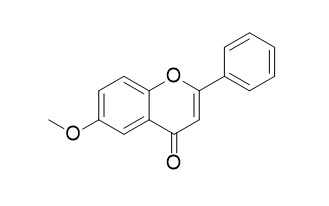
6-MethoxyflavoneCAS# 26964-24-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 26964-24-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H12O3 | M.Wt | 252.2 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 6-Methoxyflavone can be a potential candidate for the development of an effective immunomodulator via the suppression of NFAT-mediated T cell activation. The relative inactivity of 6-methoxyflavanone at α1β2 GABAA receptors and it's partial agonist action at ρ1W328 M GABA receptors suggest that it exhibits a unique profile not matched by other flavonoids. | |||||

6-Methoxyflavone Dilution Calculator

6-Methoxyflavone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9651 mL | 19.8255 mL | 39.6511 mL | 79.3021 mL | 99.1277 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.793 mL | 3.9651 mL | 7.9302 mL | 15.8604 mL | 19.8255 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3965 mL | 1.9826 mL | 3.9651 mL | 7.9302 mL | 9.9128 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0793 mL | 0.3965 mL | 0.793 mL | 1.586 mL | 1.9826 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0397 mL | 0.1983 mL | 0.3965 mL | 0.793 mL | 0.9913 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (+)-Dihydrocinchonine
Catalog No.:BCN9929
CAS No.:485-65-4
- 4-Phenylmorpholine
Catalog No.:BCN9928
CAS No.:92-53-5
- Sanguinarine nitrate
Catalog No.:BCN9927
CAS No.:4752-86-7
- trans-Stilbene
Catalog No.:BCN9926
CAS No.:103-30-0
- Furanoeudesma 1,3-diene
Catalog No.:BCN9925
CAS No.:87605-93-4
- Demissidine
Catalog No.:BCN9924
CAS No.:474-08-8
- 2-(Beta-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)benzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN9923
CAS No.:618-65-5
- (1S)-Chrysanthemolactone
Catalog No.:BCN9922
CAS No.:14087-71-9
- 3'',4'',5,7-Tetrahydroxy 3,6,8-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9921
CAS No.:61451-85-2
- Quinizarin
Catalog No.:BCN9920
CAS No.:81-64-1
- Trioxsalen
Catalog No.:BCN9919
CAS No.:3902-71-4
- Geraldol
Catalog No.:BCN9918
CAS No.:21511-25-1
- Pseudopelletierine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9931
CAS No.:6164-62-1
- 3-Carene
Catalog No.:BCN9932
CAS No.:13466-78-9
- Sodium pyruvate
Catalog No.:BCN9933
CAS No.:113-24-6
- Nortropinone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9934
CAS No.:25602-68-0
- 2,4-Dimethylphenol
Catalog No.:BCN9935
CAS No.:105-67-9
- Carvacrol methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN9936
CAS No.:6379-73-3
- Cevadine
Catalog No.:BCN9937
CAS No.:62-59-9
- Apioline
Catalog No.:BCN9938
CAS No.:523-80-8
- Oleacein
Catalog No.:BCN9939
CAS No.:149183-75-5
- Enterodiol
Catalog No.:BCN9940
CAS No.:77756-22-0
- Coniine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9941
CAS No.:15991-59-0
- Ethyl salicylate
Catalog No.:BCN9942
CAS No.:118-61-6
Hispidulin alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation by inhibiting splenic Th1/Th17 cell population and keratinocyte activation.[Pubmed:32679548]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Oct;87:106767.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by hyperproliferation and abnormal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes accompanied by increased infiltration of immune cells. Previous studies have demonstrated that hispidulin (4',5,7-trihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone, HPD) has various pharmacological benefits such as anti-fungal, anti-inflammation, and anti-allergic effects. This study investigated the effectiveness of HPD to treat psoriasis using an imiquimod (IMQ)-induced mouse model and activated keratinocytes. IMQ was topically applied to the back skin of mice for six consecutive days, and the mice were orally administered HPD. Based on the histological observation and immunological analysis, oral administration of HPD suppressed psoriatic characteristics including skin thickness, psoriasis area severity index, transepidermal water loss, and neutrophil infiltration. HPD alleviated pathologically increased levels of immunoglobulin G2a, myeloperoxidase, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Splenic Th1 and Th17 cell populations were also reduced by HPD in the murine model. In addition, in activated keratinocytes, HPD inhibited gene expression of Th1- and Th17-associated cytokines and chemokines, and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB. In summary, HPD alleviates psoriasis skin inflammation in vivo and in vitro. Therefore, we suggest that HPD would be a potent therapeutic candidate for the treatment of psoriasis.
