1-O-p-CoumaroylglycerolCAS# 106055-11-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 106055-11-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 54528247 | Appearance | Powder |
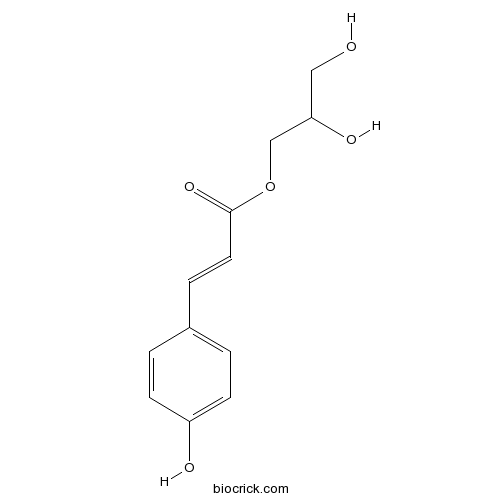
| Formula | C12H14O5 | M.Wt | 238.24 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoid | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,3-dihydroxypropyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C=CC(=O)OCC(CO)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YUQSZTOOHLGKGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H14O5/c13-7-11(15)8-17-12(16)6-3-9-1-4-10(14)5-2-9/h1-6,11,13-15H,7-8H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

1-O-p-Coumaroylglycerol Dilution Calculator

1-O-p-Coumaroylglycerol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1974 mL | 20.9872 mL | 41.9745 mL | 83.949 mL | 104.9362 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8395 mL | 4.1974 mL | 8.3949 mL | 16.7898 mL | 20.9872 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4197 mL | 2.0987 mL | 4.1974 mL | 8.3949 mL | 10.4936 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0839 mL | 0.4197 mL | 0.8395 mL | 1.679 mL | 2.0987 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.042 mL | 0.2099 mL | 0.4197 mL | 0.8395 mL | 1.0494 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- N1,N5,N10-Tri-p-coumaroylspermidine
Catalog No.:BCN9283
CAS No.:131086-78-7
- Juncuenin D
Catalog No.:BCN9282
CAS No.:1161681-24-8
- 9,10-Didehydroeffususol A
Catalog No.:BCN9281
CAS No.:1869082-57-4
- 2,7-Dihydroxy-1,6-dimethylpyrene
Catalog No.:BCN9280
CAS No.:468103-76-6
- Integracin A
Catalog No.:BCN9279
CAS No.:224186-03-2
- Cassamedine
Catalog No.:BCN9278
CAS No.:16408-75-6
- Cinnamolide
Catalog No.:BCN9277
CAS No.:23599-47-5
- Machigline
Catalog No.:BCN9276
CAS No.:87264-30-0
- Effususol A
Catalog No.:BCN9275
CAS No.:1869082-58-5
- Phoyunbene B
Catalog No.:BCN9274
CAS No.:886747-62-2
- 3-(3-Hydroxybutyl)phenol
Catalog No.:BCN9273
CAS No.:854464-95-2
- 6-Methoxyspirotryprostatin B
Catalog No.:BCN9272
CAS No.:1031727-28-2
- Phoyunbene C
Catalog No.:BCN9285
CAS No.:886747-63-3
- Palmitone
Catalog No.:BCN9286
CAS No.:502-73-8
- Oregonin
Catalog No.:BCN9287
CAS No.:55303-93-0
- Browniine
Catalog No.:BCN9288
CAS No.:5140-42-1
- Rubanthrone A
Catalog No.:BCN9289
CAS No.:441764-20-1
- 6'-O-Galloylsalidroside
Catalog No.:BCN9290
CAS No.:83013-86-9
- Lycojaponicuminol C
Catalog No.:BCN9291
CAS No.:1651839-34-7
- Juncutol
Catalog No.:BCN9292
CAS No.:1021950-14-0
- Latinone
Catalog No.:BCN9293
CAS No.:79157-36-1
- Dehydrojuncuenin B
Catalog No.:BCN9294
CAS No.:1161681-28-2
- Isoboldine
Catalog No.:BCN9295
CAS No.:3019-51-0
- (+)-Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN9296
CAS No.:23513-53-3
Purification of Phenylpropanoids from the Scaly Bulbs of Lilium Longiflorum by CPC and Determination of Their DPP-IV Inhibitory Potentials.[Pubmed:32149232]
ACS Omega. 2020 Feb 20;5(8):4050-4057.
