Biotin-HPDPPyridyldithiol-biotin compound CAS# 129179-83-5 |
- Sulfo-NHS-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3576
CAS No.:119616-38-5
- Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3578
CAS No.:127062-22-0
- NHS-SS-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3581
CAS No.:142439-92-7
- Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3580
CAS No.:325143-98-4
- Biotin Hydrazide
Catalog No.:BCC3582
CAS No.:66640-86-6
- Iodoacetyl-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3584
CAS No.:93285-75-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 129179-83-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15949894 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C124H37N5O3S3 | M.Wt | 1740.9 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Biotin HPDP | ||
| Solubility | ≥101.4mg/ml in DMSO | ||
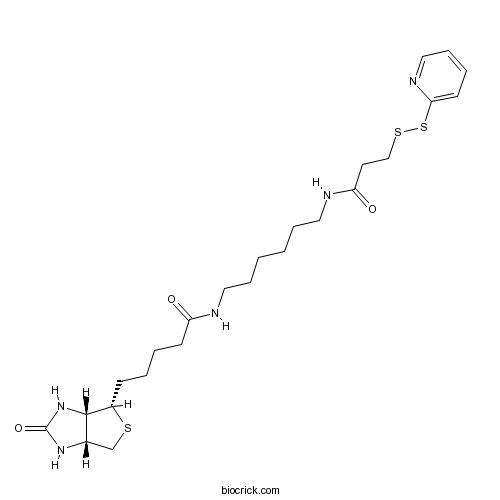
| Chemical Name | 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]-N-[6-[3-(pyridin-2-yldisulfanyl)propanoylamino]hexyl]pentanamide | ||
| SMILES | C1C2C(C(S1)CCCCC(=O)NCCCCCCNC(=O)CCSSC3=CC=CC=N3)NC(=O)N2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QLPHBNRMJLFRGO-YDHSSHFGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H37N5O3S3/c30-20(10-4-3-9-19-23-18(17-33-19)28-24(32)29-23)25-13-6-1-2-7-14-26-21(31)12-16-34-35-22-11-5-8-15-27-22/h5,8,11,15,18-19,23H,1-4,6-7,9-10,12-14,16-17H2,(H,25,30)(H,26,31)(H2,28,29,32)/t18-,19-,23-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Biotin-HPDP is a sulfhydryl-reactive biotinylation agent. |

Biotin-HPDP Dilution Calculator

Biotin-HPDP Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.5744 mL | 2.8721 mL | 5.7442 mL | 11.4883 mL | 14.3604 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1149 mL | 0.5744 mL | 1.1488 mL | 2.2977 mL | 2.8721 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0574 mL | 0.2872 mL | 0.5744 mL | 1.1488 mL | 1.436 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0115 mL | 0.0574 mL | 0.1149 mL | 0.2298 mL | 0.2872 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0057 mL | 0.0287 mL | 0.0574 mL | 0.1149 mL | 0.1436 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Biotin-HPDP (N-[6-(biotinamido)hexyl]-3’-(2’-pyridyldithio)propionamide), a sulfhydryl-reactive biotinylation agent, is a water-insoluble reagent that requires the dissolution of suitable solvents, including dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and dimethylformamide (DMF), prior to the addition into aqueous reactions. Biotin-HPDP consists of a bicyclic biotin rings structure, a 1,6-diaminohexane spacer group attached to the valeric acid side chain of biotin and a sulfhydryl-reactive group at the end of the spacer. The pyridyl disulfide group at the end of biotin-HPDP is able to react with free thiol groups on proteins and other molecules forming a disulfide bond and releasing pyridine-2-thione. The long spacer arm of biotin-HPDP enables the modified molecule to better bind to the avidin or streptavidin probes.
Reference
Bioconjugate Techniques , 2nd ed. By Greg T.Hermanson (Pierce Biotechnology, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL). Academic Press (an imprint of Elsevier): London, Amsterdam, Burlington, San Diego . 2008. ISBN 978-0-12-370501-3.