Flavonoids from Scutellaria baicalensis inhibit senescence-associated secretory phenotype production by interrupting IkappaBzeta/C/EBPbeta pathway: Inhibition of age-related inflammation.[Pubmed:32554301]
Phytomedicine. 2020 Jun 5;76:153255.
BACKGROUND: Prolonged exposure to the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) with age leads to chronic low-grade inflammation in neighboring cells and tissues, causing many chronic degenerative diseases. PURPOSE: The effects on SASP production of the ethanol extract from Scutellaria radix and 17 isolated flavonoid constituents were examined in vitro and in vivo. METHODS: Cellular senescence was induced by bleomycin. Expression of the SASP and cell signaling molecules was detected using ELISA, RT-qPCR, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence staining. To investigate the in vivo effects, 21-month-old aged rats were used. RESULTS: The ethanol extract and 5 compounds including 1 (Oroxylin A; 5,7-dihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone), 5 (2',6',5,7-tetrahydroxy-8-methoxyflavone), 8 (2',5,7-trihydroxyflavone), 10 (2',5,7-trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone) and 11 (2',5,7-trihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone) potently reduced IL-6 and IL-8 production and gene expression of the SASP, including IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, GM-CSF, CXCL1, MCP-2, and MMP-3. This finding indicates the important role of the B-ring 2'hydroxyl group in flavonoid molecules. Furthermore, compounds 8 and 11, the strongest SASP inhibitors, decreased the expression of IkappaBzeta and C/EBPbeta protein without affecting either BrdU uptake or the expression of senescence markers, such as pRb and p21. Finally, the oral administration of compound 8 to aged rats at 2 and 4 mg/kg/day for 10 days significantly inhibited the gene expression of SASP and IkappaBzeta in kidneys. This is the first report of the strong SASP inhibitory action of flavonoids from Scutellaria radix on in vitro and in vivo senescence models. The inhibitory action was shown to be mediated mainly by interfering with the IkappaBzeta/C/EBPbeta signaling pathway. CONCLUSION: Targeting production of the SASP using flavonoids from Scutellaria radix or its extract might help reduce low-grade sterile inflammation and control age-related diseases.
Hispidulin Inhibits Mast Cell-Mediated Allergic Inflammation through Down-Regulation of Histamine Release and Inflammatory Cytokines.[Pubmed:31195760]
Molecules. 2019 Jun 5;24(11). pii: molecules24112131.
Hispidulin (4',5,7-trihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone) is a natural compound derived from traditional Chinese medicinal herbs, and it is known to have an anti-inflammatory effect. Here, we investigated the effect of hispidulin on the immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated allergic responses in rat basophilic leukemia (RBL)-2H3 mast cells. When RBL-2H3 cells were sensitized with anti-dinitrophenyl (anti-DNP) IgE and subsequently stimulated with DNP-human serum albumin (HSA), histamine and beta-hexosaminidase were released from the cells by degranulation of activated mast cells. However, pretreatment with hispidulin before the stimulation of DNP-HSA markedly attenuated release of both in anti-DNP IgE-sensitized cells. Furthermore, we investigated whether hispidulin inhibits anti-DNP IgE and DNP-HSA-induced passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA), as an animal model for Type I allergies. Hispidulin markedly decreased the PCA reaction and allergic edema of ears in mice. In addition, activated RBL-2H3 cells induced the expression of inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-4), which are critical for the pathogenesis of allergic disease, through the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Inhibition of JNK activation by hispidulin treatment reduced the induction of cytokine expression in the activated mast cells. Our results indicate that hispidulin might be a possible therapeutic candidate for allergic inflammatory diseases through the suppression of degranulation and inflammatory cytokines expression.
