WedelolactoneCAS# 524-12-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 524-12-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281813 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
| Formula | C16H10O7 | M.Wt | 314.3 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 250 mg/mL (795.54 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
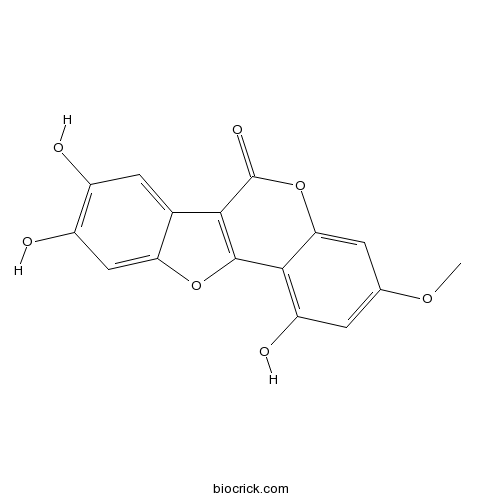
| Chemical Name | 1,8,9-trihydroxy-3-methoxy-[1]benzofuro[3,2-c]chromen-6-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=C2C(=C1)OC(=O)C3=C2OC4=CC(=C(C=C43)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XQDCKJKKMFWXGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H10O7/c1-21-6-2-10(19)14-12(3-6)23-16(20)13-7-4-8(17)9(18)5-11(7)22-15(13)14/h2-5,17-19H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Wedelolactone is a potent Î2-arrestin-biased G protein-coupled receptor-35 (GPR35) agonist, GPR35 has been shown to be a target of the asthma drugs cromolyn disodium and nedocromil sodium. Wedelolactone has anti-inflammatory, growth inhibitory, anti-cancer, anti-fibrotic, and pro-apoptotic effects. Wedelolactone stimulates ER genomic and non-genomic signalling pathways; it can significantly inhibit the activation of LX-2 cells, the underlying mechanisms of which included inducing Bcl-2 family involved apoptosis, up-regulating phosphorylated status of ERK and JNK expressions, and inhibiting NF-κB mediated activity. |
| Targets | Androgen Receptor | Bcl-2/Bax | ERK | JNK | p38MAPK | p65 | NF-kB | IkB | PPAR | GPR | IKK |
| In vitro | Inhibitory effect of Ecliptae herba extract and its component wedelolactone on pre-osteoclastic proliferation and differentiation.[Pubmed: 25267578]J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Nov 18;157:206-11.Ecliptae herba, also known as "Mo-Han-Lian", has long been used in China to nourish Kidney and thereafter strengthen bones. Accumulating evidence indicates that extracts of Ecliptae herba have antiosteoporotic effect. However, the effective compounds and cellular mode of action are still unclear. To investigate the effect of ethyl acetate extract of Ecliptae herba (EAE) and its component Wedelolactone on proliferation and differentiation of preosteoclastic RAW264.7 cells as well as proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC).
Wedelolactone inhibits adipogenesis through the ERK pathway in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells.[Pubmed: 22678810]J Cell Biochem. 2012 Nov;113(11):3436-45.Wedelolactone is an herbal medicine that is used to treat septic shock, hepatitis and venom poisoning. Although in differentiated and cancer cells, Wedelolactone has been identified as anti-inflammatory, growth inhibitory, and pro-apoptotic, the effects of Wedelolactone on stem cell differentiation remain largely unknown.
Wedelolactone disrupts the interaction of EZH2-EED complex and inhibits PRC2-dependent cancer.[Pubmed: 25944687]Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13049-59.Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which is responsible for the trimethylation of H3K27 (H3K27me3), plays a part in tumorigenesis, development and/or maintenance of adult tissue specificity. The pivotal role of PRC2 in cancer makes it a therapeutic target for epigenetic cancer therapy. However, natural compounds targeting the enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) - embryonic ectoderm development (EED) interaction to disable PRC2 complex are scarcely reported.
