Wedelia chinensis
Wedelia chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Wedelia chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
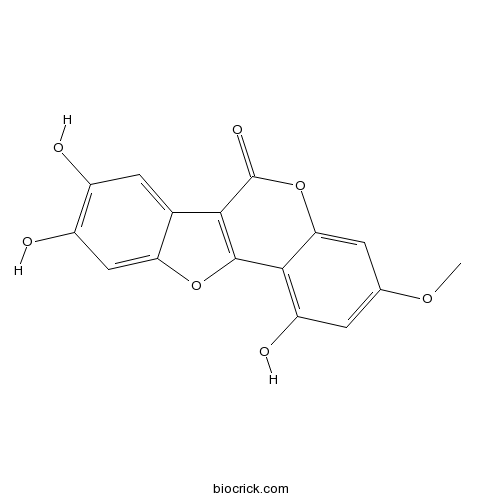
BCN2766
Isodemethylwedelolacton350681-33-3
Instructions

-
BCN5672
Wedelolactone524-12-9
Instructions
Absolute Structures of Wedelolide Derivatives and Structure-Activity Relationships of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory ent-Kaurene Diterpenes from Aerial Parts of Wedelia spp. Collected in Indonesia and Japan.[Pubmed: 29863070]
Two sesquiterpene lactones with the (9R)-eudesman-9,12-olide framework, wedelolides I and J, have been isolated together with five eudesmanolide sesquiterpenes and twelve ent-kaurene diterpenes from the aerial parts of Indonesian Wedelia prostrata. The absolute configurations of wedelolides I and J, proposed in the previous communication, were proven by comparing their experimental Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) spectra with the calculated ECD spectrum of wedelolide I. The phytochemical study on the aerial parts of Okinawan Wedelia chinensis led to the isolation of three other eudesmanolide sesquiterpenes in addition to the three sesquiterpenes and eleven diterpenes isolated from the Indonesian W. prostrata as above. However, the wedelolide derivatives found in the Indonesian plant were not detected. Among these compounds, most of the diterpenes inhibited protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) 1B activity, and a structure-activity relationship study revealed that the cinnamoyl group enhanced inhibitory activity. Therefore, two ent-kaurene derivatives with and without a cinnamoyl group were examined for the ability to accumulate phosphorylated-Akt (p-Akt) because PTP1B dephosphorylates signal transduction from the insulin receptor such as phosphorylated Akt, a key downstream effector. However, neither compound enhanced insulin-stimulated p-Akt levels in two human hepatoma cell lines (Huh-7 and HepG2) at non-cytotoxic doses.
Exploration of Wedelia chinensis leaf-assisted silver nanoparticles for antioxidant, antibacterial and in vitro cytotoxic applications.[Pubmed: 29567263]
None
A standardized herbal extract mitigates tumor inflammation and augments chemotherapy effect of docetaxel in prostate cancer.[Pubmed: 29142311]
Activation of the NFκB pathway is often associated with advanced cancer and has thus been regarded as a rational therapeutic target. Wedelia chinensis is rich in luteolin, apigenin, and wedelolactone that act synergistically to suppress androgen receptor activity in prostate cancer. Interestingly, our evaluation of a standardized Wedelia chinensis herbal extract (WCE) concluded its efficacy on hormone-refractory prostate cancer through systemic mechanisms. Oral administration of WCE significantly attenuated tumor growth and metastasis in orthotopic PC-3 and DU145 xenografts. Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of these tumors revealed that WCE suppressed the expression of IKKα/β phosphorylation and downstream cytokines/chemokines, e.g., IL6, CXCL1, and CXCL8. Through restraining the cytokines expression, WCE reduced tumor-elicited infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and endothelial cells into the tumors, therefore inhibiting angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. In MDSCs, WCE also reduced STAT3 activation, downregulated S100A8 expression and prevented their expansion. Use of WCE in combination with docetaxel significantly suppressed docetaxel-induced NFκB activation, boosted the therapeutic effect and reduced the systemic toxicity caused by docetaxel monotherapy. These data suggest that a standardized preparation of Wedelia chinensis extract improved prostate cancer therapy through immunomodulation and has potential application as an adjuvant agent for castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Protective effects of wedelolactone on dextran sodium sulfate induced murine colitis partly through inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome activation via AMPK signaling.[Pubmed: 28750357]
It has been reported that the ethanol extract of Wedelia chinensis attenuates murine colitis. Wedelolactone (WEL), a coumestane-type compound with many pharmacological activities, was isolated from W. chinensis. The present study aims to investigate the beneficial effects and underlying mechanisms of WEL on ulcerative colitis. In a dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced mouse model, oral administration of WEL (50mg/kg) significantly attenuated pathological colonic damage and inhibited inflammatory infiltration, myeloperoxidase and alkaline phosphatase activities through MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways, while activating AMPK in colons treated with DSS. Further study revealed that WEL treatment dramatically inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome activation and caspase-1 phosphorylation to decrease IL-1β release in colons treated with DSS. In addition, WEL effectively regulates the disorder of skeleton proteins in colonic epithelial cells NCM460 exposed to TNF-α and protects the intestinal barrier function by activating AMPK in vivo. In summary, the AMPK-NLRP3-IL-1β signaling axis plays an important role in colitis following WEL treatments. These findings provide new insights into the pharmacological actions of WEL as a potential therapeutic agent for colitis.
Two new kaurane-type diterpenoids from Wedelia chinensis (Osbeck.) Merr.[Pubmed: 28475376]
None
Anti-angiogenic activity and mechanism of kaurane diterpenoids from Wedelia chinensis.[Pubmed: 26969382]
Wedelia chinensis is a traditional medicinal herb used in Asia and it has been reported to possess various bioactivities including anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. However, its anti-angiogenic activity has never been reported.


