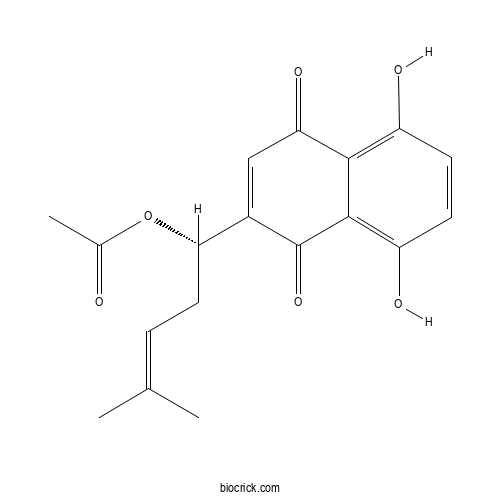
AcetylalkanninCAS# 34232-27-4 |
- Acetylshikonin
Catalog No.:BCN2665
CAS No.:24502-78-1
- Shikonin acetyl
Catalog No.:BCN2452
CAS No.:54984-93-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 34232-27-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9967285.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H18O6 | M.Wt | 330.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Alkannin acetate | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(1S)-1-(5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-dioxonaphthalen-2-yl)-4-methylpent-3-enyl] acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC(C1=CC(=O)C2=C(C=CC(=C2C1=O)O)O)OC(=O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WNFXUXZJJKTDOZ-HNNXBMFYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H18O6/c1-9(2)4-7-15(24-10(3)19)11-8-14(22)16-12(20)5-6-13(21)17(16)18(11)23/h4-6,8,15,20-21H,7H2,1-3H3/t15-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Acetylalkannin Dilution Calculator

Acetylalkannin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0272 mL | 15.1359 mL | 30.2718 mL | 60.5437 mL | 75.6796 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6054 mL | 3.0272 mL | 6.0544 mL | 12.1087 mL | 15.1359 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3027 mL | 1.5136 mL | 3.0272 mL | 6.0544 mL | 7.568 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0605 mL | 0.3027 mL | 0.6054 mL | 1.2109 mL | 1.5136 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0303 mL | 0.1514 mL | 0.3027 mL | 0.6054 mL | 0.7568 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Agrimoniin
Catalog No.:BCX1033
CAS No.:82203-01-8
- Ciwujianoside C1
Catalog No.:BCX1032
CAS No.:114906-73-9
- Ciwujianoside C4
Catalog No.:BCX1031
CAS No.:114906-75-1
- Ciwujianoside D1
Catalog No.:BCX1030
CAS No.:114912-35-5
- Ciwujianoside D2
Catalog No.:BCX1029
CAS No.:114892-57-8
- 6-Hydroxymusizin 8-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1028
CAS No.:23566-96-3
- 18α,20β-Glycyrrhizic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1027
CAS No.:83896-44-0
- Gallic acid 4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1026
CAS No.:84274-52-2
- Flavanone hydrazone
Catalog No.:BCX1025
CAS No.:1692-46-2
- Notoginsenoside D
Catalog No.:BCX1024
CAS No.:193895-50-0
- Pseudoginsenoside
Catalog No.:BCX1023
CAS No.:96158-07-5
- Diphylloside A
Catalog No.:BCX1022
CAS No.:113558-11-5
- Isoferulic Acid
Catalog No.:BCX1035
CAS No.:537-73-5
- α-Norbixin
Catalog No.:BCX1036
CAS No.:626-76-6
- 6-Iodo 5,7,3',4',5'-Pentamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1037
CAS No.:1192850-63-7
- 3β,13-dihydroxy-ursan-28-oic acid-13-lactone
Catalog No.:BCX1038
CAS No.:29428-70-4
- Regaloside H
Catalog No.:BCX1039
CAS No.:126239-77-8
- (+)-trans-Khellactone
Catalog No.:BCX1040
CAS No.:20516-17-0
- (-)-cis-Khellactone
Catalog No.:BCX1041
CAS No.:54712-23-1
- L-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronorharman-3-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1042
CAS No.:42438-90-4
- 13β,21-Dihydroxyeurycomanone
Catalog No.:BCX1043
CAS No.:138874-44-9
- Wilforlide B
Catalog No.:BCX1044
CAS No.:84104-70-1
- Advantame
Catalog No.:BCX1045
CAS No.:714229-20-6
- Rhododenol
Catalog No.:BCX1046
CAS No.:69617-84-1
[Effect of acetylalkannin from Arnebia euchroma on proliferation, migration, and invasion of human melanoma A375 cells].[Pubmed:37802847]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Sep;48(18):5049-5055.
