BMS 309403FABP4 inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 300657-03-8 |
- MK-4827
Catalog No.:BCC1761
CAS No.:1038915-60-4
- Iniparib (BSI-201)
Catalog No.:BCC2208
CAS No.:160003-66-7
- AG-14361
Catalog No.:BCC2209
CAS No.:328543-09-5
- PJ34 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2210
CAS No.:344458-15-7
- Rucaparib (AG-014699,PF-01367338)
Catalog No.:BCC2207
CAS No.:459868-92-9
- Veliparib dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2076
CAS No.:912445-05-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 300657-03-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16122583 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C31H26N2O3 | M.Wt | 474.55 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (210.73 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
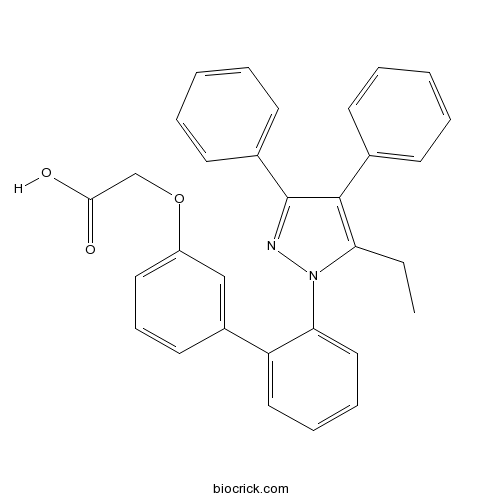
| Chemical Name | 2-[3-[2-(5-ethyl-3,4-diphenylpyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]phenoxy]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC1=C(C(=NN1C2=CC=CC=C2C3=CC(=CC=C3)OCC(=O)O)C4=CC=CC=C4)C5=CC=CC=C5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SJRVJRYZAQYCEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C31H26N2O3/c1-2-27-30(22-12-5-3-6-13-22)31(23-14-7-4-8-15-23)32-33(27)28-19-10-9-18-26(28)24-16-11-17-25(20-24)36-21-29(34)35/h3-20H,2,21H2,1H3,(H,34,35) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte (FABP4) inhibitor (Ki values are <2, 250 and 350 nM for FABP4, FABP3 and FABP5 respectively). Decreases fatty acid uptake in adipocytes in vitro and reduces atherosclerotic lesion area in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. Reduces blood glucose levels and increases insulin sensitivity in a mouse model of obesity. Orally active. |

BMS 309403 Dilution Calculator

BMS 309403 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1073 mL | 10.5363 mL | 21.0726 mL | 42.1452 mL | 52.6815 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4215 mL | 2.1073 mL | 4.2145 mL | 8.429 mL | 10.5363 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2107 mL | 1.0536 mL | 2.1073 mL | 4.2145 mL | 5.2681 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0421 mL | 0.2107 mL | 0.4215 mL | 0.8429 mL | 1.0536 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0211 mL | 0.1054 mL | 0.2107 mL | 0.4215 mL | 0.5268 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
BMS309403 is specifically designed to target FABP4 with a Ki value less than 2 nM. It is a potent and selective FABP4 inhibitor.[1]
Fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) are small-molecular weight hydrophobic proteins containing a large hydrophobic cavity, into which naturally occurring long-chain fatty acids and synthetic hydrophobic ligands can be accepted. FABPs act as transporters of endogenous fatty acids from the cell surface to various sites of fatty acid storage and metabolism. In addition to the roles of FABP4 in regulating lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity, recent pharmacological and biological findings have indicated a regulatory function of FABP4 in inflammation. FABP4 is expressed mainly to macrophages and inflammatory response[1,2]
BMS309403 is an aromatic biphenyl azol compound that competes with fatty acids for the binding pocket of A-FABP with high specificity. BMs30940323 has been shown to lower Mcp-1 secretion from thp-1 macrophages.[3,4]
Chronic administration of BMS309403 (15 mg/kg/day; from 12 to 18 weeks of age) in ApoE-/-mice significantly improved therelaxations, maximal relaxation and EC50 to UK14304, acetylcholine and A23187. Mice orally BMS309403 significantly increased glucose uptake in myotubes in a time and dose dependent manner. Administered with BMS309403 are effectively protected against severe atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes.[3,4]
References:
[1]Okada T, Hiromura M, Otsuka M etal. , Synthesis of BMS-309403-related compounds, including [¹⁴C]BMS-309403, a radioligand for adipocyte fatty acid binding protein. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(1):164-8.
[2]Suhre K, Römisch-Margl W, de Angelis MH etal. , Identification of a potential biomarker for FABP4 inhibition: the power of lipidomics in preclinical drug testing. J Biomol Screen. 2011 Jun;16(5):467-75
[3] Lin W1, Huang X, Zhang Letal. , BMS309403 stimulates glucose uptake in myotubes through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44570.
[4] Lee MY, Li H, Xiao Y, Zhou Z, Xu A, Vanhoutte PM. Chronic administration of BMS309403 improves endothelial function in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice and in cultured human endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;162(7):1564-76.