|
| Kinase Assay | Anti-inflammatory gallic Acid and wedelolactone are G protein-coupled receptor-35 agonists.[Pubmed: 22488351 ]Wedelolactone exhibits anti-fibrotic effects on human hepatic stellate cell line LX-2.[Pubmed: 23791612]Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;714(1-3):105-11.Wedelolactone is a major coumarin of Eclipta prostrata, which is used for preventing liver damage. However the effects of Wedelolactone on hepatic fibrosis remained unexplored. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the anti-fibrotic effects of Wedelolactone on activated human hepatic stellate cell (HSC) line LX-2 and the possible underlying mechanisms by means of MTT assay,
Pharmacology. 2012;89(3-4):211-9.G protein-coupled receptor-35 (GPR35) has been shown to be a target of the asthma drugs cromolyn disodium and nedocromil sodium. Gallic acid and caffeic acids are reported to modulate allergic reactions via unknown mode(s) of action.
|
| Cell Research | Wedelolactone induces growth of breast cancer cells by stimulation of estrogen receptor signalling.[Pubmed: 25934092]J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Apr 28;152:76-83.Wedelolactone, a plant coumestan, was shown to act as anti-cancer agent for breast and prostate carcinomas in vitro and in vivo targeting multiple cellular proteins including androgen receptors, 5-lipoxygenase and topoisomerase IIα. It is cytotoxic to breast, prostate, pituitary and myeloma cancer cell lines in vitro at μM concentrations. In this study, however, a novel biological activity of nM dose of Wedelolactone was demonstrated.
|

Wedelolactone Dilution Calculator

Wedelolactone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1817 mL | 15.9084 mL | 31.8167 mL | 63.6335 mL | 79.5418 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6363 mL | 3.1817 mL | 6.3633 mL | 12.7267 mL | 15.9084 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3182 mL | 1.5908 mL | 3.1817 mL | 6.3633 mL | 7.9542 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0636 mL | 0.3182 mL | 0.6363 mL | 1.2727 mL | 1.5908 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0318 mL | 0.1591 mL | 0.3182 mL | 0.6363 mL | 0.7954 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Epistephamiersine
Catalog No.:BCN5671
CAS No.:52389-15-8
- Erysotramidine
Catalog No.:BCN5670
CAS No.:52358-58-4
- 2-Benzoyl-1,3,4,4a,5,8a-hexahydro-6(2H)-isoquinolinone
Catalog No.:BCC8559
CAS No.:52346-14-2
- Alnusone
Catalog No.:BCN8108
CAS No.:52330-11-7
- 6alpha-Chloro-5beta-hydroxywithaferin A
Catalog No.:BCN8007
CAS No.:52329-20-1
- Dimethylcurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN2748
CAS No.:52328-98-0
- Tetramethylcurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN2746
CAS No.:52328-97-9
- p,p-hydroxy-curucumin
Catalog No.:BCC8890
CAS No.:52328-96-8
- Vindorosine
Catalog No.:BCN5668
CAS No.:5231-60-7
- Anisatin
Catalog No.:BCC8118
CAS No.:5230-87-5
- Flavoglaucin
Catalog No.:BCN6398
CAS No.:523-73-9
- Evolitrine
Catalog No.:BCN8350
CAS No.:523-66-0
- gamma-Fagarine
Catalog No.:BCN5673
CAS No.:524-15-2
- Dauricine
Catalog No.:BCN4977
CAS No.:524-17-4
- Fraxin
Catalog No.:BCN1237
CAS No.:524-30-1
- 2-APB
Catalog No.:BCC6978
CAS No.:524-95-8
- Noricaritin
Catalog No.:BCN5353
CAS No.:5240-95-9
- (R)-DPN
Catalog No.:BCC7939
CAS No.:524047-78-7
- H-Phe-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3008
CAS No.:5241-58-7
- Boc-D-Trp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3457
CAS No.:5241-64-5
- Boc-D-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3426
CAS No.:5241-66-7
- Cochlearine
Catalog No.:BCN1929
CAS No.:52418-07-2
- Oxeladin Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC3831
CAS No.:52432-72-1
- Isobutylshikonin
Catalog No.:BCN3005
CAS No.:52438-12-7
Anti-inflammatory gallic Acid and wedelolactone are G protein-coupled receptor-35 agonists.[Pubmed:22488351]
Pharmacology. 2012;89(3-4):211-9.