This study aimed to explore the effect and mechanism of Acetylalkannin from Arnebia euchroma on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human melanoma A375 cells. A375 cells were divided into a blank group, and low-, medium-, and high-dose Acetylalkannin groups(0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mumol.L~(-1)). The MTT assay was used to detect cell proliferation. Cell scratch and transwell migration assays were used to detect cell migration ability, and the transwell invasion assay was used to detect cell invasion ability. Western blot was used to detect the protein expression of migration and invasion-related N-cadherin, vimentin, matrix metalloproteina-se-9(MMP-9), and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway-related Wnt1, Axin2, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta(GSK-3beta), phosphorylated GSK-3beta(p-GSK-3beta), beta-catenin, cell cycle protein D_1(cyclin D_1), and p21. Real-time fluorescence-based quantitative polymerase chain reaction(real-time PCR) was used to detect the mRNA expression of E-cadherin, matrix metalloproteinase-2(MMP-2), N-cadherin, vimentin, beta-catenin, snail-1, and CD44. MTT results showed that the cell inhibition rates in the Acetylalkannin groups significantly increased as compared with that in the blank group(P<0.01). The results of cell scratch and transwell assays showed that compared with the blank group, the Acetylalkannin groups showed reduced cell migration and invasion, and migration and invasion rates(P<0.05, P<0.01) and weakened horizontal and vertical migration and invasion abilities. Western blot results showed that compared with the blank group, the high-dose Acetylalkannin group showed increased expression of Axin2 protein(P<0.05), and decreased expression of N-cadherin, vimentin, MMP-9, Wnt1, p-GSK-3beta, beta-catenin, cyclin D_1, and p21 proteins(P<0.05, P<0.01). The expression of GSK-3beta protein did not change significantly. PCR results showed that the overall trend of MMP-2, N-cadherin, vimentin, beta-catenin, snail-1, and CD44 mRNA expression was down-regulated(P<0.01), and the expression of E-cadherin mRNA increased(P<0.01). Acetylalkannin can inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human melanoma A375 cells, and its mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
Relayed chromatography - Countercurrent chromatography in series with liquid chromatography for the separation of natural products.[Pubmed:35709606]
J Chromatogr A. 2022 Aug 2;1676:463205.
Chromatography is an essential method for separating natural products. In this study, we proposed the concept of 'relayed chromatography', based on the strategy of combining different chromatography with relayed resolution by in-situ concentration technique. The following chromatographic methods were used: high-speed countercurrent chromatography (HSCCC), silica gel liquid chromatography (silica gel LC), and reverse phase liquid chromatography (reverse phase LC). The proposed strategy was effectively applied to the preparative separation of naturally existing naphthaquinones. After the first separation stage (silica gel LC), Acetylalkannin (1) was directly collected, while fractions 1, 4 and 5 were collected and respectively subjected to recycling CCC separation after concentration. Thus, deoxyshikonin (2), 8-O-methyl-11-O-acetylshikonin (6), beta-acetoxyisovalerylalkannin (7) and alkannin (8) were collected. Fraction 2 was concentrated and injected in reverse phase LC separation. After collection of isobutyrylalkannin (3), the remaining effluent from reverse phase LC retained the peak resolution (R(4,5)=0.45) and was injected into a recycling CCC elution. Finally, beta, beta-dimethylacrylalkannin (4), and isovalerylalkannin (5) were collected with sufficient resolution (R(4,5)=1.25). Eight naturally occurring naphthaquinones were thus isolated from Arnebia euchroma. The purities of all the compounds were determined by HPLC to be > 90%, and the chemical structures were determined by spectral method. Among the aforementioned compounds, 8-O-methyl-11-O-acetylshikonin (6) was separated as a new compound from A. euchroma. In conclusion, the relayed strategy that retains the resolution of the previous chromatographic stage can improve CCC separation efficiency, which may expand the range of application of CCC combined with different chromatography to the separation of natural products.
Cytotoxic naphthoquinones from Arnebia densiflora (Nordm.) Ledeb and determining new apoptosis inducers.[Pubmed:30449173]
Nat Prod Res. 2020 Jun;34(12):1669-1677.
