Vitex trifolia
Vitex trifolia
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Vitex trifolia
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5990
Agnuside11027-63-7
Instructions

-
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
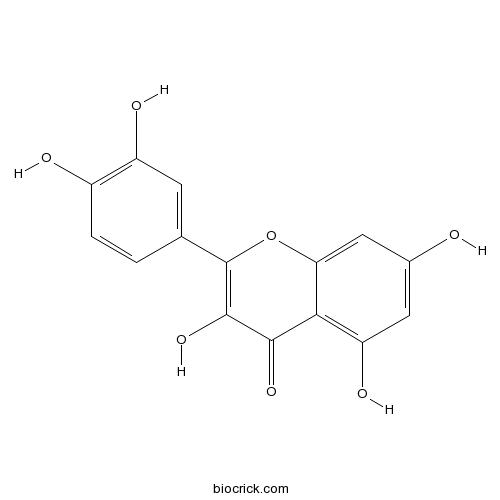
-
BCN5423
Vitexin3681-93-4
Instructions

-
BCN5020
Vitexicarpin479-91-4
Instructions
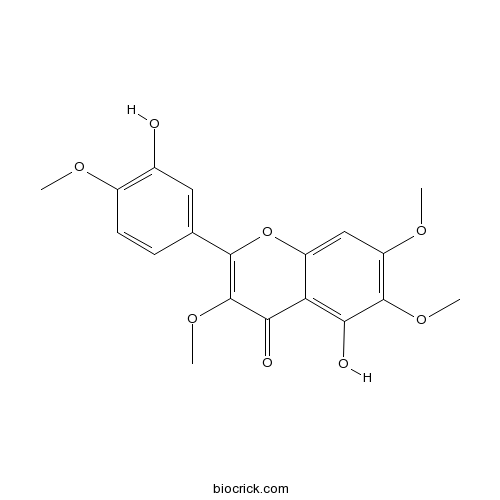
-
BCN5653
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
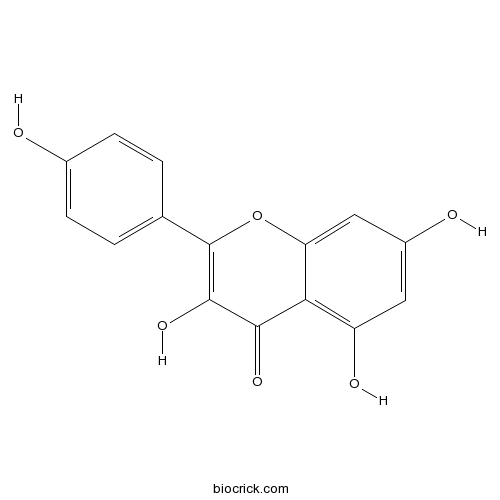
-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Anti-inflammatory diterpenes from the fruits of Vitex trifolia L. var. simplicifolia Cham.[Pubmed: 29996686]
Two new labdane-type diterpenes, named viterotulin C (1) and vitexilactone D (2), together with five known diterpenes (3-7), were isolated from the fruits of Vitex trifolia L. var. simplicifolia Cham. Their structures were elucidated by detailed analysis of spectroscopic data. All the compounds were evaluated for their inhibitory effects on nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway in HEK 293 cell line. These compounds presented inhibition on TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation, with inhibition rates ranging from 42.52 ± 10.69% to 68.86 ± 10.76% at the concentration of 50 μM.
Synthesis of (+)-Vitepyrroloid A and (+)-Vitepyrroloid B by Late-Stage Ni-Catalyzed C(sp2)-C(sp3) Cross-Electrophile Coupling.[Pubmed: 29774741]
A concise and scalable five-step synthesis of vitepyrroloids A and B, two cytotoxic labdane diterpenoid alkaloids from Vitex trifolia, is reported. The presented approach features a Ni-catalyzed cross-electrophile coupling between a (+)-sclareolide-derived alkyl iodide and 3-bromo-2-cyanopyrrole.
Terpenoids from Vitex trifolia and their anti-inflammatory activities.[Pubmed: 29429059]
None
Halimane-type diterpenoids from Vitex rotundifolia and their anti-hyperlipidemia activities.[Pubmed: 29247892]
Vitex rotundifolia is the variant of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) Vitex trifolia. Diterpenoids from V. trifolia have shown anti-hyperlipidemia activity. As part of a continuous research program of searching for anti-hyperlipidemia constituents from TCM, 95% alcohol extract of the fruits of V. rotundifolia was fully studied, and 18 diterpenoids were isolated, including eight previously undescribed compounds (viterofolins A-H). Among them, viterofolins A-B were previously undescribed rearranged halimane-type diterpenoids, viterofolins CH were previously undescribed halimane-type diterpenoids. These compounds were then firstly evaluated in lipid (Dil-LDL) uptake assay in HepG2 cells. Viterofolin H, (5S, 6R, 8R, 9R, 10S)-6-acetoxy-9-hydroxy-13 (14)-labden-16,15-olide and previtexilactone showed moderate activities in promoting LDL uptake (1.27-1.35 fold). This work laid the foundation for searching anti-hyperlipidemia natural products.
The Rosiglitazone-Like Effects of Vitexilactone, a Constituent from Vitex trifolia L. in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes.[Pubmed: 29165364]
None
Selected hepatoprotective herbal medicines: Evidence from ethnomedicinal applications, animal models, and possible mechanism of actions.[Pubmed: 29047177]
Insight into the hepatoprotective effects of medicinally important plants is important, both for physicians and researchers. Main reasons for the use of herbal medicine include their lesser cost compared with conventional drugs, lesser undesirable drug reactions and thus high safety, and reduced side effects. The present review focuses on the composition, pharmacology, and results of experimental trials of selected medicinal plants: Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn., Glycyrrhiza glabra, Phyllanthus amarus Schumach. & Thonn., Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge., Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, Capparis spinosa (L.), Cichorium intybus (L.), Solanum nigrum (L.), Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn., Ginkgo biloba (L.), Woodfordia fruticosa (L.) Kurz, Vitex trifolia (L.), Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., Cuscuta chinensis (Lam.), Lycium barbarum, Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, and Litsea coreana (H. Lev.). The probable modes of action of these plants include immunomodulation, stimulation of hepatic DNA synthesis, simulation of superoxide dismutase and glutathione reductase to inhibit oxidation in hepatocytes, reduction of intracellular reactive oxygen species by enhancing levels of antioxidants, suppression of ethanol-induced lipid accumulation, inhibition of nucleic acid polymerases to downregulate viral mRNA transcription and translation, free radical scavenging and reduction of hepatic fibrosis by decreasing the levels of transforming growth factor beta-1, and collagen synthesis in hepatic cells. However, further research is needed to identify, characterize, and standardize the active ingredients, useful compounds, and their preparations for the treatment of liver diseases.
Comparative Evaluation of Polyphenol Contents and Antioxidant Activities between Ethanol Extracts of Vitex negundo and Vitex trifolia L. Leaves by Different Methods.[Pubmed: 28953235]
None


