BrinzolamideCA II inhibitor CAS# 138890-62-7 |
- ARL 67156 trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7004
CAS No.:1021868-83-6
- Lansoprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1058
CAS No.:103577-45-3
- Sodium Orthovanadate
Catalog No.:BCC3856
CAS No.:13721-39-6
- BTB06584
Catalog No.:BCC5106
CAS No.:219793-45-0
- Resibufogenin
Catalog No.:BCN5366
CAS No.:465-39-4
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 138890-62-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 68844 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H21N3O5S3 | M.Wt | 383.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AL-4862 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (260.75 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
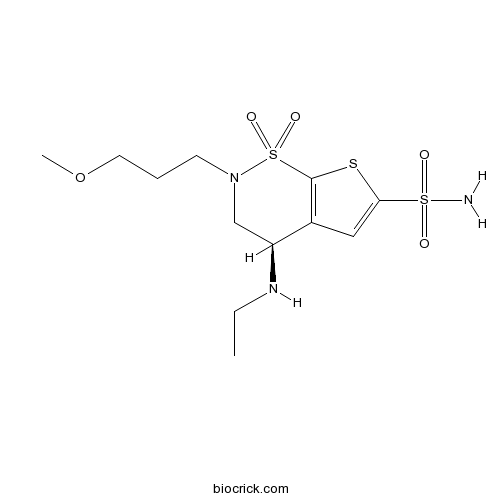
| Chemical Name | (4R)-4-(ethylamino)-2-(3-methoxypropyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydrothieno[3,2-e]thiazine-6-sulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CCNC1CN(S(=O)(=O)C2=C1C=C(S2)S(=O)(=O)N)CCCOC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HCRKCZRJWPKOAR-JTQLQIEISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H21N3O5S3/c1-3-14-10-8-15(5-4-6-20-2)23(18,19)12-9(10)7-11(21-12)22(13,16)17/h7,10,14H,3-6,8H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,16,17)/t10-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Brinzolamide(AL 4862) is a potent carbonic anhydrase II inhibitor with IC50 of 3.19 nM.
Target: carbonic anhydrase II
Brinzolamide (< 1 mg) ophthalmic suspension lowers intraocular pressure in Dutch-belted pigmented rabbits in a dose-dependent manner with an onset within 0.5 hour and a peak response by 1-2 hours. Brinzolamide (0.6 mg) ophthalmic suspension lowers intraocular pressure in laser-treated glaucomatous cynomolgus monkeys in a dose-dependent manner with an onset within 1 hour and a peak response by 3 hours. Brinzolamide dosages of 30 mg/kg, produces a 44% reduction in intestinal charcoal meal progression, but 1 and 10 mg/kg produced 8% and 18% decreases, respectively, in male CD-1 mice. Brinzolamide of 1 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and 30 mg/kg prolongs barbiturate sleep time by 57%, 15%, and 35%, respectively, in male CD-1 mice [1]. Brinzolamide (< 3%) produces significantly greater mean percent intraocular pressure reductions and mean intraocular pressure reductions compared with placebo in patients with primary, open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. The optimal intraocular pressure-lowering concentration of brinzolamide is 1%, brinzolamide 1% is well tolerated by patients with primary open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension when administered twice daily [2]. References: | |||||

Brinzolamide Dilution Calculator

Brinzolamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6075 mL | 13.0375 mL | 26.0749 mL | 52.1499 mL | 65.1873 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5215 mL | 2.6075 mL | 5.215 mL | 10.43 mL | 13.0375 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2607 mL | 1.3037 mL | 2.6075 mL | 5.215 mL | 6.5187 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0521 mL | 0.2607 mL | 0.5215 mL | 1.043 mL | 1.3037 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0261 mL | 0.1304 mL | 0.2607 mL | 0.5215 mL | 0.6519 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Brinzolamide is a potent and selective inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase type II (CA II) with IC50 value of 3.19nM [1].
Brinzolamide is the newest topical CAI to be successfully developed and marketed. It is a safe and efficacious glaucoma drug. In the in vitro assay, brinzolamide has its highest affinity (Ki of 0.13nM) and inhibitory potency (IC50 of 3.19 nM) for CA-II. It has much higher affinity and greater potency for CA-II than for CA-I and CAIV. In the in vivo models, administration of brinzolamide significantly reduces the intraocular pressure (IOP) both in the pigmented rabbits and cynomolgus monkeys with ocular hypertension induced by argon laser trabeculoplasty [1].