Glycosylation of Methoxylated Flavonoids in the Cultures of Isaria fumosorosea KCH J2.[Pubmed:30304815]
Molecules. 2018 Oct 9;23(10). pii: molecules23102578.
Flavonoids are widely described plant secondary metabolites with high and diverse pro-health properties. In nature, they occur mostly in the form of glycosides. Our research showed that an excellent way to obtain the sugar derivatives of flavonoids is through biotransformations with the use of entomopathogenic filamentous fungi as biocatalysts. In the current paper, we described the biotransformations of five methoxylated flavonoid compounds (2'-methoxyflavanone, 3'-methoxyflavanone, 4'-methoxyflavanone, 6-methoxyflavanone, and 6-Methoxyflavone) in cultures of Isaria fumosorosea KCH J2. As a result, we obtained twelve new flavonoid 4-O-methylglucopyranosides. The products were purified with methods that enabled the reduction of the consumption of organic solvents (preparative TLC and flash chromatography). The structures of the products were confirmed with spectroscopic methods (NMR: (1)H, (13)C, HSQC, HMBC, COSY). The compounds obtained by us expand the library of available flavonoid derivatives and can be used in biological research.
Hispidulin induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo by activating AMPK signaling pathway.[Pubmed:30218072]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 May;40(5):666-676.
Hispidulin (4',5,7-trihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone) is a phenolic flavonoid isolated from the medicinal plant S. involucrata, which exhibits anti-neoplastic activity against several types of cancer. However, the mechanism underlying its anti-cancer activity against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has not been fully elucidated. In this study, we investigated whether and how hispidulin-induced apoptosis of human HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. We showed that hispidulin (10, 20 mumol/L) dose-dependently inhibited cell growth and promoted apoptosis through mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in human HCC SMMC7721 cells and Huh7 cells. More importantly, we revealed that its pro-apoptotic effects depended on endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and unfolded protein response (UPR), as pretreatment with salubrinal, a selective ERS inhibitor, or shRNA targeting a UPR protein CHOP effectively abrogated hispidulin-induced cell apoptosis. Furthermore, we showed that hispidulin-induced apoptosis was mediated by activation of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway as pretreatment with Compound C, an AMPK inhibitor, or AMPK-targeting siRNA reversed the pro-apoptotic effect of hispidulin. In HCC xenograft nude mice, administration of hispidulin (25, 50 mg/kg every day, ip, for 27 days) dose-dependently suppressed the tumor growth, accompanied by inducing ERS and apoptosis in tumor tissue. Taken together, our results demonstrate that hispidulin induces ERS-mediated apoptosis in HCC cells via activating the AMPK/mTOR pathway. This study provides new insights into the anti-tumor activity of hispidulin in HCC.
[Studies on flavonoids from Scutellaria moniliorrhiza].[Pubmed:29082692]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 May;42(9):1699-1703.