In this study, phytochemical composition of Arnebia densiflora (AD) was determined and cytotoxic effects of the n-hexane extract and compounds isolated from this species on various cell lines were investigated. By means of serial chromatographic studies, 6 naphthoquinone derivatives were yielded, which are isovalerylalkannin, alpha-methyl-n-butyl alkannin, Acetylalkannin, beta-acetoxy isovalerylalkannin, alkannin and a new compound: 4-hydroxy 4-methyl valeryl alkannin. Structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated using UV, IR, 1D-2D NMR, MS and CD methods. Cytotoxic effects of the extract and isolated alkannins were investigated on L929, HeLa, HEp-2 cells. AD and the isolated compounds demonstrated moderate to strong cytotoxic effects (IC(50) range: 4.92-172.35 microg/ml). The results of DNA fragmentation and caspase-3 activity studies on HeLa cells exhibited that AD and the naphthoquinones isolated from it caused cytotoxicity through induction of apoptosis.[Formula: see text].
Bioactivity and quantitative analysis of isohexenylnaphthazarins in root periderm of two Echium spp.: E. plantagineum and E. gaditanum.[Pubmed:28633108]
Phytochemistry. 2017 Sep;141:162-170.
Isohexenylnaphthazarins are commonly found in the root periderm of several Boraginaceous plants and are known for their broad range of biological activities. The work described herein concerns the biological activity of compounds from the roots of Echium plantagineum L. and Echium gaditanum Boiss (Boraginaceae) collected from field sites in southern Spain and Australia. Bioactivity was assessed using etiolated wheat coleoptile bioassay and in vitro growth inhibitory activity in HeLa and IGROV-1 cells. The quantification of four isohexenylnaphthazarins (shikonin/alkannin, deoxyshikonin/deoxyalkannin, acetylshikonin/Acetylalkannin and dimethylacrylshikonin/dimethylacrylalkannin) was performed by LC-MS/MS using juglone as internal standard. Correlation coefficient values for the activities and concentrations of these four analytes were in the linear range and were greater than 0.99. Acetylshikonin/Acetylalkannin and dimethylacrylshikonin/dimethylacrylalkannin were present in the highest concentrations in extracts of both species. The results reveal that greatest overall inhibition was observed in both bioassays with E. gaditanum extracts. Strong correlations between time of collection, sampling location and bioactivity were identified.
Comparative Study of Naphthoquinone Contents of Selected Greek Endemic Boraginaceae Plants - Antimicrobial Activities.[Pubmed:30428205]
Nat Prod Commun. 2017 Feb;12(2):179-180.
The cyclohexane (Ch) extracts of the roots of five Greek endemic Boraginaceae plants, Onosma kaheirei Teppner, 0. graeca Boiss., 0. erecta Sibth. & Sm., Alkanna sfikasiana Kit Tan, Vold and Strid and Cynoglossum columnae Ten, were investigated for the presence of alkannin/shikonin-related compounds. All species,s except C. columnae and 0. erecta, were found to contain this type of compounds. Seven compounds were obtained after several chromatographic separations from the Ch extracts of the investigated plants: deoxyalkannin (1), 2"-(S)-alpha-methylbutyrylalkannin (2), isobutyrylalkannin (3), propionylalkannin (4), Acetylalkannin (5), beta-hydroxyisovalerylalkannin (6), and beta,beta-dimethylacrylalkannin (7). All structures were identified by ID 1H-/(1)(3)C- and 2D NMR spectroscopy, assisted also by ESI-MS. The extracts and the isolated compounds exhibiting an interesting antimicrobial profile when evaluated for their antimicrobial activity against six Gram-positive and -negative bacteria and three human pathogenic fungi.
Rapid screening, identification, and purification of neuraminidase inhibitors from Lithospermum erythrorhizon Sieb.et Zucc. by ultrafiltration with HPLC-ESI-TOF-MS combined with semipreparative HPLC.[Pubmed:27061885]
J Sep Sci. 2016 Jun;39(11):2097-104.
We put forward an efficient strategy based on bioassay guidance for the rapid screening, identification, and purification of the neuraminidase inhibitors from traditional Chinese medicines, and apply to the discovery of anti-influenza components from Lithospermiun erythrorhizon Sieb.et Zucc. Ultrafiltration with high-performance liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry was employed for the rapid screening and preliminarily identification of anti-influenza components from Zicao. Semipreparative high-performance liquid chromatography was used for the rapid separation and purification of the target compounds. NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and UV spectroscopy were used for further structural identification, and the activity of the compounds was verified by in vitro assay. Five compounds were found to have neuraminidase inhibitory activity by this method. Subsequently, the five compounds were separated by semipreparative high-performance liquid chromatography with the purity over 98% for all of them by high-performance liquid chromatography test. Combined with the NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and UV spectroscopy data, they were identified as alkannin, Acetylalkannin, isobutyrylalkannin, beta,beta-dimethylacryloylalkannin and isovalerylalkannin. The in vitro assay showed that all five compounds had good neuraminidase inhibitory activities. These results suggested that the method is highly efficient, and it can provide platform and methodology supports for the rapid discovery of anti-influenza active ingredients from complex Chinese herbal medicines.
