CrenatosideCAS# 61276-16-2 |
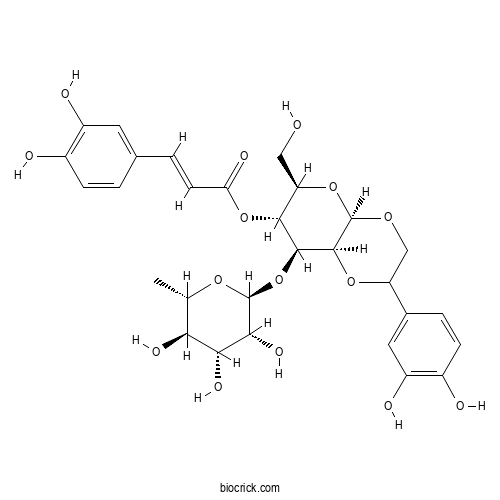
- Crenatoside
Catalog No.:BCX2177
CAS No.:Crenatoside
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 61276-16-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6441894 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C29H34O15 | M.Wt | 622.6 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(4aR,6R,7R,8S,8aS)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-8-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-3,4a,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-2H-pyrano[2,3-b][1,4]dioxin-7-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C3C(OCC(O3)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)O)O)OC(C2OC(=O)C=CC5=CC(=C(C=C5)O)O)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FPOYEEKZOOLVJA-DNBQVIFESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H34O15/c1-12-22(36)23(37)24(38)28(40-12)44-26-25(43-21(35)7-3-13-2-5-15(31)17(33)8-13)19(10-30)42-29-27(26)41-20(11-39-29)14-4-6-16(32)18(34)9-14/h2-9,12,19-20,22-34,36-38H,10-11H2,1H3/b7-3+/t12-,19+,20?,22-,23+,24+,25+,26-,27-,28-,29+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Crenatoside Dilution Calculator

Crenatoside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6062 mL | 8.0308 mL | 16.0617 mL | 32.1234 mL | 40.1542 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3212 mL | 1.6062 mL | 3.2123 mL | 6.4247 mL | 8.0308 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1606 mL | 0.8031 mL | 1.6062 mL | 3.2123 mL | 4.0154 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0321 mL | 0.1606 mL | 0.3212 mL | 0.6425 mL | 0.8031 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0161 mL | 0.0803 mL | 0.1606 mL | 0.3212 mL | 0.4015 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Curdionolide B
Catalog No.:BCX0497
CAS No.:1190225-68-3
- 7,4'-Di-O-methylaromadendrin
Catalog No.:BCX0496
CAS No.:41515-76-8
- Sanggenol C
Catalog No.:BCX0495
CAS No.:174423-32-6
- Rugulolide D
Catalog No.:BCX0494
CAS No.:3002032-69-8
- Sanggenon E
Catalog No.:BCX0493
CAS No.:81381-69-3
- 4-Hydroxy-4-methylcyclohex-2-en-1-one
Catalog No.:BCX0492
CAS No.:70150-56-0
- 7-epi-α-Cyperone
Catalog No.:BCX0491
CAS No.:547-26-2
- Ethyl 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCX0490
CAS No.:4143-00-4
- 2,4-Dihydroxybezaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCX0489
CAS No.:95-01-2
- Rugulolide B
Catalog No.:BCX0488
CAS No.:3002032-71-2
- Rugulolide A
Catalog No.:BCX0487
CAS No.:3002032-70-1
- Oxyphyllone D
Catalog No.:BCX0486
CAS No.:1190094-25-7
- Erythrinin E
Catalog No.:BCX0499
CAS No.:2731101-51-0
- Isocrenatoside
Catalog No.:BCX0500
CAS No.:221895-09-6
- Teuhetenone A
Catalog No.:BCX0501
CAS No.:152481-80-6
- Oxyphyllenodiol A
Catalog No.:BCX0502
CAS No.:363610-30-4
- 6-Demethoxyirigenin
Catalog No.:BCX0503
CAS No.:1348833-10-2
- Vavain
Catalog No.:BCX0504
CAS No.:199996-77-5
- Iristectorin B
Catalog No.:BCX0505
CAS No.:94396-09-5
- Methylconiferin
Catalog No.:BCX0506
CAS No.:883150-46-7
- 1β-Hydroxy-8α-methoxyeremophila-7(11),9-dien-12,8β-olide
Catalog No.:BCX0507
CAS No.:849700-45-4
- (S)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-phenylheptan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCX0508
CAS No.:1220110-76-8
- Moracin N
Catalog No.:BCX0509
CAS No.:135248-05-4
- D-Mannosamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCX0510
CAS No.:5505-63-5
Efficacy of verbascoside, echinacoside, crenatoside on altitude-induced fatigue in rats and possible mechanism.[Pubmed:37679981]
J Tradit Chin Med. 2023 Oct;43(5):934-943.
OBJECTIVE: To study the efficacy and mechanism of three phenylethanoid glycosides (PhGs) (verbascoside, echinacoside, and Crenatoside) on altitude-induced fatigue in rats. METHODS: Altitude-induced fatigue model rats were established in a large hypobaric chamber. Swimming time, energy storage substances, metabolic enzymes, and metabolites were used to evaluate the anti-fatigue activities and mechanism of three PhGs (verbascoside, echinacoside, and Crenatoside) (150 mg/kg, intragastric administration) in the hypoxic environment. RESULTS: The three PhGs, especially verbascoside, could prolong the swimming time of rats, ameliorate the edema and inflammatory infiltration of liver and skeletal muscle, increase the level of energy storage substances, reduce the decomposition of proteins, and exhibit positive effects on the metabolism-related enzyme activity and metabolites. CONCLUSIONS: The PhGs, especially verbascoside, are very potential with anti-fatigue activity in hypoxia. The mechanism may be explained with regulation of energy metabolism and reduction of oxidative stress.
