3'-Sialyllactose Sodium SaltCAS# 128596-80-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 128596-80-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 155899187.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H38NNaO19 | M.Wt | 655.53 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
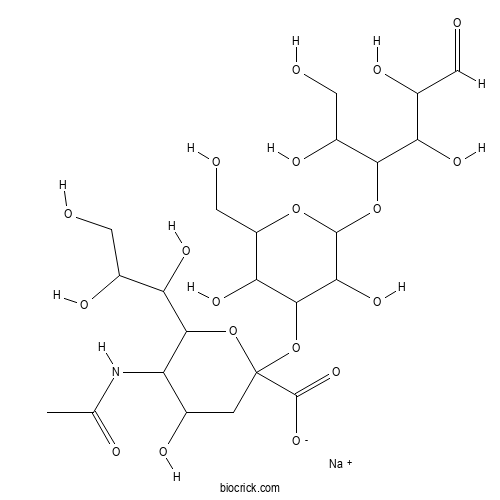
| Chemical Name | sodium;5-acetamido-2-[3,5-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-(1,2,4,5-tetrahydroxy-6-oxohexan-3-yl)oxyoxan-4-yl]oxy-4-hydroxy-6-(1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)oxane-2-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)NC1C(CC(OC1C(C(CO)O)O)(C(=O)[O-])OC2C(C(OC(C2O)OC(C(CO)O)C(C(C=O)O)O)CO)O)O.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LTWFUJWFLMHANB-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H39NO19.Na/c1-7(29)24-13-8(30)2-23(22(38)39,42-19(13)15(35)10(32)4-26)43-20-16(36)12(6-28)40-21(17(20)37)41-18(11(33)5-27)14(34)9(31)3-25;/h3,8-21,26-28,30-37H,2,4-6H2,1H3,(H,24,29)(H,38,39);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

3'-Sialyllactose Sodium Salt Dilution Calculator

3'-Sialyllactose Sodium Salt Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5255 mL | 7.6274 mL | 15.2548 mL | 30.5097 mL | 38.1371 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3051 mL | 1.5255 mL | 3.051 mL | 6.1019 mL | 7.6274 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1525 mL | 0.7627 mL | 1.5255 mL | 3.051 mL | 3.8137 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0305 mL | 0.1525 mL | 0.3051 mL | 0.6102 mL | 0.7627 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0153 mL | 0.0763 mL | 0.1525 mL | 0.3051 mL | 0.3814 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 6'-Sialyllactose Sodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCX1083
CAS No.:157574-76-0
- 6-Iodo Diosmin
Catalog No.:BCX1082
CAS No.:1431536-92-3
- Pseudostellarin B
Catalog No.:BCX1081
CAS No.:156430-21-6
- Rhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCX1080
CAS No.:34202-83-0
- 4-Deoxy-4α-phorbol
Catalog No.:BCX1079
CAS No.:37415-57-9
- 6-Methoxyldihydrochelerythrine chloride
Catalog No.:BCX1078
CAS No.:1071676-04-4
- Avenanthramide C
Catalog No.:BCX1077
CAS No.:116764-15-9
- Pseudoginsenoside Rh1
Catalog No.:BCX1076
CAS No.:97744-96-2
- γ-Tocopherol
Catalog No.:BCX1075
CAS No.:54-28-4
- Momilacton A
Catalog No.:BCX1074
CAS No.:51415-07-7
- Momilacton B
Catalog No.:BCX1073
CAS No.:51415-08-8
- Prunetinoside
Catalog No.:BCX1072
CAS No.:89595-66-4
- Indican
Catalog No.:BCX1085
CAS No.:487-60-5
- Kuwanon W
Catalog No.:BCX1086
CAS No.:95518-95-9
- Avenanthramide E
Catalog No.:BCX1087
CAS No.:93755-77-2
- 4'-O-methyl-Neochlorogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1088
CAS No.:1234369-77-7
- 4'-O-methyl-Chlorogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1089
CAS No.:57496-29-4
- 4'-O-methylether-Homoeriodictyol 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1090
CAS No.:1612225-01-0
- 3-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1091
CAS No.:1899-30-5
- Methyl lucidenate F
Catalog No.:BCX1092
CAS No.:98665-10-2
- 5-O-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)shikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1093
CAS No.:1338228-77-5
- 5-O-Feruloylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1094
CAS No.:1338228-73-1
- 5-O-Coumaroylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1095
CAS No.:111614-47-2
- 5-O-Sinapoylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1096
CAS No.:2704629-41-2
Functional in vitro screening of probiotic strains for inoculation of piglets as a prophylactic measure towards Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection.[Pubmed:33333101]
J Microbiol Methods. 2021 Jan;180:106126.
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), being the major cause of post-weaning diarrhoea (PWD) in newly weaned piglets, induces poor performance and economic losses in pig production. This functional in vitro screening study investigated probiotic strains for use in suckling piglets as a prophylactic strategy towards PWD. Nine strains were evaluated based on their ability to: enhance intestinal epithelial barrier function, reduce adherence of ETEC F18 to intestinal cells, inhibit growth of ETEC F18, and grow on porcine milk oligosaccharides. Strains included in the screening were of the species Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, Bifidobacterium and Bacillus. Our in vitro screening demonstrated genus-, species and strain-specific differences in the mode of action of the tested probiotic strains. Some of the tested bifidobacteria were able to grow on the two porcine milk oligosaccharides, 3'-sialyllactose sodium salt (3'SL) and Lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT), whereas most lactic acid bacteria strains and both Bacillus subtilis strains failed to do so. All probiotic strains inhibited growth of ETEC F18 on agar plates. All but the bifidobacteria reduced binding of ETEC F18 to Caco-2 cell monolayers, with the Enterococcus faecium strain having the most profound effect. All three lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis counteracted the ETEC F18-induced permeability across Caco-2 cell monolayers with the E. faecium strain exhibiting the most pronounced protective effect. The findings from this in vitro screening study indicate that, when selecting probiotic strains for suckling piglets as a prophylactic strategy towards PWD, it would be advantageous to choose a multi-species product including strains with different modes of action in order to increase the likelihood of achieving beneficial effects in vivo.