Cytotoxic compounds from endemic Arnebia purpurea.[Pubmed:25973485]
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Apr;10(4):595-6.
Phytochemical studies of the roots and aerial parts of endemic Arnebia purpurea S. Erik & H. Sumbul resulted in the isolation and characterization of four naphthoquinones [isovalerylalkannin (1), alpha-methyl-n-butanoyl alkannin (2), Acetylalkannin (3), and alkannin (4)], a triterpene derivative [3-O-acetyl-oleanolic acid (5)], a steroid [beta-sitosterol (6)], three flavonoid glycosides [isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside (7), kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside (8), kaempferol 3-O-(5"-acetyl) apiofuranoside 7-O-rhamnopyranoside (9)] and a phenolic acid [rosmarinic acid (10)]. 3-O-Acetyl-oleanolic acid, isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside, kaempferol-3-O-mrutinoside, and kaempferol 3-O-(5"-acetyl) apiofuranoside 7-O-rhamnopyranoside are reported from an Arnebia species for the first time. Cytotoxic activities on L929 murine fibrosarcoma cell line of the isolated compounds were investigated using MTT assay. Naphthoquinones (1-4) showed intermediate cytotoxic activity in comparison with the standard, doxorubicin.
Shikonin and its derivatives inhibit the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and synergistically kill glioblastoma cells in combination with erlotinib.[Pubmed:25688715]
Int J Cancer. 2015 Sep 15;137(6):1446-56.
Overexpression and mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene play a causal role in tumorigenesis and resistance to treatment of glioblastoma (GBM). EGFR inhibitors such as erlotinib are currently used for the treatment of GBM; however, their efficacy has been limited due to drug resistance. New treatment strategies are therefore urgently needed. Shikonin, a natural naphthoquinone, induces both apoptosis and necroptosis in human glioma cells, but the effectiveness of erlotinib-shikonin combination treatment as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms is unknown yet. In this study, we investigated erlotinib in combination with shikonin and 14 shikonin derivatives in parental U87MG and transfected U87MG.DeltaEGFR GBM cells. Most of the shikonin derivatives revealed strong cytotoxicity. Shikonin together with five other derivatives, namely deoxyshikonin, isobutyrylshikonin, acetylshikonin, beta,beta-dimethylacrylshikonin and Acetylalkannin showed synergistic cytotoxicity toward U87MG.DeltaEGFR in combination with erlotinib. Moreover, the combined cytotoxic effect of shikonin and erlotinib was further confirmed with another three EGFR-expressing cell lines, BS153, A431 and DK-MG. Shikonin not only dose-dependently inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and decreased phosphorylation of EGFR downstream molecules, including AKT, P44/42MAPK and PLCgamma1, but also together with erlotinib synergistically inhibited DeltaEGFR phosphorylation in U87MG.DeltaEGFR cells as determined by Loewe additivity and Bliss independence drug interaction models. These results suggest that the combination of erlotinib with shikonin or its derivatives might be a potential strategy to overcome drug resistance to erlotinib.
Isolation and chemopreventive evaluation of novel naphthoquinone compounds from Alkanna tinctoria.[Pubmed:24025561]
Anticancer Drugs. 2013 Nov;24(10):1058-68.