By means of preparative HPTLC and column chromatography over silica gel and Sephadex LH-20, nineteen flavonoids were isolated and purified from the whole plants of Scutellaria moniliorrhiza. Based on the physico-chemical properties and spectral data, their structures were identified as apigenin (1), luteolin (2), wogonin (3), oroxylin A (4), 6-methoxynaringein (5), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxyflavone (6), 5,7,8-trimethoxyflavone (7), 3,5,6,7-tetramethoxyflavone (8), 7-hydroxy-4',5,6,8-tetramethoxyflavone (9), 5,7,2'-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavanone (10), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone (11), 5,7-dihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy -flavone (12), 5,2',6'-trihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (13), 5,7,2'-trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone (14), 5,2'-dihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavanone (15), 2'-hydroxy-5,7,8-trimethoxyflavone (16), 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (17), 5,2'-dihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (18), and 5-hydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxyflavone (19). For the first time, compounds 1-19 were isolated from S. moniliorrhiza, and compounds 6, 8, 9, 12, 19 were isolated from the Scutellaria genus.
Two novel bioactive sulfated guaiane sesquiterpenoid salt alkaloids from the aerial parts of Scorzonera divaricata.[Pubmed:29066296]
Fitoterapia. 2018 Jan;124:113-119.
Extracts of the aerial parts of Scorzonera divaricata afforded sulfoscorzonin D (1) and sulfoscorzonin E (2), two novel pyrrolidine inner salt alkaloids with a sulfated guaiane sesquiterpene lactone nucleus, along with 22 known compounds. Especially, sulfoscorzonin D containing a unusual monoterpene moiety is very rare. The structures of new compounds were established using spectroscopic analysis including one- and two-dimensional NMR and HRESIMS. The cytotoxicities of compounds 1-4 and 10 against three tumor cell lines (K562, Hela, and HepG2) were evaluated using the MTT assay. Compounds 2 and 10 exhibited moderate cytotoxic activity. The biological properties of 1-3, 5-8, 10-14, and 16-24, were screened against nine different gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Compounds 1, 5-8, 10, and 18, showed potent antibacterial activities. CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS STUDIED IN THIS ARTICLE: Glucozaluzanin C (PubChem CID: 442320); 1beta,4alpha-dihydroxy-5alpha,6beta,7alpha,11betaH-eudermn-12; 6-olide (CID: 11119093); oleanolic acid (CID: 10494); lup-20(29)-ene-3beta,28-diol (CID: 72326); (22E)-5alpha,8alpha-epidioxyergosta-6,22-dien-3beta-ol (CID: 5469431); ergosta-3beta,5alpha, 6beta-trialcohol (CID: 44558918); stigma-5-en-3-O-beta-glucoside (CID: 5742590); vomifoliol (CID: 12444927); trans-caffeic acid (CID: 689043); trans-p-hydroxy coumaric acid (CID: 637542); 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl ferulate (CID: 11500646); 7,3',4'-trihydroxyflavonol (CID: 5281614); tricin (ID: 5281702); luteolin (CID: 5280445); diosmetin (CID: 5281612); 5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone (CID: 5281703); 5,7-dihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone (CID: 5320315); methyl-3,4-dihydroxy benzoate (CID: 287064); m-hydroxy benzoic acid (CID: 7420); 7-hydroxy-coumarin (CID: 5281426); and scopoletin (CID: 5280460).
The flavonoid 6-methoxyflavone allays cisplatin-induced neuropathic allodynia and hypoalgesia.[Pubmed:28962077]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:1725-1733.