G protein-coupled receptor-35 (GPR35) has been shown to be a target of the asthma drugs cromolyn disodium and nedocromil sodium. Gallic acid and caffeic acids are reported to modulate allergic reactions via unknown mode(s) of action. Here we attempt to elucidate whether both phenolic acids share a common mode of action with the two asthma drugs. Label-free dynamic mass redistribution (DMR) assays showed that both phenolic acids triggered robust DMR signals in HT-29 cells, whose characteristics were similar to that of cromolyn disodium. Both phenolic acids resulted in detectable beta-arrestin translocation signals in an engineered U2OS cell line stably expressing a C-terminal-modified GPR35, but with lower efficacy than cromolyn disodium. Antiallergic Wedelolactone was found to be a potent beta-arrestin-biased GPR35 agonist. These results suggest that certain anti-inflammatory phytochemicals including gallic acid and Wedelolactone may modulate inflammatory allergic action via their agonism at GPR35. GPR35 may represent a target for the treatment of allergic disorders including asthma.
Wedelolactone exhibits anti-fibrotic effects on human hepatic stellate cell line LX-2.[Pubmed:23791612]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;714(1-3):105-11.
Wedelolactone is a major coumarin of Eclipta prostrata, which is used for preventing liver damage. However the effects of Wedelolactone on hepatic fibrosis remained unexplored. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the anti-fibrotic effects of Wedelolactone on activated human hepatic stellate cell (HSC) line LX-2 and the possible underlying mechanisms by means of MTT assay, Hoechst staining, as well as real-time quantitative PCR and western blot. The results showed that Wedelolactone reduced the cellular viability of LX-2 in a time and dose-dependent manner. After treatment of Wedelolactone, the expressions of collagen I and alpha-smooth muscle actin, two biomarkers of LX-2 activation, were remarkably decreased. The apoptosis of LX-2 cells was induced by Wedelolactone accompanied with the decreasing expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and increasing expression of pro-apoptotic Bax. In addition, phosphorylated status of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) was up-regulated, but not in p38. Moreover, Wedelolactone significantly repressed the level of phosphorylated inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB (IkappaB) and p65 in nucleus in spite of tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulation. In conclusion, Wedelolactone could significantly inhibit the activation of LX-2 cells, the underlying mechanisms of which included inducing Bcl-2 family involved apoptosis, up-regulating phosphorylated status of ERK and JNK expressions, and inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) mediated activity. Wedelolactone might present as a useful tool for the prevention and treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
Wedelolactone disrupts the interaction of EZH2-EED complex and inhibits PRC2-dependent cancer.[Pubmed:25944687]
Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13049-59.
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which is responsible for the trimethylation of H3K27 (H3K27me3), plays a part in tumorigenesis, development and/or maintenance of adult tissue specificity. The pivotal role of PRC2 in cancer makes it a therapeutic target for epigenetic cancer therapy. However, natural compounds targeting the enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) - embryonic ectoderm development (EED) interaction to disable PRC2 complex are scarcely reported. Here, we reported the screening and identification of natural compounds which could disrupt the EZH2-EED interaction. One of these compounds, Wedelolactone, binds to EED with a high affinity (KD = 2.82 muM), blocks the EZH2-EED interaction in vitro, induces the degradation of PRC2 core components and modulates the expression of detected PRC2 downstream targets and cancer-related genes. Furthermore, some PRC2-dependent cancer cells undergone growth arrest upon treatment with Wedelolactone. Thus, Wedelolactone and its derivatives which target the EZH2-EED interaction could be candidates for the treatment of PRC2-dependent cancer.
Wedelolactone induces growth of breast cancer cells by stimulation of estrogen receptor signalling.[Pubmed:25934092]
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Aug;152:76-83.