Botanically derived natural products have recently become an attractive source of new chemotherapeutic agents. To explore active anticolorectal cancer compounds, we carried out phytochemical studies on Alkanna tinctoria and isolated eight quinone compounds. Using different spectral methods, compounds were identified as alkannin (1), Acetylalkannin (2), angelylalkannin (3), 5-methoxyangenylalkannin (4), dimethylacryl alkannin (5), arnebifuranone (6), alkanfuranol (7), and alkandiol (8). Compounds 4, 7, and 8 are novel compounds. The structures of the three novel compounds were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic evidence including high-resolution mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. The antiproliferative effects of these eight compounds on HCT-116 and SW-480 human colorectal cancer cells were determined using the MTS method. Cell cycle and apoptosis were determined using flow cytometry. Enzymatic activities of caspases were determined using a colorimetric assay, and interactions of compound 4 and caspase 9 were explored by docking analysis. Among the eight compounds, alkannin (1), angelylalkannin (3), and 5-methoxyangenylalkannin (4) showed strong antiproliferative effects, whereas compound 4 showed the most potent effects. Compound 4 arrested cancer cells in the S and G2/M phases, and significantly induced cell apoptosis. The apoptotic effects of compound 4 were supported by caspase assay and docking analysis. The structural-functional relationship assay suggested that to increase anticancer potential, future modifications on alkannin (1) should focus on the hydroxyl groups at C-5 and C-8.
Antimicrobial and cytotoxic isohexenylnaphthazarins from Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Jonst. (Boraginaceae) callus and cell suspension culture.[Pubmed:23208466]
Molecules. 2012 Dec 3;17(12):14310-22.
The phytochemical investigation of the n-hexane extract from callus and cell suspension culture of Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Jonst. resulted in the isolation of nine isohexenylnaphthazarins: deoxyalkannin (1), alkannin (2), Acetylalkannin (3), isobutyrylalkannin (4), β-hydroxyisovalerylalkannin (5), 2''-(S)-α-methylbutyrylalkannin (6), propionylalkannin (7), teracrylalkannin (8) and acetylshikonin (9). Their structures were determined by MS and NMR spectroscopy. Pigments 2–8 are isolated for the first time from Arnebia in vitro cultures, 4 and 7 are reported in the present work as novel metabolites within the Arnebia genus, while 9 is a known constituent of both natural roots and in vitro cultures of A. euchroma. Moreover, methyl jasmonate and 1-monoglyceryl olate, palmitate and stearate are reported for the first time within the Boraginaceae family. The antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of all isolated pigment compounds were tested, revealing a very interesting profile.
ALCAPs induce mitochondrial apoptosis and activate DNA damage response by generating ROS and inhibiting topoisomerase I enzyme activity in K562 leukemia cell line.[Pubmed:21624350]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jun 17;409(4):738-44.
Endemic Alkanna cappadocica was used to isolate novel antitumor molecules from Turkish landscapes in our previous studies. In this study, deoxyalkannin (ALCAP1), beta,beta-dimethylacrylalkannin (ALCAP2), Acetylalkannin (ALCAP3), and alkannin (ALCAP4) as well as the novel isolated compounds 5-methoxydeoxyalkannin (ALCAP5), 8-methoxydeoxyalkannin (ALCAP6), 5-methoxyAcetylalkannin (ALCAP7), 5-methoxy-beta,beta-dimethylacrylalkannin (ALCAP8) were characterized. The topoisomerase I (topo I) inhibitory activity of ALCAPs was investigated using in vitro plasmid relaxation assay and found that ALCAP2, 3, 4 and 7 were potent inhibitors at 2-6muM concentrations. Further, DNA damage response to ALCAP treatments was also studied by measuring the H2AX((S139)) and ATM((S1981)) phosphorylations. ALCAP2, 7 and 8 induced the DNA damage and apoptosis, consistently resulted in PARP cleavage at nanomolar concentrations in K562 leukemia cells. Moreover, when the free radical (ROS) generating capacity of the compounds was studied by 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein-diacetate assay using flow cytometry, we found that a known antioxidant N-acetyl-cysteine almost completely abrogated the H2AX((S139)) phosphorylations and the caspase 3 cleavage and activation. Thus, gammaH2AX((S139)) foci formation remained higher than the control, and an increase in CHK2((T68)) phosphorylation was observed by ALCAP2 and 7 treatments suggested that, these compounds can be potential therapeutics against tumor cell growth because of their unique DNA damaging abilities additional to enzyme inhibition similar to those of doxorubicin.
Cytotoxic naphthoquinones from Alkanna cappadocica ( perpendicular).[Pubmed:20405844]
J Nat Prod. 2010 May 28;73(5):860-4.