As an inhibitor of CA, brinzolamide is also used to assess cerebral blood flow reserve as it can conserve CO2 in the tissues, and the CO2 can then act on blood vessels and produce vasodilatation. Moreover, brinzolamide is proved to be safe and efficacious for reducing intraocular pressure [1].
References:
[1] DeSantis L. Preclinical overview of brinzolamide. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000 Jan;44 Suppl 2:S119-29.
- 1-Acetylpiperazine
Catalog No.:BCC8448
CAS No.:13889-98-0
- 5'-Methoxyhexahydrocurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN7049
CAS No.:138870-96-9
- Pasakbumin B
Catalog No.:BCN2991
CAS No.:138809-10-6
- 8'-Oxo-6-hydroxydihydrophaseic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7046
CAS No.:1388075-44-2
- Fmoc-D-Thr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3555
CAS No.:138797-71-4
- Isomangiferolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4768
CAS No.:13878-92-7
- Fmoc-N-Me-Ile-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3214
CAS No.:138775-22-1
- Fmoc-D-2-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3290
CAS No.:138774-94-4
- Fmoc-D-1-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3284
CAS No.:138774-49-3
- Eugenol rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCN6201
CAS No.:138772-01-7
- LP 20 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6266
CAS No.:1386928-34-2
- Securitinine
Catalog No.:BCN6986
CAS No.:13861-71-7
- Entadamide-A-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8452
CAS No.:138916-58-2
- Ibandronate sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4665
CAS No.:138926-19-9
- Rutaretin
Catalog No.:BCN4710
CAS No.:13895-92-6
- Isocoronarin D
Catalog No.:BCN6202
CAS No.:138965-88-5
- Coronarin D ethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6203
CAS No.:138965-89-6
- Capsazepine
Catalog No.:BCC1451
CAS No.:138977-28-3
- Ziprasidone hydrochloride monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC2072
CAS No.:138982-67-9
- 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN6214
CAS No.:139-85-5
- Carmine
Catalog No.:BCN2223
CAS No.:1390-65-4
- Catalpin
Catalog No.:BCN6205
CAS No.:1390-72-3
- Oplodiol
Catalog No.:BCN6204
CAS No.:13902-62-0
- JMV 449
Catalog No.:BCC5863
CAS No.:139026-66-7
Additive effects and safety of fixed combination therapy with 1% brinzolamide and 0.5% timolol versus 1% dorzolamide and 0.5% timolol in prostaglandin-treated glaucoma patients.[Pubmed:28371482]
Acta Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec;95(8):e720-e726.
PURPOSE: To compare the additive effects and safety of 1% Brinzolamide/0.5% timolol fixed combination (BTFC) versus the low-dose regimen of 1% dorzolamide/0.5% timolol fixed combination (DTFC) in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension (OAG/OH) following treatment with prostaglandin analogues (PGAs). METHODS: A prospective, randomized, double-masked, multicentre, parallel-group and active-controlled study included 201 Japanese OAG/OH patients who had been treated with PGA. Efficacy was assessed as the change in intra-ocular pressure (IOP) from baseline after weeks 4 and 8. Safety was assessed with adverse event rates, ocular discomfort score, blur scale, blood pressure and heart rates, best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and slit lamp examinations. RESULTS: Intra-ocular pressure (IOP) change from baseline at 9 AM/11 AM pooled over the 8 weeks was -3.3/-3.3 mmHg in the BTFC group and -2.9/-3.4 mmHg in the DTFC group, demonstrating non-inferiority of BTFC to DTFC. Ocular irritation was frequently seen in DTFC group. Although blurred vision was frequently seen in BTFC group, it was transient and blurring became the equivalent 3 min after instillation between two groups. No noteworthy issue was observed in other safety outcome. CONCLUSION: Non-inferiority of BTFC to DTFC in IOP reduction was demonstrated after adding onto PGA therapy in Japanese OAG/OH patients. Although the score of blurred vision was transiently higher in BTFC than DTFC, treatment difference decreased and disappeared with time. Thus, BTFC can be considered as a safe and effective agent for glaucoma treatment.
Comparison of dorzolamide/timolol vs brinzolamide/brimonidine fixed combination therapy in the management of primary open-angle glaucoma.[Pubmed:27445072]
Eur J Ophthalmol. 2017 Mar 10;27(2):160-163.