Wedelolactone, a plant coumestan, was shown to act as anti-cancer agent for breast and prostate carcinomas in vitro and in vivo targeting multiple cellular proteins including androgen receptors, 5-lipoxygenase and topoisomerase IIalpha. It is cytotoxic to breast, prostate, pituitary and myeloma cancer cell lines in vitro at muM concentrations. In this study, however, a novel biological activity of nM dose of Wedelolactone was demonstrated. Wedelolactone acts as agonist of estrogen receptors (ER) alpha and beta as demonstrated by transactivation of estrogen response element (ERE) in cells transiently expressing either ERalpha or ERbeta and by molecular docking of this coumestan into ligand binding pocket of both ERalpha and ERbeta. In breast cancer cells, Wedelolactone stimulates growth of estrogen receptor-positive cells, expression of estrogen-responsive genes and activates rapid non-genomic estrogen signalling. All these effects can be inhibited by pretreatment with pure ER antagonist ICI 182,780 and they are not observed in ER-negative breast cancer cells. We conclude that Wedelolactone acts as phytoestrogen in breast cancer cells by stimulating ER genomic and non-genomic signalling pathways.
Inhibitory effect of Ecliptae herba extract and its component wedelolactone on pre-osteoclastic proliferation and differentiation.[Pubmed:25267578]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Nov 18;157:206-11.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Ecliptae herba, also known as "Mo-Han-Lian", has long been used in China to nourish Kidney and thereafter strengthen bones. Accumulating evidence indicates that extracts of Ecliptae herba have antiosteoporotic effect. However, the effective compounds and cellular mode of action are still unclear. To investigate the effect of ethyl acetate extract of Ecliptae herba (EAE) and its component Wedelolactone on proliferation and differentiation of preosteoclastic RAW264.7 cells as well as proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC). MATERIALS AND METHODS: RAW264.7 and BMSC were examined for proliferation by a 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) method. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) activity of RAW264.7 was measured by using p-nitrophenyl sodium phosphate (pNPP) assay after the cells were treated with 30ng/ml receptor activator for nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) plus various concentrations of EAE, Wedelolactone or alendronate. The formation of multinucleated TRAP-positive RAW264.7 cells was observed by using a TRAP-staining kit. RESULTS: Treatment of RAW264.7 cells with EAE at high doses (20microg/ml and 40microg/ml) or Wedelolactone at 10microg/ml resulted in a decrease in proliferation of RAW264.7 cells. Low doses of EAE (5, 10microg/ml) and Wedelolactone (2.5microg/ml) inhibited RANKL-induced TRAP activity by 20.3%, 37.9%, and 48.3%. The inhibitory effect of Wedelolactone is more potent than that of alendronate, an anti-resorptive drug. Morphological changes revealed that 5microg/ml EAE and 2.5microg/ml Wedelolactone reduced the number of multinucleated osteoclast-like cells. At the high doses, EAE (20microg/ml) and Wedelolactone (10microg/ml) inhibited the growth of BMSC. CONCLUSIONS: EAE and its component Wedelolactone inhibited osteoclast RAW264.7 proliferation and differentiation at the low doses, but at the high doses, showed cytotoxic effect on BMSC. These results indicated that EAE and wedelolatone might be potential alternative therapy for osteoporosis.
Wedelolactone inhibits adipogenesis through the ERK pathway in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells.[Pubmed:22678810]
J Cell Biochem. 2012 Nov;113(11):3436-45.
Wedelolactone is an herbal medicine that is used to treat septic shock, hepatitis and venom poisoning. Although in differentiated and cancer cells, Wedelolactone has been identified as anti-inflammatory, growth inhibitory, and pro-apoptotic, the effects of Wedelolactone on stem cell differentiation remain largely unknown. Here, we report that Wedelolactone inhibits the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs). Wedelolactone reduced the formation of lipid droplets and the expression of adipogenesis-related proteins, such as CCAAT enhancer-binding protein-alpha (C/EBP-alpha), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma), lipoprotein lipase (LPL), and adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein aP2 (aP2). Wedelolactone mediated this process by sustaining ERK activity. In addition, inhibition of ERK activity with PD98059 resulted in reversion of the Wedelolactone-mediated inhibition of adipogenic differentiation. Taken together, these results indicate that Wedelolactone inhibits adipogenic differentiation through ERK pathway and suggest a novel inhibitory effect of Wedelolactone on adipogenic differentiation in hAMSCs.


