BW 373U86Non-peptide delta agonist,potent and selective CAS# 155836-50-3 |
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- Calcineurin Autoinhibitory Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2456
CAS No.:148067-21-4
- DL-AP3
Catalog No.:BCC2459
CAS No.:20263-06-3
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 155836-50-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 119029 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H37N3O2 | M.Wt | 435.61 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. HCl | ||
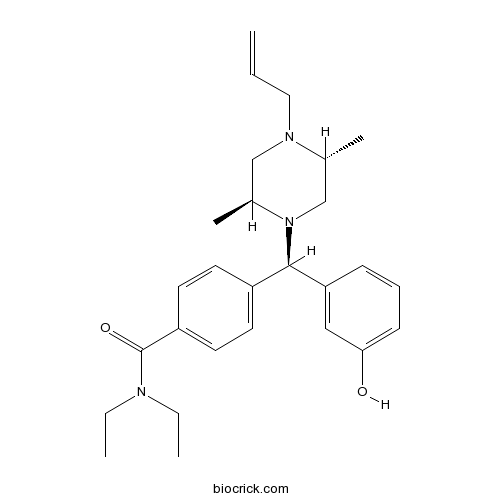
| Chemical Name | 4-[(R)-[(2S,5R)-2,5-dimethyl-4-prop-2-enylpiperazin-1-yl]-(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide | ||
| SMILES | CCN(CC)C(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(C2=CC(=CC=C2)O)N3CC(N(CC3C)CC=C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LBLDMHBSVIVJPM-YZIHRLCOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H37N3O2/c1-6-16-29-18-21(5)30(19-20(29)4)26(24-10-9-11-25(31)17-24)22-12-14-23(15-13-22)27(32)28(7-2)8-3/h6,9-15,17,20-21,26,31H,1,7-8,16,18-19H2,2-5H3/t20-,21+,26-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective non-peptide δ-opioid receptor agonist. Ki values are 1.8, 15 and 34 nM for δ, μ and κ receptors respectively. Centrally active following systemic administration in vivo. |

BW 373U86 Dilution Calculator

BW 373U86 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2956 mL | 11.4782 mL | 22.9563 mL | 45.9126 mL | 57.3908 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4591 mL | 2.2956 mL | 4.5913 mL | 9.1825 mL | 11.4782 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2296 mL | 1.1478 mL | 2.2956 mL | 4.5913 mL | 5.7391 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0459 mL | 0.2296 mL | 0.4591 mL | 0.9183 mL | 1.1478 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.023 mL | 0.1148 mL | 0.2296 mL | 0.4591 mL | 0.5739 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ki: 1.8, 15, 85 and 34 nM for delta, mu, epsilon and kappa receptor
Opioid receptors are heterogeneous and at least four types, mu,.delta, kappa and epsilon, are known to exist. Currently, all clinically used opiates act through the mu receptor to induce analgesia; however, they also induce unwanted side effects such as respiratory depression, dependence, constipation and muscle rigidity.BW 373U86 is a novel, potent and selective nonpeptidic delta opioid receptor agonist.
In vitro: BW 373U86 was a potent delta receptor-selective ligand in receptor binding assays. The Ki values were 1 .8 ± 0.4, 15 ± 3, 85 ± 4 and 34 ± 3 nM for delta, mu, epsilon and kappa receptor binding sites, respectively. BW 373U86 inhibited electncally evoked muscle contraction of mouse vas deferens with an ED50 value of 0.2 ± 0.06 nM [1].
In vivo: BW 373U86 inhibited the acoustic startle reflex after subcutaneous administration from 0.2- to 2-mg/kg doses in rats, and this inhibition was blocked by naltnndole. BW 373U86 also induced a dose-dependent increase of locomotor activity in rats at similar doses. This effect was inhibited by naltnndole [3].
Clinical trial: Up to now, BW 373U86 is still in the preclinical development stage.
Reference:
[1] Chang KJ, Rigdon GC, Howard JL, McNutt RW. A novel, potent and selective nonpeptidic delta opioid receptor agonist BW 373U86. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Nov;267(2):852-7.
