portion of an Urtica fissa rhizome decoction used for arthritis. Several compounds were found to possess significant anticomplement and anti-inflammatory activities. This study revealed that glycosides played an important role in the therapeutic effects of Urtica fissa rhizome.
Two new secolignans from the roots of Urtica fissa.[Pubmed: 29224377]
None
The chemical constituents from Urtica fissa leaves.[Pubmed: 28971690]
None
Two new secolignans with in vitro anti-inflammatory activities from Urtica fissa rhizomes.[Pubmed: 28243817]
Two new secolignans, urticin A (1) and urticin B (2), were isolated from the ethanol extract of Urtica fissa rhizomes. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic evidence (UV, IR, HR-ESI-MS, and NMR). Urticin A and urticin B possessed in vitro anti-inflammatory activities, which significantly inhibited the TNF-α and NO release induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 cells.
Inhibition of spontaneous canine benign prostatic hyperplasia by an Urtica fissa polysaccharide fraction.[Pubmed: 25473922]
In this study, we investigated the inhibition of spontaneous canine benign prostatic hyperplasia by a crude polysaccharide fraction extracted from Urtica fissa roots and stems. After oral administration of U. fissa polysaccharide fraction for 3 months, the dog prostatic volume reduced significantly when compared to that before treatment using CT examination. The high-dosage U. fissa polysaccharide fraction (120 mg/kg body weight/day) and finasteride (0.5 mg/kg body weight/day) treatments showed both almost 30 % reduction of the initial prostatic volume. At the end of the administration of U. fissa polysaccharide fraction, the prostates were excised, and the volumes were measured by water displacement. The prostatic volume showed significant decrease by 11 %, 15 %, and 21 % for the 30, 60, and 120 mg/kg/day U. fissa polysaccharide fraction treatment groups, respectively, compared to the control group. Histological observation found that U. fissa polysaccharide fraction inhibited the dog prostatic epithelial cells proliferation and enlarged glandular lumen diameter. The crude polysaccharide fraction of U. fissa is a possible new candidate for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Structure of a polysaccharide from Urtica fissa determined by NMR spectra.[Pubmed: 22587799]
A polysaccharide, isolated and purified from the aqueous extract of nettle plant Urtica fissa, was found to consist of D-glucose and D-arabinose. Molecular weight was determined to be Mn 4140. The NMR experiments (¹H, ¹³C, ¹H--¹H COSY, TOCSY, HSQC, NOESY, and HMBC) revealed the structure as the following repeating unit: -->6)-α-D-Glcp-(1-->6)-α-D-Glcp-(1-->6)-β-D-Glcp--(1-->5)-β-D-Araf-(1-->3)-β-D-Glcp-(1-->.
Three new secolignan glycosides from Urtica fissa E. Pritz.[Pubmed: 22124934]
Three new secolignan glycosides {3,4-trans-4-[bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-2-oxotetrahydrafuran-3-yl}methyl-O-β-glucopyranoside (1), {3,4-trans-4-[(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-2-oxotetrahydrafuran-3-yl}methyl-O-β-glucopyranoside (2) and {3,4-cis-4-[(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-2-oxotetrahydrafuran-3-yl}methyl-O-β-glucopyranoside (3) were isolated from the roots of Urtica fissa E. Pritz. Their structures were identified by spectral methods including 1D NMR, 2D NMR and HR-EI-MS.
Structural characterization of polysaccharides from the roots of Urtica fissa.[Pubmed: 20183259]
Three polysaccharides were isolated from the roots of Urtica fissa by extraction, ultrafiltration, anion-exchange, and gel-filtration chromatography. The structures were characterized using acetylation, methylation, and spectral methods (GCMS, NMR). All three polysaccharides are mainly composed of D-arabinofuranosyl, D-galactopyranosyl, D-glucopyranosyl residues with different structural characteristics. Polysaccharide A of MW 5.2 x 10(3) contained a linear chain of 1-linked beta-D-glucopyranosyl, 1,6-linked beta-D-glucopyranosyl, 1,6-linked alpha-galactopyranosyl, and 1,5-linked beta-arabinofuranosyl moieties. Polysaccharide B of MW 7.7 x 10(4) possessed a chain consisting of 1,5-linked alpha-D-arabinofuranosyl, 1,3-linked beta-D-mannopyranosyl, 1,6-linked beta-D-glucopyranosyl, and 1,6-linked alpha-D-galactopyranosyl residues, but 4-O of alpha-D-galactopyranosyl residues were branched by terminal beta-D-glucopyranosyl residues. Polysaccharide C of MW 5.3 x 10(4) composed of a chain of 1,5-linked alpha-D-arabinofuranosyl, 1,4-linked beta-D-galactopyranosyl, 1,5-linked beta-D-xylopyranosyl, 1,4-linked beta-D-mannopyranosyl, 1-linked beta-D-glucopyranosyl residues, and the terminal beta-D-glucopyranosyl residues are attached to 3-O positions of 1,6-linked alpha-D-glucopyranosyl residues.
Effects of the polysaccharide fraction of Urtica fissa on castrated rat prostate hyperplasia induced by testosterone propionate.[Pubmed: 18242969]
A crude polysaccharide fraction of Urtica fissa roots and stems (UFP) was obtained by water extraction and ultrafiltration, and its effect on castrated rat prostate hyperplasia induced by testosterone propionate was evaluated by the volume index, wet and dry weight index and histopathological tests. Results showed that the crude polysaccharide fraction significantly inhibited prostatic hyperplasia in animal models at doses of 62.5, 125, 250 mg/kg body wt. (administered orally). Treatment with UFP at 62.5 mg/kg body wt. decreased the volume index by 32%, the wet weight index by 17% and the dry weight index by 23%, respectively. In the high-dose group (UFP at 250 mg/kg body wt.), the indexes of volume, wet weight and dry weight decreased further by 37%, 25% and 33%, respectively. Histopathological examination showed that proliferation of prostatic epithelial cells and fibrotic tissues were significantly inhibited.


