Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott
Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott
Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott , the Pagoda Tree (Chinese Scholar, Japanese pagodatree; syn. Sophora japonica) is a species of small tree or shrub in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family Fabaceae. It was formerly included within a broader interpretation of the genus Sophora. The species of Styphnolobium differ from Sophora in lacking the ability to form symbioses with rhizobia (nitrogen fixing bacteria) on their roots. S. japonicum (formerly Sophora japonica) is one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine. Used to make the strong, springy curved "enju wood" handle used on the traditional Japanese woodworking adze, called the chouna. It has abortifacient, antibacterial, anticholesterolemic, antiinflammatory, antispasmodic, diuretic, emetic, emollient, febrifuge, hypotensive, purgative, styptic, and tonic properties.
Products from Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1684
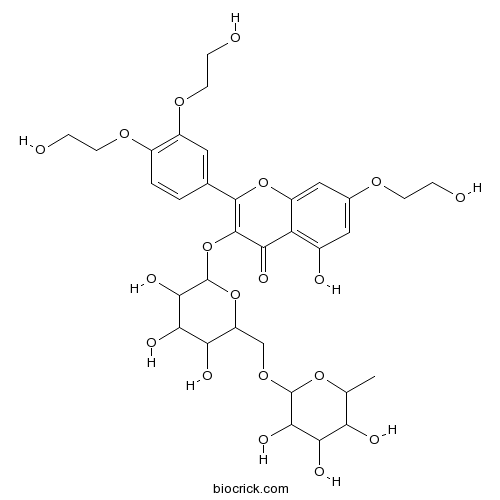
Rutin 153-18-4
PDF
-
BCN5528
Betulin 473-98-3
PDF

-
BCN5156
Oxysophocarpine 26904-64-3
PDF

-
BCN5971
Sophocarpine 145572-44-7
PDF

-
BCN1236
Maackiain 19908-48-6
PDF

-
BCN2294
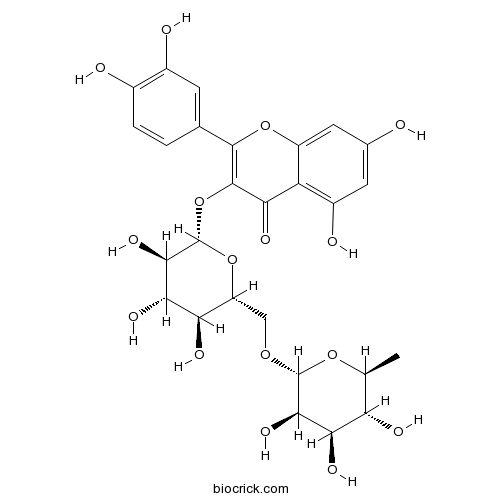
Sophoricoside 152-95-4
PDF

-
BCN6049
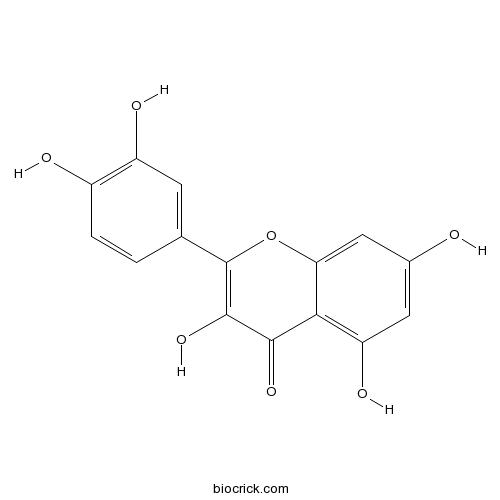
Quercetin 117-39-5
PDF
-
BCN5665
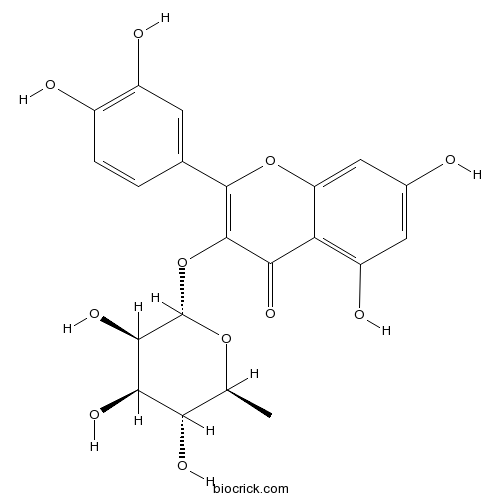
Quercitrin 522-12-3
PDF
-
BCN3828
Troxerutin 7085-55-4
PDF