- 5-O-Methylhierochin D
Catalog No.:BCN4526
CAS No.:155836-29-6
- 25-O-Methylalisol A
Catalog No.:BCN3456
CAS No.:155801-00-6
- 3-beta-O-(cis-p-Coumaroyl)corosolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1553
CAS No.:155800-17-2
- 4-IBP
Catalog No.:BCC6777
CAS No.:155798-08-6
- Hierochin D
Catalog No.:BCN1702
CAS No.:155759-02-7
- Peujaponiside
Catalog No.:BCN8261
CAS No.:155740-16-2
- Pizotifen
Catalog No.:BCC4215
CAS No.:15574-96-6
- Mecarbinate
Catalog No.:BCC4919
CAS No.:15574-49-9
- Isomagnolone
Catalog No.:BCN1701
CAS No.:155709-41-4
- Simonsinol
Catalog No.:BCN1700
CAS No.:155709-40-3
- Notoginsenoside Ft1
Catalog No.:BCN6434
CAS No.:155683-00-4
- PG-9 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6779
CAS No.:155649-00-6
- RJR-2403
Catalog No.:BCC1901
CAS No.:15585-43-0
- 9,10-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3106
CAS No.:155861-51-1
- LE 135
Catalog No.:BCC7242
CAS No.:155877-83-1
- Gipsoside
Catalog No.:BCN8482
CAS No.:15588-68-8
- Edultin
Catalog No.:BCC8321
CAS No.:15591-75-0
- Rabdoternin F
Catalog No.:BCN6399
CAS No.:155977-87-0
- 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4795
CAS No.:156-38-7
- Sodium butyrate
Catalog No.:BCC4720
CAS No.:156-54-7
- H-HoArg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3226
CAS No.:156-86-5
- Angelidiol
Catalog No.:BCN7964
CAS No.:156009-77-7
- Qianhucoumarin E
Catalog No.:BCN3506
CAS No.:156041-02-0
- Alvimopan
Catalog No.:BCC1347
CAS No.:156053-89-3
Binding of BW 373U86, a non-peptidic delta opioid receptor agonist, is not regulated by guanine nucleotides and sodium.[Pubmed:8223952]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 15;246(3):289-92.
BW 373U86 is a novel, non-peptidic delta-opioid receptor ligand with agonist properties in mouse brain and in the mouse isolated vas deferens. The sensitivity of BW 373U86, and of the peptide delta-opioid agonists [D-Pen2,D-Pen5]enkephalin (DPDPE) and [D-Ala2,Glu4]deltorphin, to regulation by guanine nucleotides and sodium was evaluated in competition studies against the 5 selective radioligand [3H]naltrindole. The IC50 values for DPDPE and [D-Ala2,Glu4]deltorphin were significantly increased in brain and mouse vas deferens in the presence of Gpp(NH)p and NaCl. In contrast, the IC50 values for BW 373U86 were not altered in the presence of Gpp(NH)p and NaCl in either tissue. The data indicate that the agonist properties of BW 373U86 may not be affected by the supposed uncoupling of the alpha-subunit of the G-protein from a receptor thought to be G-protein linked.
Dopamine-dependent behavioural stimulation by non-peptide delta opioids BW 373U86 and SNC 80: 3. Facilitation of D1 and D2 responses in unilaterally 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats.[Pubmed:9832944]
Behav Pharmacol. 1998 Feb;9(1):15-21.
In unilaterally 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats the ability of two non-peptide delta-opioid agonists, BW 373U86 and SNC 80, to induce motor asymmetries, alone or in combination with low doses of specific D1 or D2 agonists, was investigated. BW 373U86 and SNC 80 failed to induce motor asymmetries by themselves, but elicited contralateral turning after pretreatment with a dose of SKF 38393, a D1 agonist, or quinpirole, a D2 agonist, which per se did not induce contralateral turning. BW 373U86 also potentiated contralateral turning induced by threshold doses of quinpirole. Facilitation of D1-dependent contralateral turning was associated with a potentiation of c-fos expression, as estimated by Fos-like immunoreactivity, in the dorsal caudate-putamen, particularly in its lateral aspect. Potentiation of D2-dependent contralateral turning was associated with a reduction of c-fos expression in the medial caudate-putamen. It is concluded that stimulation of delta-opioid receptors facilitates the expression of D1 and D2 responses arising from the denervated striatum.
Comparison of receptor mechanisms and efficacy requirements for delta-agonist-induced convulsive activity and antinociception in mice.[Pubmed:12388657]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):723-9.