PURPOSE: To compare the efficiency of Brinzolamide/brimonidine fixed combination vs the dorzolamide/timolol fixed combination. METHODS: Forty-four eyes of 44 patients were divided in 2 groups treated either with dorzolamide/timolol twice a day (group A) or with Brinzolamide/brimonidine twice a day (group B). Complete ophthalmic examination including Goldmann applanation tonometry was performed before treatment administration and 1, 4, 8, and 12 weeks afterwards. The intraocular pressure (IOP) was measured twice a day (morning at 9 AM and afternoon at 4 PM). RESULTS: At the end of the follow-up period (12 weeks), mean morning IOP reduction was 7.0 +/- 2.8 mm Hg in group A and 8.4 +/- 1.9 mm Hg in group B. A significant difference was found (p = 0.0343). In contrast, mean afternoon IOP reduction was 8.6 +/- 2.7 mm Hg in group A and 7.9 +/- 1.6 mm Hg in group B and no significant difference was found (p = 0.3413). No significant adverse effects were observed in either group. CONCLUSIONS: Brinzolamide/brimonidine seems to be an effective and safe alternative beta-blocker free fixed combination, especially for patients with comorbidities, having its own antihypertensive profile.
Effect of prophylactic intraocular pressure-lowering medication (brinzolamide) on intraocular pressure after ranibizumab intravitreal injection: A case-control study.[Pubmed:27905340]
Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct;64(10):762-766.
PURPOSE: To observe the effect of prophylactic intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering medication (Brinzolamide) on IOP after ranibizumab intravitreal injections (IVIs). MATERIALS AND METHODS: This prospective case-control study included 352 eyes from 352 patients (1 eye per patient) who were treated with ranibizumab intravitreal injection and divided randomly into two groups. Two hundred and three patients in control group only received the ranibizumab IVI, but 149 patients in case group received one drop of prophylactic intraocular Brinzolamide preinjection. The IOP was measured by noncontact tonometer before injection, at 10, 30, 120 min and 1 day after injection in a sitting position. RESULTS: The mean IOP measured before injection, at 10, 30, 120 min and 1 day after injection individually were 15.79 +/- 2.21 mmHg, 19.33 +/- 4.86 mmHg, 16.64 +/- 2.93 mmHg, 16.17 +/- 3.13 mmHg, and 15.07 +/- 2.55 mmHg in case group and were 15.82 +/- 2.57 mmHg, 21.34 +/- 5.88 mmHg, 18.17 +/- 4.06 mmHg, 17.59 +/- 4.42 mmHg, and15.48 +/- 2.92 mmHg in control group. Comparing two groups, the mean increase on IOP was statistically significant at 10, 30, 120 min postinjection (P < 0.05). CONCLUSIONS: IVI of ranibizumab causes a considerable short-term transient rise on IOP in most patients. The effect of prophylactic IOP-lowering medication on IOP after IVIs can be statistically significant from 10 min to 2 h after IVIs.
The 24-Hour Effects of Brinzolamide/Brimonidine Fixed Combination and Timolol on Intraocular Pressure and Ocular Perfusion Pressure.[Pubmed:28129020]
J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Apr;33(3):161-169.
PURPOSE: To determine the 24-h effects of Brinzolamide/brimonidine tartrate 1%/0.2% fixed combination (BBFC) on intraocular pressure (IOP), ocular perfusion pressure (OPP), blood pressure (BP), and heart rate (HR). METHODS: Sixty subjects with open angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension (OHTN) were admitted overnight for 24-h monitoring of IOP, BP, and HR. All subjects underwent the first, baseline 24-h study after washout of all medications, if necessary. Subjects were then randomized to receive either (1) timolol maleate 0.5% twice daily or (2) BBFC 3 times daily. After 4 weeks of treatment, all subjects completed a follow-up 24-h study visit. At each study visit, IOP, BP, and HR were measured every 2 h in the habitual position. OPP was calculated as 2/3[diastolic BP +1/3(systolic BP-diastolic BP)]-IOP. RESULTS: Treatment with BBFC significantly lowered IOP during the diurnal period (-2.7 +/- 0.4 mmHg; P < 0.01) and nocturnal period (-0.8 +/- 0.3 mmHg; P < 0.01). Timolol similarly reduced IOP during the diurnal period, but did not lower IOP overnight. Over a 24-h period, BBFC achieved a significantly greater IOP reduction than timolol (-0.7 +/- 0.4 mmHg; P = 0.04). BBFC failed to achieve an increase in OPP during any time period, while timolol increased OPP during the diurnal period only. A significantly greater reduction in HR occurred in the timolol group. CONCLUSIONS: BBFC significantly lowers IOP during both the diurnal and nocturnal periods, but has no effect on OPP. Timolol only lowers IOP during the diurnal period.


