ScopolinCAS# 531-44-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 531-44-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 439514 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C16H18O9 | M.Wt | 354.3 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 7-Hydroxy 6-methoxycoumarin 7-glucoside; Scopoletin 7-glucoside; Scopoloside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol and water; practically insoluble in chloroform | ||
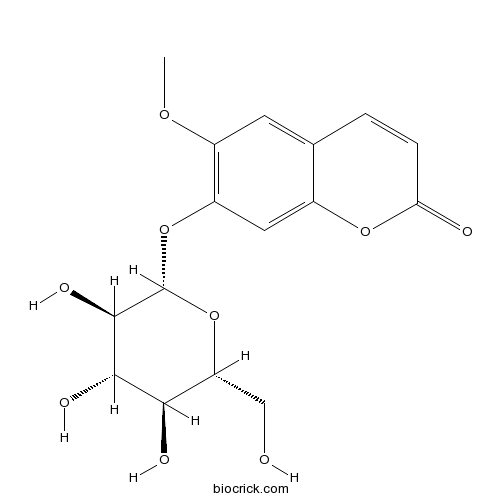
| Chemical Name | 6-methoxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C=CC(=O)O2)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SGTCGCCQZOUMJJ-YMILTQATSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H18O9/c1-22-9-4-7-2-3-12(18)23-8(7)5-10(9)24-16-15(21)14(20)13(19)11(6-17)25-16/h2-5,11,13-17,19-21H,6H2,1H3/t11-,13-,14+,15-,16-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Scopolin exhibits significant and dose-related antinociceptive effects, it is a potential acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. Scopolin can reduce the clinical symptoms of rat AIA by inhibiting inflammation and angiogenesis, it may be a potent agent for angiogenesis related diseases.Scopolin and related coumarins has fungitoxic effect on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, which is a way to overcome sunflower head rot. |
| Targets | VEGFR | IL Receptor | AChR | Antifection |
| In vivo | Scopolin isolated from Erycibe obtusifolia Benth stems suppresses adjuvant-induced rat arthritis by inhibiting inflammation and angiogenesis.[Pubmed: 19327410]Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Jul;9(7-8):859-69.Despite Scopolin is a main coumarin constituent in the stems of Erycibe obtusifolia Benth, a herb drug that has long been utilized in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, little information is available about the pharmacological activities of this compound.
The present study was performed to investigate the anti-rheumatic effects of Scopolin in adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in rats, and explore the underlying mechanisms of action in views of anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties in the synovial tissues.
Fungitoxic effect of scopolin and related coumarins on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. A way to overcome sunflower head rot.[Reference: WebLink]Euphytica, 2006, 147(3):451-460.The content of coumarins, as probable phytoalexins, was analysed in four sunflower genotypes that ranged in responses to head rot from highly susceptible to highly resistant.
|
| Kinase Assay | Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of scopolin and scopoletin discovered by virtual screening of natural products.[Pubmed: 15566295]J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6248-54.For the targeting selection of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors from natural sources we generated a structure-based pharmacophore model utilizing an in silico filtering experiment for the discovery of promising candidates out of a 3D multiconformational database consisting of more than 110,000 natural products. |
| Animal Research | Antinociceptive properties of coumarins, steroid and dihydrostyryl-2-pyrones from Polygala sabulosa (Polygalaceae) in mice.[Pubmed: 16393470 ]J Pharm Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;58(1):107-12.We have investigated the possible antinociceptive action of the extract, fractions and pure compounds obtained from the whole plant Polygala sabulosa A. W. Bennett (Polygalaceae) in acetic acid-induced visceral pain in mice.
|

Scopolin Dilution Calculator

Scopolin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8225 mL | 14.1123 mL | 28.2247 mL | 56.4493 mL | 70.5617 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5645 mL | 2.8225 mL | 5.6449 mL | 11.2899 mL | 14.1123 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2822 mL | 1.4112 mL | 2.8225 mL | 5.6449 mL | 7.0562 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0564 mL | 0.2822 mL | 0.5645 mL | 1.129 mL | 1.4112 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0282 mL | 0.1411 mL | 0.2822 mL | 0.5645 mL | 0.7056 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Coniferin
Catalog No.:BCN5700
CAS No.:531-29-3
- Androsin
Catalog No.:BCN3842
CAS No.:531-28-2
- Dichotomin
Catalog No.:BCN2836
CAS No.:53093-47-3
- 9,13-Epidioxy-8(14)-abieten-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1426
CAS No.:5309-35-3
- Morellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3073
CAS No.:5304-71-2
- Scutebarbatine J
Catalog No.:BCN8134
CAS No.:960302-85-6
- T-5224
Catalog No.:BCC5383
CAS No.:530141-72-1
- Murralongin
Catalog No.:BCN5696
CAS No.:53011-72-6
- Salinomycin
Catalog No.:BCC1916
CAS No.:53003-10-4
- CDI (1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole)
Catalog No.:BCC2809
CAS No.:530-62-1
- Sinapic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3539
CAS No.:530-59-6
- Syringic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5699
CAS No.:530-57-4
- 7-Methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN2707
CAS No.:531-59-9
- Esculin
Catalog No.:BCN5904
CAS No.:531-75-9
- Coumarin-3-Carboxylic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC9220
CAS No.:531-81-7
- 4',7-Isoflavandiol
Catalog No.:BCN2855
CAS No.:531-95-3
- Boc-Pyr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3329
CAS No.:53100-44-0
- Rapamycin (Sirolimus)
Catalog No.:BCC3592
CAS No.:53123-88-9
- Buprenorphine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5215
CAS No.:53152-21-9
- Euscaphic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5702
CAS No.:53155-25-2
- Delphinidin-3-sambubioside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3148
CAS No.:53158-73-9
- Acemetacin
Catalog No.:BCC4424
CAS No.:53164-05-9
- Pirfenidone
Catalog No.:BCC5086
CAS No.:53179-13-8
- 6-Aminoindole
Catalog No.:BCC8763
CAS No.:5318-27-4
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of scopolin and scopoletin discovered by virtual screening of natural products.[Pubmed:15566295]
J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6248-54.