Toxicological safety assessment of the human-identical milk oligosaccharide 3'-sialyllactose sodium salt.[Pubmed:31418894]
J Appl Toxicol. 2019 Oct;39(10):1378-1393.
Human breastmilk is a mixture of nutrients, hormones and bioactive molecules that are vital for infant growth and development. Infant formula (IF) lacks many of these compounds, most notably human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), which are abundant in breastmilk but scarce in IF. Sialyllactoses, such as 3'-sialyllactose, constitute a large portion of the HMO fraction. To produce IF that matches breastmilk more closely, biosynthesized human-identical milk oligosaccharides (structurally identical to HMOs) such as 3'-sialyllactose sodium salt (3'-SL) are proposed for use in IF and foods for the general population. The safety assessment of 3'-SL comprised in vitro genotoxicity tests and a 90-day oral (gavage) toxicity study. This is the first 90-day study conducted with 3'-SL using neonatal rats (7 days old at the start of dosing-equivalent age to newborn human infants in terms of central nervous system and reproductive development), demonstrating the safety of 3'-SL for consumption by infants, the most sensitive age group. The neonatal rats received 3'-SL at doses up to 5,000 mg/kg body weight (BW)/day and reference controls received 5,000 mg/kg BW/day of fructooligosaccharide (an ingredient approved for use in IF) for comparison with the high-dose 3'-SL group, followed by a 4-week recovery period. There was no evidence of genotoxicity in vitro. In the absence of any test item-related adverse effects in the 90-day study, the high dose (5,000 mg/kg BW/day) was established as the no-observed-adverse-effect level. This confirms the safety of 3'-SL for use in IF for infants, as well as in functional foods for the general population.
Toxicological evaluation of 3'-sialyllactose sodium salt.[Pubmed:29407203]
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;94:83-90.
The safety of 3'-sialyllactose (3'-SL) sodium salt was evaluated by testing for gene mutations, in vivo and in vitro clastogenic activity, and animal toxicity in beagle dogs and rats. The results of all mutagenicity and genotoxicity tests were negative, indicating that 3'-SL does not have any mutagenic or clastogenic potential. The mean lethal dose (LD(50)) of 3'-SL sodium salt was well above 20 g/kg body weight (bw) in rats. A dose escalation acute toxicity study in Beagle dogs also indicated no treatment-related abnormalities. Subsequent 28-day and 90-day toxicity studies in Sprague- Dawley (SD) rats involved dietary exposure to 500, 1,000, and 2000 mg/kg bw of 3'-SL sodium salt and a water (vehicle) control. There were no treatment-related abnormalities on clinical observations, body weight, food consumption, behavior, hematology, clinical chemistry, organ weights, relative organ weights, urinalysis parameters, or necropsy and histopathological findings. The No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) of 3'-SL sodium salt was determined to be higher than 2000 mg/kg bw/day in an oral subchronic toxicity study in rats, indicating that the substance is an ordinary carbohydrate with the lowest toxicity rating. Results confirm that 3'-SL sodium salt has a toxicity profile similar to other non-digestible carbohydrates and naturally occurring human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) and support its safety for human consumption in foods.
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in rhesus monkeys using a novel antiadhesion compound.[Pubmed:10579973]
Gastroenterology. 1999 Dec;117(6):1316-25.
BACKGROUND & AIMS: Helicobacter pylori can be eradicated by administration of antimicrobials, but resistant strains have emerged, and there is a need for novel therapeutic approaches against this infection. This study aimed to determine the safety and efficacy of 3'-sialyllactose sodium salt (3'SL), an oligosaccharide that occurs naturally in human and bovine milk and that can inhibit the adhesion of H. pylori to human epithelial cells in vitro. METHODS: Twelve H. pylori-positive rhesus monkeys were given 3'SL, either alone (regimens 1 and 2; n = 6) or in combination with omeprazole (regimen 3; n = 4), or bismuth subsalicylate (regimen 4; n = 6). Videogastroscopies were performed before, during, and after treatment, and gastric biopsy specimens were obtained for quantitative cultures and histology. The H. pylori strains colonizing the animals were genotyped. RESULTS: After regimen 1 or 2, 2 of 6 animals were cured permanently, and a third animal was transiently cleared. The 3 other animals remained persistently colonized and did not respond to regimen 3. Regimen 4 resulted in transient decreases in colony counts in 3 of 6 other animals. Gastritis was suppressed only in the 2 animals who became persistently H. pylori negative. There was no apparent relation between 3'SL efficacy and any of the H. pylori tested genotypes. No side effects were observed in any of the animals receiving 3'SL. CONCLUSIONS: Antiadhesive therapy is safe; it can cure or decrease H. pylori colonization in some rhesus monkeys, but the addition of a proton pump inhibitor or bismuth subsalicylate does not increase cure rate.