Delta-opioid receptor-selective agonists produce antinociception and convulsions in several species, including mice. This article examines two hypotheses in mice: 1) that antinociception and convulsive activity are mediated through the same type of delta-receptor and 2) that greater delta-agonist efficacy is required for antinociception than for convulsive activity. Delta-mediated antinociception was evaluated in the acetic acid-induced abdominal constriction assay, which involves a low-intensity noxious stimulus; convulsive activity was indicated as a mild tonic-clonic convulsive episode followed by a period of catalepsy. In delta-opioid receptor knockout mice [DOR-1(-/-)], the nonpeptidic delta-agonists (+/-)-4-[(R*)-[(2S*,5R*)-2,5-dimethyl-4-(2-propenyl)-1- piperazinyl]-(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide hydrochloride (BW373U86) and (+)-4-[(R)-[(2S,5R)-2,5-dimethyl-4-(2-propenyl)-1-piperazinyl]-(3-methoxyphenyl)m ethyl]-N, N-diethylbenzamide (SNC80) failed to produce convulsive behavior demonstrating the absolute involvement of DOR-1 in this effect. In NIH Swiss mice expressing delta-opioid receptors, BW373U86 produced both antinociception and convulsive activity. These effects were antagonized by the putative delta(1)-receptor-selective antagonist 7-benzylidenenaltrexone and the putative delta(2)-receptor-selective antagonist naltriben. Tolerance developed to both the convulsive and antinociceptive effects of BW373U86. Tolerance to the convulsive, but not the antinociceptive, effects of BW373U86 was largely prevented when the antagonist naltrindole was given 20 min after each dose of the agonist in a 3-day treatment paradigm. The convulsive action of BW373U86 was also less sensitive than the antinociceptive action to treatment with the irreversible delta-antagonist naltrindole isothiocyanate. Collectively, these data suggest that the convulsive and antinociceptive activities of delta-agonists are mediated through the same receptor but that the receptor reserve for delta-mediated convulsive activity is greater than for delta-mediated antinociceptive activity.
A novel, potent and selective nonpeptidic delta opioid receptor agonist BW373U86.[Pubmed:8246159]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Nov;267(2):852-7.
Four different opioid receptor binding assays and three different isolated tissue studies were used to screen for delta receptor-selective nonpeptidic compounds. (+/-)-4-((alpha-R*)-alpha-((2S*,5R*)-4-Allyl-2,5- dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-hydroxybenzyl)-N,N-diethylbenzamide (BW373U86) was a potent delta receptor-selective ligand in receptor binding assays. The Ki values were 1.8 +/- 0.4, 15 +/- 3, 85 +/- 4 and 34 +/- 3 nM for delta, mu, epsilon and kappa receptor binding sites, respectively. BW373U86 inhibited electrically evoked muscle contraction of mouse vas deferens with an ED50 value of 0.2 +/- 0.06 nM. This inhibitory effect of BW373U86 was antagonized by the delta receptor-selective antagonist naltrindole in a competitive manner: the Schild plot indicated a slope of 1 and a pA2 value of 9.43 (Ke = 3.7 x 10(-10) M), which is consistent with the high affinity of naltrindole in delta receptors. BW373U86 did not interact significantly with other receptors. BW373U86 inhibited the acoustic startle reflex after subcutaneous administration from 0.2- to 2-mg/kg doses in rats, and this inhibition was blocked by naltrindole. BW373U86 also induced a dose-dependent increase of locomotor activity in rats at similar doses. This effect was inhibited by naltrindole. These data suggest that BW373U86 is a potent and selective nonpeptidic delta agonist, and it elicits distinct in vivo pharmacological activities.
A novel delta opioid agonist, BW373U86, in squirrel monkeys responding under a schedule of shock titration.[Pubmed:8246162]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Nov;267(2):875-82.
The squirrel monkey titration procedure was used to assess the antinociceptive effects of the novel delta opioid agonist (+/-)-4-(a-R*)-a(2S*,5R*)-4-allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-hydroxyb enzyl)- N,N-diethylbenzamide (BW373U86). Under this procedure shock increased every 15 sec from 0.01 to 2.0 mA in 30 steps. Five responses terminated the shock for 15 sec, after which the shock resumed at a lower intensity. The intensity at which the monkeys maintained the shock 50% of the time (median shock level, MSL) was determined. BW373U86 (1.0-30.0 mg/kg i.m.) increased MSL, but these increases were not dose-dependent and lasted only 15 min or less. Doses of BW373U86 that increased MSL often produced tremors and/or convulsions immediately after administration. When 1.0 mg/kg of naltrindole, a delta opioid antagonist, was given in combination with BW373U86, doses of BW373U86 up to 30 mg/kg no longer increased MSL nor did tremors and/or convulsions occur. Doses of BW373U86 (0.01-0.3 mg/kg i.m.) that did not increase MSL when administered alone shifted the dose-effect curve for the mu agonist l-methadone to the left. These shifts were antagonized dose-dependently by naltrindole. In monkeys that were tolerant to morphine, BW373U86 (0.03-0.1 mg/kg i.m.) shifted the morphine dose-effect curve leftward. In addition, BW373U86 altered the effects of the partial opioid agonists, buprenorphine, nalbuphine, butorphanol and levallorphan such that doses of these drugs that did not increase MSL when administered alone, often did so in the presence of BW373U86. Taken together, these findings indicate that BW373U86 has a delta agonist profile in the squirrel monkey; however, its antinociceptive effects in the shock titration procedure may be due to its toxic effects.


