Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells.Lipid metabolism is the break down or storage of fats for energy; these fats are obtained from consuming food and absorbing them or they are synthesized by an animal's liver. Lipid metabolism does exist in plants, though the processes differ in some ways when compared to animals. Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing these fats. Lipid metabolism often begins with hydrolysis,which occurs when a chemical breaks down as a reaction to coming in contact with water.Since lipids (fats) are hydrophobic, hydrolysis in lipid metabolism occurs in the cytoplasm which ends up creating glycerol and fatty acids.[3][4] Due to the hydrophobic nature of lipids they require special transport proteins known as lipoproteins, which are hydrophilic. Lipoproteins are categorized by their density levels. The varying densities between the types of lipoproteins are characteristic to what type of fats they transport. A number of these lipoproteins are synthesized in the liver, but not all of them originate from this organ.
Products for Lipid Metabolism
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
BCC6184
Fatostatin ACell permeable inhibitor of SREBP activation

-
BCC6201
GPBAR-AGPBA receptor (TGR5) agonist

-
BCC6617
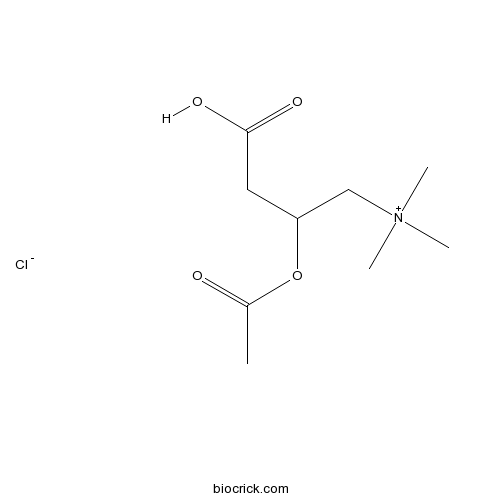
(±)-Acetylcarnitine chloridecholinergic agonist
-
BCC6659
(±)-Decanoylcarnitine chloridecholinergic agonist
-
BCC6680
(±)-Hexanoylcarnitine chloridecholinergic agonist

-
BCC6690
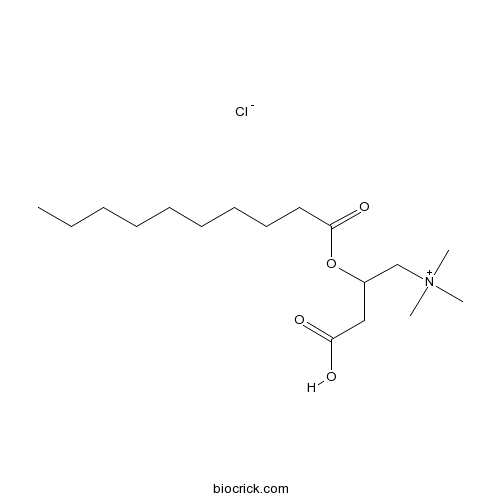
(±)-Lauroylcarnitine chloride
-
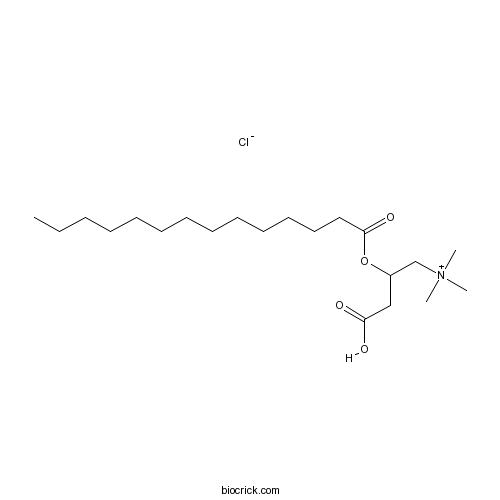
BCC6698
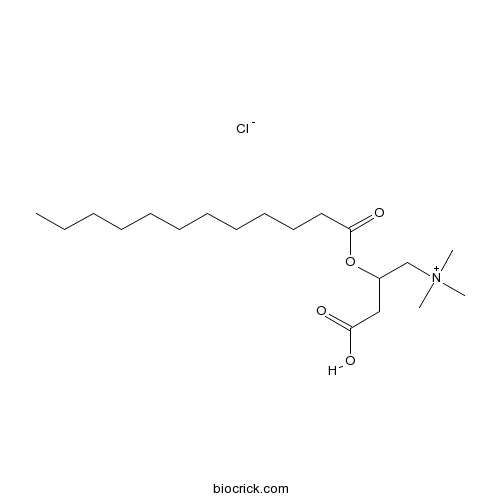
(±)-Myristoylcarnitine chloridecholinergic agonist
-
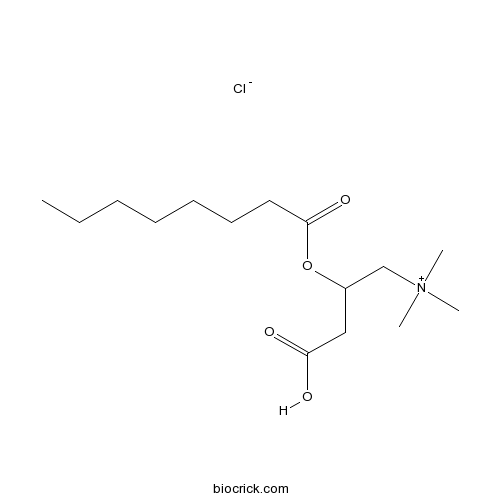
BCC6715
(±)-Octanoylcarnitine chloride
-
BCC6719
(±)-Propionylcarnitine chloride

-
BCC7279
R 59-022Diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor; increases PKC activity
-
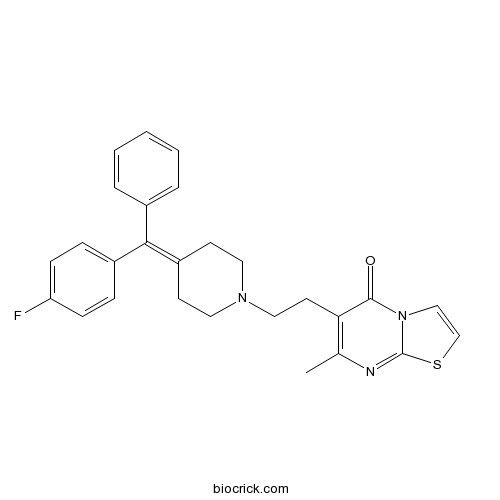
BCC7880
SC 26196

-
BCC8046
BMS 309403FABP4 inhibitor,potent and selective