Bisabolone oxide ACAS# 22567-38-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 22567-38-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90807 | Appearance | Powder |
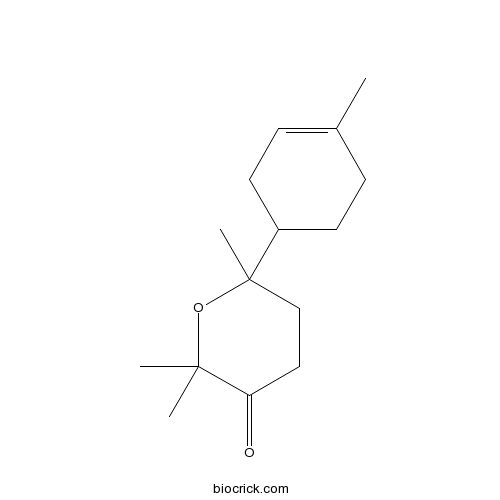
| Formula | C15H24O2 | M.Wt | 236.35 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,2,6-trimethyl-6-(4-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)oxan-3-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CCC(CC1)C2(CCC(=O)C(O2)(C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MJWZYBQLHJQQJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H24O2/c1-11-5-7-12(8-6-11)15(4)10-9-13(16)14(2,3)17-15/h5,12H,6-10H2,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Bisabolone oxide A Dilution Calculator

Bisabolone oxide A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.231 mL | 21.1551 mL | 42.3101 mL | 84.6203 mL | 105.7753 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8462 mL | 4.231 mL | 8.462 mL | 16.9241 mL | 21.1551 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4231 mL | 2.1155 mL | 4.231 mL | 8.462 mL | 10.5775 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0846 mL | 0.4231 mL | 0.8462 mL | 1.6924 mL | 2.1155 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0423 mL | 0.2116 mL | 0.4231 mL | 0.8462 mL | 1.0578 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Bisisorhapontigenin E
Catalog No.:BCN9090
CAS No.:
- Delphinidin 3-O-galactoside
Catalog No.:BCN9089
CAS No.:197250-28-5
- (-)-Isobicyclogermacrenal
Catalog No.:BCN9088
CAS No.:73256-82-3
- Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, 3-[[(2E)-3-[4-(D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxyphenyl]-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl...
Catalog No.:BCN9087
CAS No.:1629852-63-6
- Cucurbitacin Q1
Catalog No.:BCN9086
CAS No.:99530-82-2
- (3r)-7,2'-Dihydroxy-3',4'-dimethoxyisoflavan
Catalog No.:BCN9085
CAS No.:64474-51-7
- (-)-Sesamin
Catalog No.:BCN9084
CAS No.:13079-95-3
- (3β,7β,12β,20Z )- 3,7,12- trihydroxy-11,15,23-trioxo-lanost-8,20-dien-26-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9083
CAS No.:1961358-02-0
- Calenduloside E
Catalog No.:BCN9082
CAS No.:26020-14-4
- Chol-8-en-24-oic acid, 7,15-dihydroxy-4,4,14-trimethyl-3,11-dioxo-, (5α)-
Catalog No.:BCN9081
CAS No.:942936-54-1
- Lanosta-8,20(22)-dien-26-oic acid, 15-hydroxy-3,11,23-trioxo-, (15α,20Z)-
Catalog No.:BCN9080
CAS No.:1961358-01-9
- Sodium deoxycholate
Catalog No.:BCN9079
CAS No.:302-95-4
- (5S,6S,7S,8R)-8-Chloro-5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-phenylethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromen-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN9092
CAS No.:626236-06-4
- Ephedrine
Catalog No.:BCN9093
CAS No.:299-42-3
- Cyanidin 3-O- galactopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9094
CAS No.:142506-26-1
- Febrifugine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN9095
CAS No.:32434-42-7
- Malvidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9096
CAS No.:18470-06-9
- Delphinidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9097
CAS No.:50986-17-9
- Petunidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9098
CAS No.:71991-88-3
- α-Terpinene
Catalog No.:BCN9099
CAS No.:99-86-5
- Cyanidin 3-O-arabinoside
Catalog No.:BCN9100
CAS No.:792868-19-0
- Bisisorhapontigenin F
Catalog No.:BCN9101
CAS No.:
- 3-(2-Hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanone
Catalog No.:BCN9102
CAS No.:151752-07-7
- (3R)-2,3-Dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-3-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN9103
CAS No.:849727-88-4
Chemical composition and biological activities of an essential oil from the aerial parts of Artemisia Gmelinii weber ex Stechm.[Pubmed:31177847]
Nat Prod Res. 2019 Jun 7:1-4.