For the targeting selection of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors from natural sources we generated a structure-based pharmacophore model utilizing an in silico filtering experiment for the discovery of promising candidates out of a 3D multiconformational database consisting of more than 110,000 natural products. In our study, scopoletin (1) and its glucoside Scopolin (2) emerged as potential AChE inhibitors by the virtual screening procedure. They were isolated by different chromatographic methods from the medicinal plant Scopolia carniolica Jaqc. and tested in an enzyme assay using Ellman's reagent. They showed moderate, but significant, dose-dependent and long-lasting inhibitory activities. In the in vivo experiments (icv application of 2 micromol) 1 and 2 increased the extracellular acetylcholine (ACh) concentration in rat brain to about 170% and 300% compared to basal release, respectively. At the same concentration, the positive control galanthamine increased the ACh concentration to about the same level as 1. These are the first in vivo results indicating an effect of coumarins on brain ACh.
Scopolin isolated from Erycibe obtusifolia Benth stems suppresses adjuvant-induced rat arthritis by inhibiting inflammation and angiogenesis.[Pubmed:19327410]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Jul;9(7-8):859-69.
Despite Scopolin is a main coumarin constituent in the stems of Erycibe obtusifolia Benth, a herb drug that has long been utilized in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, little information is available about the pharmacological activities of this compound. The present study was performed to investigate the anti-rheumatic effects of Scopolin in adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in rats, and explore the underlying mechanisms of action in views of anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties in the synovial tissues. Scopolin (50, 100 mg/kg), injected intraperitoneally for 10 days from the onset of secondary response, significantly inhibited both inoculated and non-inoculated paw swelling as well as articular index scores in AIA. Meanwhile, the mean body weight of rats treated with Scopolin was higher than that of model group. Rats treated with high dose of Scopolin (100 mg/kg) preserved a nearly normal histological architecture of the joints and showed a significant reduction of the new blood vessels in the synovial tissues. Additionally, Scopolin could reduce IL-6, VEGF and FGF-2 expressions in rat synovial tissues. In conclusion, Scopolin can reduce the clinical symptoms of rat AIA by inhibiting inflammation and angiogenesis, and this compound may be a potent agent for angiogenesis related diseases and can serve as a structural base for screening more potent synthetic analogs.
Antinociceptive properties of coumarins, steroid and dihydrostyryl-2-pyrones from Polygala sabulosa (Polygalaceae) in mice.[Pubmed:16393470]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;58(1):107-12.
We have investigated the possible antinociceptive action of the extract, fractions and pure compounds obtained from the whole plant Polygala sabulosa A. W. Bennett (Polygalaceae) in acetic acid-induced visceral pain in mice. Intraperitoneal injection of animals with the hydroalcoholic extract and fractions (CH(2)Cl(2), EtOAc, n-BuOH, aqueous fraction) (1-100 mg kg(-1)) caused a dose-related and significant inhibition of the acetic acid-induced visceral nociceptive response. The CH(2)Cl(2), EtOAc and n-BuOH fractions were more potent than the hydroalcoholic extract and aqueous fraction. The isolated compounds dihydrostyryl-2-pyrones (1, 2, 3), styryl-2-pyrone (7), alpha-spinasterol (9), scopoletin (10) and two esters of the coumarin (scopoletin) obtained semisynthetically, acetylscopoletin (10a) and benzoylscopoletin (10b) (0.001-10 mg kg(-1)), exhibited significant and dose-related antinociceptive effects against acetic acid-induced visceral pain. The results distinguished, for the first time, the extract, fractions and pure compounds obtained from P. sabulosa that produced marked antinociception against the acetic acid-induced visceral nociceptive response, supporting the ethnomedical use of P. sabulosa.