- Gancaonin M
Catalog No.:BCN4757
CAS No.:129145-51-3
- 2-(2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)propane-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCC8475
CAS No.:129141-48-6
- CGRP 8-37 (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5717
CAS No.:129121-73-9
- ENMD-2076 L-(+)-Tartaric acid
Catalog No.:BCC2185
CAS No.:1291074-87-7
- Evodosin A
Catalog No.:BCN7322
CAS No.:1291053-38-7
- Rivastigmine Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC3851
CAS No.:129101-54-8
- Buclizine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4516
CAS No.:129-74-8
- SP 600125
Catalog No.:BCC2474
CAS No.:129-56-6
- Methysergide maleate
Catalog No.:BCC5698
CAS No.:129-49-7
- Suramin hexasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7079
CAS No.:129-46-4
- Maohuoside A
Catalog No.:BCN5348
CAS No.:128988-55-6
- Fargesol
Catalog No.:BCN6421
CAS No.:128855-64-1
- Iberiotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC6932
CAS No.:129203-60-7
- (2S,3S)-(-)-Glucodistylin
Catalog No.:BCN6156
CAS No.:129212-92-6
- 15-Dihydroepioxylubimin
Catalog No.:BCN4800
CAS No.:129214-59-1
- IKKε-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5514
CAS No.:1292310-49-6
- Hoechst 33258 analog 6
Catalog No.:BCC1628
CAS No.:129244-66-2
- Perospirone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9118
CAS No.:129273-38-7
- Pierreione B
Catalog No.:BCN6855
CAS No.:1292766-21-2
- Boscialin
Catalog No.:BCN7323
CAS No.:129277-03-8
- PF-2545920
Catalog No.:BCC2279
CAS No.:1292799-56-4
- Semilicoisoflavone B
Catalog No.:BCN2931
CAS No.:129280-33-7
- Isoangustone A
Catalog No.:BCN6819
CAS No.:129280-34-8
- Licorisoflavan A
Catalog No.:BCN6662
CAS No.:129314-37-0
Functional proteomics approaches for the identification of transnitrosylase and denitrosylase targets.[Pubmed:23428400]
Methods. 2013 Aug 1;62(2):151-60.
Protein S-nitrosylation is a dynamic post-translational modification (PTM) of specific cysteines within a target protein. Both proteins and small molecules are known to regulate the attachment and removal of this PTM, and proteins exhibiting such a function are transnitrosylase or denitrosylase candidates. With the advent of the biotin switch technique coupled to high-throughput proteomics workflows, the identification and quantification of large numbers of S-nitrosylated proteins and peptides is now possible. Proper analysis and interpretation of high throughout and quantitative proteomics data will help identify specific transnitrosylase and denitrosylase target peptide sequences and contribute to an understanding of the function and regulation of specific S-nitrosylation events. Here we describe the application of a quantitative proteomics approach using isotope-coded affinity tags (ICAT) in the biotin switch approach for the identification of transnitrosylation and denitrosylation targets of thioredoxin 1, an enigmatic protein with both reported transnitrosylase and denitrosylase activities.
Camptothecin promotes the production of nitric oxide that triggers subsequent S-nitrosoproteome-mediated signaling cascades in endothelial cells.[Pubmed:26239883]
Vascul Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;90:27-35.
Camptothecin (CPT) has been used for colorectal cancer therapy. At low concentration of 10(-9)M, CPT modulates endothelial nitric oxide production following the phosphorylation of LKB1 Ser431, AMPK-alpha Thr172, eNOS Ser633 and Ser1177. Elevated nitric oxide (NO) was observed by FA-OMe fluorescent probe. 726 S-nitrosoproteins were identified by iTRAQ quantitative proteomics. IPA analysis indicated that ERK/MAPK was closely linked in the signaling network. Further studies showed that CPT phosphorylated p38 MAPK Thr180/Tyr182 and dephosphorylated Tau Ser199/202. CPT also suppressed the TNF-alpha-induced expression of the inflammasome and cyclooxygenase 2. All this suggests that in addition to the original character of CPT in attenuating the binding of topoisomerase I and DNA in cancer cells, the role of CPT in triggering NO production and the subsequent S-nitrosylated signaling including anti-inflammatory effects in endothelial cells are proposed here. CPT, therefore, provides a potential application addition in preventing vascular disorders.