In a continuing program to discover new anticancer agents from plants, especially naphthoquinones from the Alkanna genus, Alkanna cappadocica was investigated. Bioassay-guided fractionation of a dichloromethane/methanol (1:1) extract of the roots led to the isolation of four new and four known naphthoquinones. The known compounds are 11-deoxyalkannin (1), beta,beta-dimethylacrylalkannin (2), 11-O-Acetylalkannin (3), and alkannin (4). The new compounds 5-O-methyl-11-deoxyalkannin (5), 8-O-methyl-11-deoxyalkannin (6), 5-O-methyl-11-O-Acetylalkannin (7), and 5-O-methyl-beta,beta-dimethylacrylalkannin (8) were characterized by spectroscopic analyses (LC-ESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR). Cytotoxicity of the isolated compounds was evaluated versus 12 human cancer cell lines, HT-29, MDA-MB-231, PC-3, AU565, Hep G2, LNCaP, MCF7, HeLa, SK-BR-3, DU 145, Saos-2, and Hep 3B together with two normal cell lines, VERO and 3T3, by using the MTT assay. Compound 7 showed remarkable cytotoxicity with IC(50) values between 0.09 and 14.07 muM. It was more potent than the other compounds in six out of 12 cancer cell lines and the positive controls doxorubicin and etoposide. The mono-O-methylated alkannin derivatives and their cytotoxicities are reported for the first time.
Antibacterial and antiviral naphthazarins from Maharanga bicolor.[Pubmed:17867562]
Pharmazie. 2007 Aug;62(8):633-5.
Maharanga bicolor, Boraginaceae, is used in the Nepalese ethnomedicine for the treatment of several diseases. In the course of screening investigations the dichloromethane extract of the roots of Maharanga bicolor was found to inhibit the growth of gram positive bacteria. Bio-assay directed fractionation led to the isolation of five active naphthazarins, deoxyalkannin (1), alkannin (2), Acetylalkannin (3), alkannin beta-hydroxyisovalerate (4) and alkannin beta-acetoxyisovalerate (5). Compounds 2-5 showed antibacterial activity against multi resistant human pathogenic Staphylococcus and Enterococcus species and 1, 4 and 5 showed antiviral activity against herpes simplex virus type-1.
Analysis of alkannin derivatives from Alkanna species by high-performance liquid chromatography/photodiode array/mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:17080496]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2006 Dec;20(12):1359-74.
Alkannin, shikonin (A/S) and their derivatives are enantiomeric hydroxynaphthoquinone red pigments found in the roots of almost 150 species of the Boraginaceae family. A/S have been shown to exhibit strong wound healing, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities and recent extensive research has well established their antitumor properties. A/S and their derivatives comprise the active ingredients of several pharmaceutical and cosmetic preparations. Although A/S have been efficiently synthesized and have been produced by cell tissue cultures in high yield, most of the pharmaceutical preparations worldwide contain A/S extracted from the roots of Boraginaceous species, found in nature. In the present study, a high-performance liquid chromatography/photodiode array/mass spectrometry (HPLC/PDA/MS) method was established to identify monomeric hydroxynaphthoquinones of the alkannin series and other metabolites from Boraginaceous root extracts. This method can be applied for the identification of alkannin derivatives and other metabolites from Boraginaceous cell cultures, and also to determine active ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations containing A/S derivatives. A phytochemical investigation of the Alkanna genus grown in Greece was also performed. Fifty-three root samples belonging to 10 species of the genus Alkanna (A. calliensis, A. corcyrensis, A. graeca, A. methanaea, A. orientalis, A. pindicola, A. primuliflora, A. sieberi, A. stribrnyi and A. tinctoria) were collected from several regions of the Greek flora and analyzed for their constituent hydroxynaphthoquinones and other metabolites. In most of the above Alkanna samples tested, the main hydroxynaphthoquinones were determined to be beta,beta-dimethylacrylalkannin, isovalerylalkannin + alpha-methyl-n-butylalkannin and Acetylalkannin. The hydroxynaphthoquinone constituents and their proportions were found to vary among Alkanna species. Unknown metabolites (not monomeric hydroxynaphthoquinones) were detected by HPLC-PDA-MS, while in several Alkanna species hydroxynaphthoquinones were detected for the first time.
Cytotoxicity in vitro of naphthazarin derivatives from Onosma arenaria.[Pubmed:16718737]
Phytother Res. 2006 Jul;20(7):602-4.
The cytotoxicity of naphthazarin derivatives isolated from the roots of Onosma arenaria on human cervix adenocarcinoma cells (HeLa) and leukaemia K562 cells, as well on non-malignant peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) was studied. The results show that beta-hydroxyisovalerylalkannin, Acetylalkannin and the pigment fraction exhibited high cytotoxicity in vitro against the tested cell lines, as well the healthy PBMC before or after activation with phytohaemagglutinin.