- HMBA Linker
Catalog No.:BCC2831
CAS No.:3006-96-0
- SKF 77434 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7144
CAS No.:300561-58-4
- Dehydrocorydalin
Catalog No.:BCN2474
CAS No.:30045-16-0
- Boc-Asn-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2587
CAS No.:30044-67-8
- Ro 28-1675
Catalog No.:BCC4124
CAS No.:300353-13-3
- Diphyllin O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8065
CAS No.:30021-77-3
- HEAT hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6683
CAS No.:30007-39-7
- Isoline
Catalog No.:BCN2063
CAS No.:30000-36-3
- Hypotaurine
Catalog No.:BCN1749
CAS No.:300-84-5
- H-Tyr(3,5-I2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3263
CAS No.:300-39-0
- Arecoline hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN2913
CAS No.:300-08-3
- YM 202074
Catalog No.:BCC7682
CAS No.:299900-84-8
- TG003
Catalog No.:BCC4416
CAS No.:300801-52-9
- RS 504393
Catalog No.:BCC1910
CAS No.:300816-15-3
- Ciluprevir (BILN-2061)
Catalog No.:BCC1482
CAS No.:300832-84-2
- GSA 10
Catalog No.:BCC6329
CAS No.:300833-95-8
- 4-CMTB
Catalog No.:BCC6250
CAS No.:300851-67-6
- Methyl Linolenate
Catalog No.:BCN8318
CAS No.:301-00-8
- Oleamide
Catalog No.:BCC6827
CAS No.:301-02-0
- Robinin
Catalog No.:BCN5208
CAS No.:301-19-9
- Malvidin-3-O-galactoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3030
CAS No.:30113-37-2
- Tianeptine sodium
Catalog No.:BCC2506
CAS No.:30123-17-2
- TCS 359
Catalog No.:BCC1183
CAS No.:301305-73-7
- CH 223191
Catalog No.:BCC3896
CAS No.:301326-22-7
Synthesis of BMS-309403-related compounds, including [(1)(4)C]BMS-309403, a radioligand for adipocyte fatty acid binding protein.[Pubmed:22223390]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(1):164-8.
Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (A-FABP; FABP4), which is predominantly expressed in macrophages and adipose tissue, regulates fatty acid storage and lipolysis, and is also an important mediator of inflammation. Here, we report a synthesis of (14)C-labeled 2-[2'-(5-ethyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)biphenyl-3-yloxy]acetic acid (BMS309403), a potent and selective small-molecular FABP4 inhibitor, as a chemical tool for investigating the roles of FABP4 in inflammatory and metabolic disorders. The structure-activity relationship of several BMS derivatives for inhibition of FABP4 is also reported.
Effect of fill weight, capsule shell, and sinker design on the dissolution behavior of capsule formulations of a weak acid drug candidate BMS-309403.[Pubmed:14601962]
Pharm Dev Technol. 2003;8(4):379-83.
Two strengths of BMS-309403 capsules were developed from a common stock granulation. Dissolution testing of the capsules was conducted utilizing the USP apparatus 2 (paddle) with a neutral pH dissolution medium. Unexpectedly, the lower-strength capsules exhibited slower dissolution than the higher-strength capsules filled with the same stock granulation. Higher variability was also observed for the lower-strength capsules. This was found to be mainly caused by a low fill weight in a relatively large size hard gelatin capsule shell. Instead of bursting open, some gelatin capsule shells softened and collapsed onto the granulation, which delayed the release of the active drug. The problem was aggravated by the use of coil sinkers which hindered the medium flow around the capsules. Switching from the gelatin capsule shells to the HPMC (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) shells reversed the dissolution rate ranking between the two capsule strengths. However, both dissolved at a slower rate initially than the gelatin capsules due to the inherent dissolution rate of the HPMC shells at pH 6.8. Notably, the HPMC shells did not occlude the granulation as observed with the gelatin shells. The study demonstrated that the dissolution of capsule formulations in neutral pH media was significantly affected by the fill weight, sinker design, and capsule shell type. Careful selection of these parameters is essential to objectively evaluate the in vitro drug release.
BMS309403 stimulates glucose uptake in myotubes through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed:22952994]
PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44570.
BMS309403 is a biphenyl azole inhibitor against fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) and regarded as a lead compound for effective treatment of obesity related cardio-metabolic diseases. Here we discovered an off-target activity of BMS309403 in that it stimulates glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes in a temporal and dose dependent manner via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway but independent of FABPs. Further analysis indicated that BMS309403 activates AMPK through increasing the ratio of intracellular AMP:ATP while decreasing mitochondrial membrane potential. These findings provide mechanistic insights on the action of BMS309403.
Treatment of diabetes and atherosclerosis by inhibiting fatty-acid-binding protein aP2.[Pubmed:17554340]
Nature. 2007 Jun 21;447(7147):959-65.
Adipocyte fatty-acid-binding protein, aP2 (FABP4) is expressed in adipocytes and macrophages, and integrates inflammatory and metabolic responses. Studies in aP2-deficient mice have shown that this lipid chaperone has a significant role in several aspects of metabolic syndrome, including type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis. Here we demonstrate that an orally active small-molecule inhibitor of aP2 is an effective therapeutic agent against severe atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes in mouse models. In macrophage and adipocyte cell lines with or without aP2, we also show the target specificity of this chemical intervention and its mechanisms of action on metabolic and inflammatory pathways. Our findings demonstrate that targeting aP2 with small-molecule inhibitors is possible and can lead to a new class of powerful therapeutic agents to prevent and treat metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis.
Potent and selective biphenyl azole inhibitors of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (aFABP).[Pubmed:17502136]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Jun 15;17(12):3511-5.
Herein we report the first disclosure of biphenyl azoles that are nanomolar binders of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (aFABP or aP2) with up to thousand-fold selectivity against muscle fatty acid binding protein and epidermal fatty acid binding protein. In addition a new radio-ligand to determine binding against the three fatty acid binding proteins was also synthesized.