S-sulfhydration/desulfhydration and S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation: a common paradigm for gasotransmitter signaling by H2S and NO.[Pubmed:23811297]
Methods. 2013 Aug 1;62(2):177-81.
Sulfhydryl groups on protein Cys residues undergo an array of oxidative reactions and modifications, giving rise to a virtual redox zip code with physiological and pathophysiological relevance for modulation of protein structure and functions. While over two decades of studies have established NO-dependent S-nitrosylation as ubiquitous and fundamental for the regulation of diverse protein activities, proteomic methods for studying H2S-dependent S-sulfhydration have only recently been described and now suggest that this is also an abundant modification with potential for global physiological importance. Notably, protein S-sulfhydration and S-nitrosylation bear striking similarities in terms of their chemical and biological determinants, as well as reversal of these modifications via group-transfer to glutathione, followed by the removal from glutathione by enzymes that have apparently evolved to selectively catalyze denitrosylation and desulfhydration. Here we review determinants of protein and low-molecular-weight thiol S-sulfhydration/desulfhydration, similarities with S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation, and methods that are being employed to investigate and quantify these gasotransmitter-mediated cell signaling systems.
Exploration of Fas S-Nitrosylation by the Biotin Switch Assay.[Pubmed:28078594]
Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1557:199-206.
S-nitrosylation is the covalent attachment of nitric oxide radical to the thiol side chain of cysteine. The death receptor Fas/CD95 can be S-nitrosylated in cancer cell lines by NO donors or iNOS activation. This posttranslational modification (PTM) induces Fas aggregation into lipid rafts and enhances FasL-mediated signaling and apoptosis. In this report, we describe the detection of Fas S-nitrosylation by the most commonly used method, the biotin switch assay (BSA) technique, that allows the detection of this very labile covalent modification in cells or tissues. Briefly, this technique relies on the ability of ascorbate to reduce the covalent bond between the NO radical and the protein, allowing the exchange of the NO radical with a thiol reactive Biotin-HPDP. The biotinylated proteins are then easily purified by using NeutrAvidin resin, separated by SDS-PAGE resolution and analyzed by Western blotting.
Surface potential variations on a silicon nanowire transistor in biomolecular modification and detection.[Pubmed:21343647]
Nanotechnology. 2011 Apr 1;22(13):135503.
Using a silicon nanowire field-effect transistor (SiNW-FET) for biomolecule detections, we selected 3-(mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPTMS), N-[6-(biotinamido)hexyl]-3(')-(2(')-pyridyldithio) propionamide (Biotin-HPDP), and avidin, respectively, as the designated linker, receptor, and target molecules as a study model, where the biotin molecules were modified on the SiNW-FET to act as a receptor for avidin. We applied high-resolution scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) to detect the modified/bound biomolecules by measuring the induced change of the surface potential (DeltaPhi(s)) on the SiNW-FET under ambient conditions. After biotin-immobilization and avidin-binding, the DeltaPhi(s) on the SiNW-FET characterized by KPFM was demonstrated to correlate to the conductance change inside the SiNW-FET acquired in aqueous solution. The DeltaPhi(s) values on the SiNW-FET caused by the same biotin-immobilization and avidin-binding were also measured from drain current versus gate voltage curves (I(d)-V(g)) in both aqueous condition and dried state. For comparison, we also study the DeltaPhi(s) values on a Si wafer caused by the same biotin-immobilization and avidin-binding through KPFM and zeta potential measurements. This study has demonstrated that the surface potential measurement on a SiNW-FET by KPFM can be applied as a diagnostic tool that complements the electrical detection with a SiNW-FET sensor. Although the KPFM experiments were carried out under ambient conditions, the measured surface properties of a SiNW-FET are qualitatively valid compared with those obtained by other biosensory techniques performed in liquid environment.