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a major dose limiting side-effect of several commonly used chemotherapeutic agents (such as cisplatin) that profoundly impairs patient quality of life. Unfortunately, neither prophylactic strategies nor symptomatic treatments have proven useful in this condition. Flavonoids are found ubiquitously in fruits and vegetables and exert a multiplicity of beneficial effects. In this study, the antinociceptive activity of 6-Methoxyflavone (6-MF) was investigated and evaluated in comparison with gabapentin in a rat model of CIPN. The effect on motor balance was also assessed using the rotarod and footprint analysis paradigms. 6-MF possessed both peripheral and central antinociceptive activities against tonic and phasic nociceptive stimuli. Cisplatin administration (3.0mg/kg/week, i.p.) for four consecutive weeks generated temporal mechanical allodynia (decreased paw withdrawal threshold; PWT) and thermal hypoalgesia (increased paw thermal threshold; PTT) in the bilateral hindpaws. Daily treatment with 6-MF (25, 50 and 75mg/kg/day, i.p) for four weeks attenuated the cisplatin-induced expression of nocifensive behaviors observed as a significant increase in PWT and alleviation of PTT during the third and fourth weeks of cisplatin administration. Accordingly, daily gabapentin (75mg/kg, i.p) suppressed the expression of CIPN by normalizing the PWT and hotplate response latency. However, these antinociceptive actions were associated with motor impairment exemplified by a significant decrease in rotarod endurance latency and a deficit in the uniformity of step alternation. In contrast, 6-MF was devoid of these adverse side-effects. These findings suggested that 6-MF afforded desirable neuropathic pain alleviating effects in CIPN and it was devoid of gabapentin-like unwanted motor side-effects.
Medicinal importance, pharmacological activities, and analytical aspects of hispidulin: A concise report.[Pubmed:28725632]
J Tradit Complement Med. 2016 Dec 10;7(3):360-366.
Herbal medicines have been played an important role in the human civilization since very ancient time as a food, cloth, medicine and other aspects. Some of the important drugs in the modern medicine were derived from the natural sources such as aspirin, digitalis, quinine, vincristine, vinblastine etc. Hispidulin (4', 5, 7-trihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone) is a flavones derivative found in plant such as Grindelia argentina, Arrabidaea chica, Saussurea involucrate, Crossostephium chinense, Artemisia and Salvia species. Hispidulin have antioxidant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimutagenic, and antineoplastic properties. So far, various analytical methods have been investigated and developed for detection of hispidulin in the plant materials. Productions of hispidulin through different tissue culture techniques have been also investigated. Present review summarized medicinal uses, pharmacological activities and analytical aspects of hispidulin. From the above mentioned aspects, we can conclude that, this review will be helpful to the researcher in the field of natural product for the development of novel molecule for the treatment of different disorders.
Interaction of a flavone loaded on surface-modified dextran-spooled superparamagnetic nanoparticles with beta-cyclodextrin and DNA.[Pubmed:28583036]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018 May;36(7):1908-1917.
Flavones are biologically active compounds obtained mainly from plant sources. Pharmaceutically important compounds can be delivered to the physiological target by loading them in carriers like cyclodextrins and magnetic nanoparticles. Herein, the binding of 6-Methoxyflavone to beta-cyclodextrin and DNA is studied using UV-visible absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. The loading of 6-Methoxyflavone onto a magnetic nanoparticles is employed. beta-cyclodextrin encapsulates the 6-Methoxyflavone to form an inclusion complex. beta-cyclodextrin also used to draw forth 6-Methoxyflavone loaded onto a magnetic nanoparticles. The morphology, magnetic property and the crystallite size of the nanoparticles are studied using scanning electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry and X-ray diffraction techniques, respectively. The binding of the drug-loaded magnetic nanoparticles to DNA shows that the compound is accessible to DNA and available mostly on the surface of the nanoparticles despite a modified dextan polymer supposedly encapsulates the flavone.
Screening of promising chemotherapeutic candidates from plants extracts.[Pubmed:27086008]
J Nat Med. 2016 Jul;70(3):335-60.