The scaly bulbs of Lilium longiflorum (Liliaceae) are used as a food ingredient and a traditional medicine in East Asia. A preliminary study revealed that treatment with 100 mug/mL of the ethyl acetate fraction of this plant material inhibited dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) to 58.99%. Phytochemical studies were conducted to identify the active ingredient, and five compounds, namely, 1 (2.9 mg, 75.8% purity at 320 nm), 2 (12.2 mg, 97.9% purity at 320 nm), 3 (3.1 mg, 66.5% purity at 320 nm), 4 (6.8 mg, 96.9% purity at 320 nm), and 5 (6.2 mg, 90.2% purity at 320 nm) were purified from 200 mg of the ethyl acetate fraction of L. longiflorum via centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC) with a two-phase solvent system composed of chloroform/methanol/isopropanol/water (5:2:2:4, v/v/v/v) in an ascending mode. Their structures were identified as 1-O-p-coumaroyl-2-O-beta-glucopyranosylglycerol (regaloside D, 1), 3,6'-O-diferuloylsucrose (2), 1-O-p-coumaroyl-2-O-beta-glucopyranosyl-3-O-acetylglycerol (regaloside B, 3), 1-O-p-Coumaroylglycerol (4), and 4-O-acetyl-3,6'-O-diferuloylsucrose (5), respectively, by (1)H and (13)C NMR and MS analysis. Compounds 2 and 5 exhibited DPP-IV inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 46.19 and 63.26 muM, respectively. Compounds 1, 3, and 4 did not show activities, indicating that biphenylpropanoids linked via the sugar moiety are more effective than phenylpropanoids with glycerol or glyceryl glucoside. This is the first report of simultaneous separation of five phenylpropanoids from L. longiflorum by CPC and evaluation of their DPP-IV inhibitory activities.
[Phenylpropanoids and diphenylethene compounds from roots and rhizomes of Smilax scobinicaulis].[Pubmed:23947131]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 May;38(10):1531-5.
The chemical constituents were separated and purified from the roots and rhizomes of Smilax scobinicaulis by various chromatographic methods including silica gel, Sephadex LH-20. Their structures were obtained and identified as resveratrol-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), resveratrol (2), 8-viniferin (3), ethyl caffeate (4), 1-0-caffeoylglycerol (5), 1-O-p-Coumaroylglycerol (6), 1-0-feruloylglycerol (7), grossamide (8), moracin M (9) on the analysis of spectroscopic data. Compound 1 was a new compound and compounds 3-5, 8,9 were separated from this plant for the first time.
[Chemical constituents from Imperata cylindrica].[Pubmed:23189737]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;37(15):2296-300.
Chemical investigation of Imperata cylindrica led to the isolation of thirteen compounds using various chromatographic techniques. The structure of these compounds were identified as: three phenylpropanoids, 1-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1,2,3-propanetriol ( 1 ), 1-O-p-Coumaroylglycerol (2), 4-methoxy-5-methyl coumarin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3); four organic acids, 4-hydroxybenzene carboxylic acid(4), 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (5), vanillic acid (6), 3, 4-dihydroxybutyric acid (7); one phenolic compound, salicin (8); and five triterpenes, namely, arundoin (9), cylindrin (10), fernenol (11), simiarenol (12), glutinone (13) by their physicochemical properties and spectral data analysis. Among them, compounds 1-8 were isolated from the genus Imperata for the first time.
[Studies on phenolic constituents from leaves of pineapple (Ananas comosus)].[Pubmed:17048566]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006 Aug;31(15):1242-4.
OBJECTIVE: To study the phenolic constituents of the leaves of pineapple. METHOD: Chromatographic methods were used to isolate compounds from the leaves of pineapple and spectroscopic methods were used to identify the structures of the isolated compounds. RESULT: 7 compounds, ananasate (1), 1-O-caffeoylglycerol (2), 1-O-p-Coumaroylglycerol (3), caffeic acid (4), p-coumaric acid (5), beta-sitosterol (6) and daucosterol (7), were isolated from the leaves of pineapple. CONCLUSION: 1 was a new compound, and others were obtained from this plant for the first time.


