Zanthoxylum bungeanum
Zanthoxylum bungeanum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
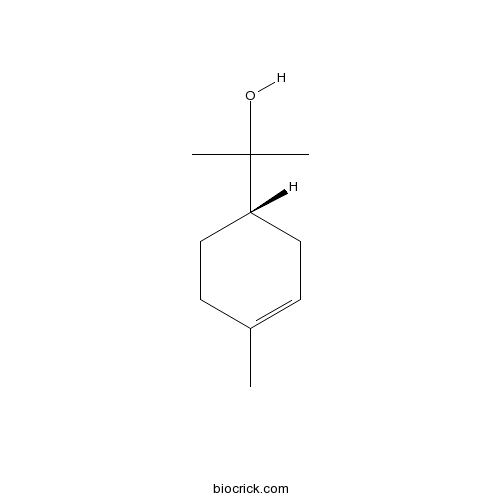
BCN8136
Alpha-Terpineol10482-56-1
Instructions
-
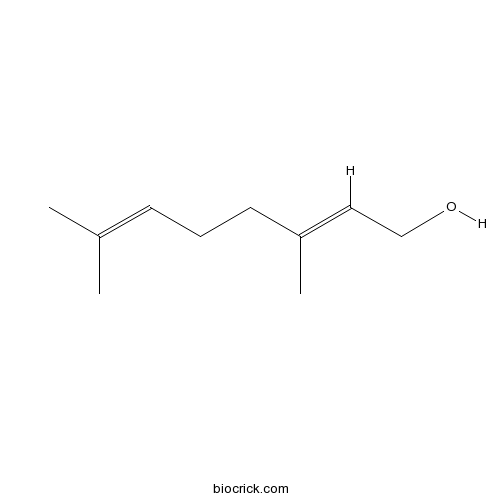
BCN2631
Geraniol106-24-1
Instructions
-
BCC8200
Linalyl Acetate115-95-7
Instructions