Over the course of our studies investigating anti-proliferative properties of compounds originating from plants against human gastric adenocarcinoma (MK-1), human uterine carcinoma (HeLa), murine melanoma (B16F10), and two human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-infected T-cell lines (MT-1 and MT-2), we have screened 582 extracted samples obtained from a variety of parts from 370 plants. A few extracts showed anti-proliferative activity against all cell lines, but upon further investigation, toxicity toward selected cell lines was recognized. After activity-guided fractionation, isolation of the active principles was achieved. Structure-activity relationship studies identified the components and functionalities responsible for the specific selectivity against each cancer cell line. The effect of polyacetylenes against MK-1 cells was more potent than against HeLa and B16F10 cells. The compound having a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl group also showed an anti-proliferative effect against B16F10 cells. Some 6-Methoxyflavone derivatives and 8-hydroxy furanocoumarins were good inhibitors of HeLa cell growth. The 17 compounds whose EC50 values were less than 1 nM did not show specific cellular selectivity. Because the cytotoxic effect of 24, 25-dihydrowithanolide D toward control cells was observed at a concentration about 100 times higher than those for the cancer cell lines, withanolide was identified as the most promising chemotherapeutic candidate in our experiments.
UHPLC-MS-based metabolomics analysis on mice bearing neoplasm (H22) for hispidulin.[Pubmed:27077962]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Jun 5;125:310-8.
Although some physiological and pathological function parameters of hepatitis and liver cancer have been investigated in relation to hispidulin (5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone), the changes of small metabolites in biofluids have been reported rarely. Recent research has shown that metabolic profiling with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOF/MS) coupled with multivariate statistical analysis provides a good understanding of hispidulin effects on mice vaccinated intraperitoneally with H22 tumor cells. Twenty-five potential biomarkers, up- or down-regulated (P<0.05 or 0.01), were identified, and 17 metabolic pathways were constructed. These potential biomarkers underpin the metabolic pathways, which are disturbed in the mice bearing neoplasm (H22). These pathways include pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis; glycine, serine and threonine metabolism; nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism; steroid hormone biosynthesis; pyrimidine metabolism; and glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. Furthermore, 4-phosphopantothenoylcysteine, glycine, niacinamide, cortisol, uracil and 5-thymidylic acid are potential biomarkers that may explain the link between hispidulin and the metabolism of mice bearing neoplasm (H22). Most of the potential biomarkers related to the function of TCA (tricarboxylic acid cycle). The rise of potential biomarkers in the drug groups promoted the up-regulation of TCA cycle compared with the model group.
Flavones Isolated from Scutellariae radix Suppress Propionibacterium Acnes-Induced Cytokine Production In Vitro and In Vivo.[Pubmed:26712724]
Molecules. 2015 Dec 24;21(1):E15.
Scutellariae radix, the root of Scutellaria baicalensis, has long been applied in traditional formulations and modern herbal medications. Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) in follicles can trigger inflammation and lead to the symptom of inflammatory acnes vulgaris. This study was aimed at evaluating the effect of Scutellariae radix extract and purified components isolated from it on inflammation induced by P. acnes in vitro and in vivo. The results showed the ethyl acetate (EA) soluble fraction from the partition of crude ethanolic extract from Scutellariae radix inhibited P. acnes-induced interleukin IL-8 and IL-1beta production in human monocytic THP-1 cells. Seven flavones were isolated from the EA fraction by repeated chromatographies, and identified as 5,7-dihydroxy-6-Methoxyflavone (FL1, oroxylin), 5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone (FL2, wogonin), 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (FL3, 7-O-methylwogonin), 5,6'-dihydroxy-6,7,8,2'-tetramethoxy flavone (FL4, skullcapflavone II), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone (FL5), 5,2',6'-trihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone (FL6, viscidulin II), and 5,7,2',5'-tetrahydroxy-8,6'-dimethoxyflavone (FL7, ganhuangenin). They all significantly suppressed P. acnes-induced IL-8 and IL-1beta production in THP-1 cells, and FL2 exerted the strongest effect with half maximal inhibition (IC50) values of 8.7 and 4.9 muM, respectively. Concomitant intradermal injection of each of the seven flavones (20 mug) with P. acnes effectively attenuated P. acnes-induced ear swelling, and decreased the production of IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in ear homogenates. Our results suggested that all the seven flavones can be potential therapeutic agents against P. acnes-induced skin inflammation.