The aerial parts of Artemisia gmelinii Weber ex Stechm were collected from the northeast of China. The essential oil was obtained by hydrodistillation and analysed by GC-MS. A set of 66 compounds were identified representing 99.1% of the oil composition. The major compounds in the oil were cyclobutaneethanol, endo-borneol, germacrene D, eucalyptol, selin-6-en-4alpha-ol, Bisabolone oxide A, caryophyllene and terpinen-4-ol. Moreover, the essential oil was evaluated for its antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anticholinesterase activities in vitro. Additionally, the antioxidant potential of the oil was evaluated using DPPH and ABTS assays. The oil showed good antidiabetic activity with an IC50 of 63.2 microg/mL, which was similar to that of the positive control acarbose, and weak anticholinesterase activities. These findings demonstrated that the essential oil of Artemisia gmelinii may be a good natural antidiabetic.
Chemo-Diversity and Antiradical Potential of Twelve Matricaria chamomilla L. Populations from Iran: Proof of Ecological Effects.[Pubmed:30987223]
Molecules. 2019 Apr 3;24(7). pii: molecules24071315.
Matricaria chamomilla L. is a popular medicinal herb that is used for healing various diseases and is widely distributed worldwide in temperate climate zones, and even in the subtropical climate of Southern and Western Iran. This study was aimed at comparing the volatile oil constituents, along with antiradical potential and HPLC analysis of methanolic extracts from twelve plant samples growing in Iran. The present research was carried out for the first time on these populations. Among seventeen identified volatile chemicals evaluated by GC/MS and GC/FID, representing 92.73-97.71% of the total oils, alpha-Bisabolone oxide A (45.64-65.41%) was the major constituent, except in case of "Sarableh" as a new chemotype, where (E)- and (Z)-gamma-bisabolene (42.76 and 40.08%, respectively) were the predominant components. Oxygenated sesquiterpenes (53.31-74.52%) were the most abundant compounds in the samples excluding "Sarableh" with 91.3% sesquiterpene hydrocarbons. "Sarableh" also exerted the most potent antioxidant capacity with EC50 = 7.76 +/- 0.3 microg/mL and 6.51 +/- 0.63 mmol TE (Trolox((R)) equivalents)/g. In addition, populations "Lali" and "Bagh Malek" contained the highest amounts of apigenin and luteolin with 1.19 +/- 0.01 mg/g and 2.20 +/- 0.0 mg/g of plant material, respectively. Our findings depict a clear correlation between phytochemical profiles and antiradical potential of M. chamomilla and geographical factors.
Composition and Bioactivities of an (E)-beta-Farnesene Chemotype of Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) Essential Oil from Nepal.[Pubmed:26434140]
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Aug;10(8):1453-7.
The essential oil of Matricaria chamomilla, collected from Nepal, was obtained by hydrodistillation and analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The major components in Nepalese chamomile oil were (E)-beta-famesene (42.2%), alpha-bisabolol oxide A (22.3%), (E,E)-alpha-famesene (8.3%), cis-bicycloether (5.0%), alpha-bisabolol oxide B (4.5%), and alpha-Bisabolone oxide A (4.0%). A cluster analysis based on the chemical compositions of 48 samples of chamomile oil reported in the literature has revealed seven chemotypes, and the oil from Nepal represents the (E)-beta-farnesene chemotype. The chamomile oil was screened for antimicrobial activity against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus niger, and toxicity toward MCF-7 breast tumor cells, Artemia salina, Chaoborus plumicornis, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Drosophila melanogaster.