-
BCN3797
Limonene138-86-3
Instructions

-
BCN3820
Stearic Acid57-11-4
Instructions

-
BCN5459
Nerolidol7212-44-4
Instructions

-
BCN4443
Xanthoxylin90-24-4
Instructions

Simultaneous Enrichment and Separation of Four Flavonoids from Zanthoxylum bungeanum Leaves by Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Macroporous Resins with Evaluation of Antioxidant Activities.[Pubmed: 30080245]
Quercitrin, hyperoside, rutin, and afzelin are the dominant flavonoids compounds from Zanthoxylum bungeanum leaves, and they play major roles in the antioxidant activity. Macroporous adsorption resin (MAR) treatment, a simple, low-cost and efficient method, was combined with ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) to enrich and purify these four flavonoids from Z. bungeanum leaves efficiently. The optimal conditions for UAE based on Response Surface Methodology (RSM) were determined to be an ethanol concentration of 60%, leaves size of 40 mesh, temperature of 50 °C and ultrasonic power of 400 W with four flavonoids contents of 120.84 mg/g. After the extraction process, five kinds of MARs (D4020, D-101, NKA-9, AB-8, and X-5) were tested through static adsorption/desorption to enrich and purify the ultrasonic-assisted extracts, and D-101 was selected as the most suitable resin. The optimal adsorption conditions were 5 bed volumes (BV) of sample solution with an initial concentration of 7.5 mg/mL and pH 5.0. Meanwhile, the optimal desorption parameters were 5 BV each of deionized water and 30% ethanol, then 10 BV 70% ethanol, and a flow rate of 2 BV/hr. Under the optimized conditions, the contents of quercitrin, hyperoside, rutin, and afzelin increased by 276.39%, 187.46%, 221.81%, and 288.45%, respectively, and the recovery yields were 85.47%, 73.53%, 81.35%, and 65.06%. In addition, laboratory preparative-scale separation indicated that the preparative separation of four flavonoids was feasible and easy. Moreover, the antioxidant activities of the purified products were significantly increased after enrichment. In conclusion, all of the results indicated that these methods are highly efficient, low cost, environmentally friendly and easy to scale up.
Dynamics of soil microbial recovery from cropland to orchard along a 20-year chronosequence in a degraded karst ecosystem.[Pubmed: 29929274]
The 'Grain for Green' project (GGP) is the largest ecological rehabilitation project in China. A large body of croplands has been abandoned or converted to shrubs or grasslands since 1999. Soil microbes are recognized as sensitive responders of environmental changes, therefore, they are considered as a key component of ecological rehabilitation. However, very limited field experiments have been conducted to investigate the responses of soil microorganisms to restoration projects, especially in karst regions of China. In order to evaluate the response of soil microbial community to ecological restoration, we determined soil microbial community composition by means of qPCR, PLFAs, and high-throughput amplicon sequencing following conversion of cropland to Chinese prickly ash (Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim) orchard (CP) along a 20-year chronosequence in a degraded karst ecosystem. Our results showed that soil nutrient contents significantly increased following cropland to CP conversion. qPCR results showed that the highest bacterial abundance was found in the 20-year CP, but bacterial abundance decreased during the first 5-year land-use conversion. Conversion of cropland to CP strongly impacted soil microbial community composition, despite the cropland sites having a long cultivation history (>50 years). However, soil bacterial diversity remained unchanged within a 20-year land-use conversion. Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Acidobacteria were the main bacterial phyla in all land-use sites. In particular, various members of Actinobacteria (e.g., Solirubrobacteraceae) tended to increase their relative abundances in responding to land-use conversion, which may imply that the shifts of soil microbial communities associated with recovering of ecological conditions. Overall, given the rapid yet differential response to ecological restoration, investigation of the belowground microbial community can provide an effective way of assessing ecological recovery of restoration projects in the karst region.
Multielement analysis of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. essential oil using ICP-MS/MS.[Pubmed: 29651525]
None
Expression Stabilities of Ten Candidate Reference Genes for RT-qPCR in Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim.[Pubmed: 29601541]
None
Isobutylhydroxyamides from Sichuan Pepper and Their Protective Activity on PC12 Cells Damaged by Corticosterone.[Pubmed: 29534566]
The pericarp of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim., commonly known as Sichuan pepper, is a widely used spice to remove fishy odor and add palatable taste. A phytochemical investigation of the 95% ethanol extract of Sichuan pepper resulted in the isolation of 21 isobutylhydroxyamides, including 8 new ones named ZP-amides G-N, among which the chiral resolution of racemic ZP-amide A and ZP-amide B was successfully accomplished. The protective activity on corticosterone-treated PC12 cells of the isolated isobutylhydroxyamides was also evaluated. The new compounds 3-5 and the known compounds 1, 1a, 2, 2a, 11, and 15 improved the survival rate of PC12 cells. The bioactivity studies disclosed the potential of Sichuan pepper to be developed as new neuroprotective functional food.
Soybean supplementation increases the resilience of microbial and nematode communities in soil to extreme rainfall in an agroforestry system.[Pubmed: 29358146]
A current challenge for ecological research in agriculture is to identify ways in which to improve the resilience of the soil food web to extreme climate events, such as severe rainfall. Plant species composition influence soil biota communities differently, which might affect the recovery of soil food web after extreme rainfall. We compared the effects of rainfall stress up on the soil microbial food web in three planting systems: a monoculture of the focal species Zanthoxylum bungeanum and mixed cultures of Z. bungeanum and Medicago sativa or Z. bungeanum and Glycine max. We tested the effect of the presence of a legume on the recovery of trophic interactions between microorganisms and nematodes after extreme rainfall. Our results indicated that all chemical properties of the soil recovered to control levels (normal rainfall) in the three planting systems 45 days after exposure to extreme rain. However, on day 45, the bulk microbial community differed from controls in the monoculture treatment, but not in the two mixed planting treatments. The nematode community did not fully recover in the monoculture or Z. bungeanum and M. sativa treatments, while nematode populations in the combined Z. bungeanum and G. max treatment were indistinguishable from controls. G. max performed better than M. sativa in terms of increasing the resilience of microbial and nematode communities to extreme rainfall. Soil microbial biomass and nematode density were positively correlated with the available carbon and nitrogen content in soil, demonstrating a link between soil health and biological properties. This study demonstrated that certain leguminous plants can stabilize the soil food web via interactions with soil biota communities after extreme rainfall.
De novo transcriptome assembly of Zanthoxylum bungeanum using Illumina sequencing for evolutionary analysis and simple sequence repeat marker development.[Pubmed: 29196697]
Zanthoxylum, an ancient economic crop in Asia, has a satisfying aromatic taste and immense medicinal values. A lack of genomic information and genetic markers has limited the evolutionary analysis and genetic improvement of Zanthoxylum species and their close relatives. To better understand the evolution, domestication, and divergence of Zanthoxylum, we present a de novo transcriptome analysis of an elite cultivar of Z. bungeanum using Illumina sequencing; we then developed simple sequence repeat markers for identification of Zanthoxylum. In total, we predicted 45,057 unigenes and 22,212 protein coding sequences, approximately 90% of which showed significant similarities to known proteins in databases. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that Zanthoxylum is relatively recent and estimated to have diverged from Citrus ca. 36.5-37.7 million years ago. We also detected a whole-genome duplication event in Zanthoxylum that occurred 14 million years ago. We found no protein coding sequences that were significantly under positive selection by Ka/Ks. Simple sequence repeat analysis divided 31 Zanthoxylum cultivars and landraces into three major groups. This Zanthoxylum reference transcriptome provides crucial information for the evolutionary study of the Zanthoxylum genus and the Rutaceae family, and facilitates the establishment of more effective Zanthoxylum breeding programs.
Anti-hypoglycemic and hepatocyte-protective effects of hyperoside from Zanthoxylum bungeanum leaves in mice with high-carbohydrate/high-fat diet and alloxan-induced diabetes.[Pubmed: 29115390]
The development of diabetes mellitus (DM) is accompanied by hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress. Hyperoside is a major bioactive component in Zanthoxylum bungeanum leaves (HZL) and is a natural antioxidant. However, the effects of HZL on DM and its mechanisms of action remain undefined. The present study evaluated the anti-hypoglycemic and hepatocyte-protective effects of HZL in mice with diabetes induced by a high-carbohydrate/high-fat diet (HFD) and alloxan. We also aimed to eludicate the underlying mechanisms. Our resutls demonstrated that the administration of HZL significantly reduced body weight gain, serum glucose levels and insulin levels in diabetic mice compared with the vehicle-treated mice. In addition, the levels of dyslipidemia markers including total cholesterol, triglyceride and low‑density lipoprotein cholesterol in the HFD-treated mice were markedly decreased. Further experiments using hepatocytes from mice revealed that HZL significantly attenuated liver injury associated with DM compared with vehicle treatment, as evidenced by lower levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase in serum and by lower levels of lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide content and inducible nitric oxide synthase activity in liver tissues. Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-associated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways were investigated to elucidate the molecular mechanisms responsible for the protective effects of HZL against diabetic liver injury. The results indicated that HZL inhibited the phosphorylation of p65/NF-κB, MAPK (including p38, JNK and ERK1/2) and activating transcription factor 3 protein expression, with an additional suppression of Bax, cytochrome c, caspase-9 and caspase-3 in the liver tissues of diabetic mice. Taken together, our findings suggest that HZL, which was effective in inhibiting oxidative stress-related pathways may be beneficial for use in the treatment of DM.