[A new labdane-type diterpenoids from Callicarpa nudiflora].[Pubmed:34467725]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Aug;46(16):4139-4144.
The purpose of the research is to study the bioactive constituents of Callicarpa nudiflora. From the 65% ethanol extract of C. nudiflora leaves, ten compounds were isolated by macroporous adsorption resin, Sephadex LH-20, ODS, silica gel, and preparative HPLC. These compounds were identified as callicapene M6(1), sterebin A(2), isomartynoside(3), Crenatoside(4), luteolin-7-O-neohesperidoside(5), apigenin-7-O-beta-D-neohesperidoside(6), isoacteoside(7), acteoside(8),(7R)-campneoside I(9), and(7S)-campneoside I(10) on the basis of NMR, HR-ESI-MS, and optical rotation data. Compound 1 was obtained as a new compound. Compounds 2 and 4 were isolated from the genus Callicarpa for the first time. Compounds 9 and 10 were isolated from C. nudiflora for the first time.
Correlational nutritional relationships and interactions between expansive holoparasite Orobanche laxissima and woody hosts on metal-rich soils.[Pubmed:34311276]
Phytochemistry. 2021 Oct;190:112844.
Plant parasitism by other plants, combined with abiotic environmental stress, offers a unique opportunity to study correlational nutritional relationships in terms of parasite-host interactions and their functional roles in nutrient cycling in ecosystems. Our study analysed the transfer of selected mineral elements, including heavy metals, from soil to different organs in hosts (Punica granatum and Fraxinus angustifolia) and from hosts to the expansive holoparasite (Orobanche laxissima) in cinnamonic soil habitats in Georgia (Caucasus). We also identified other correlated trophic and bioactive effects in the parasite-host relationship. O. laxissima was characterized by a high accumulation tendency for micro- and macroelements, such as K and Ca, and heavy metals, such as Zn, Ni, and Cd. Parasites can reduce the concentration of heavy metals in host tissues owing to this high accumulation tendency. In total, 85 compounds were identified in the examined parasite and its hosts. Despite the distinct phytochemical content of species of the infected host, the parasite produced specific metabolites with dominant phenylethanoid glycosides (PhGs), with acteoside and Crenatoside being the primary dominant compounds - ca. 98% of all polyphenols. Polyphenols in parasite specimens that are correlated with Cu and Zn are antagonistic to polyphenols correlated with Fe, Pb, Cr, and Ni. The profile of polyphenols in the host species was both qualitatively and quantitatively distinct from the profile of the compounds in the parasite and between hosts (only acteoside in group PhGs was common between the parasite and Fraxinus host), which indicates the existence of a unique compound biosynthesis pathway in the parasite. Our results demonstrated that the parasite, particularly in its flowers, exhibited higher polyphenol content, antioxidative effects (ABTS-+, DPPH, and FRAP), and inhibitory effects.
Effects of phenylethanol glycosides from Orobanche cernua Loefling on UVB-Induced skin photodamage: a comparative study.[Pubmed:33909279]
Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2021 May;20(5):599-614.
Previous study has found that Orobanche cernua Loefling(OC) and its main ingredient, acteoside, possess excellently anti-photo-aging effect. In addition to acteoside, Crenatoside, isoacteoside and 2'-acetylacteoside were also identified as the main phenylethanol glycosides (PhGs) in OC. To screen optimum effective substance and further clarify the photoprotective ingredients of OC, the effects of four major PhGs in OC were compared using UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells. Results indicated that acteoside, isoacteoside and 2'-acetylacteoside effectively decreased UVB-induced MMP-1 expression and stimulated type I procollagen synthesis through inhibition of MAPK/AP-1 and activation of TGF-beta/Smad pathway. Moreover, acteoside and 2'-acetylacteoside significantly reduced UVB-induced ROS and TARC secretion, which is involved in the inhibition of NF-kappabeta/Ikappabetaalpha and stimulation of Nrf2 antioxidant defense system. However, Crenatoside did not show any effect on the regulation of signal cascades mentioned above. Together, our results suggested that 2'-acetylacteoside and isoacteoside also served as efficient agents against UV radiation-induced skin damage. Among them, acteoside and 2'-acetylacteoside showed a higher efficiency than that of isoacteoside, which possessed great potential in treating skin photo-damage.
In vivo anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities of Orobanche crenata (Forssk.) aerial parts in relation to its phytomolecules.[Pubmed:33198532]
Nat Prod Res. 2022 Feb;36(4):1067-1072.
A total methanolic extract and its sub-extracts of Orobanche crenata (Forssk.) aerial parts were subjected to acute toxicity, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective investigations. The methanolic extract was safe upto 3 g/kg on mice. The EtOAc fraction reduced the carrageenan-induced rat paw edema better than indomethacin. It also demonstrated a drop in the elevated ALT, AST, and TB at 300 mg/kg, better than silymarin. Histopathological examination of liver cells of rats given the EtOAc fraction showed a complete absence of the CCl(4)-induced cloudy swelling. A phytochemical investigation of the n-hexane and EtOAc fractions yielded 11 compounds [indole-3-carboxylic acid (1), n-butyl palmitate (2), tyrosol (3), L-rhamnonic acid-1,4-lactone (4), beta-sitosterol/stigmasterol mixture (5/5'), beta-sitosterol/stigmasterol glycosides mixture (6/6'), chrysoeriol (7), luteolin (8), apigenin (9), Crenatoside (10), and verbascoside (11)] as identified by UV, 1D & 2D NMR and ESIMS techniques. Their reported biological actions were in relation to and supported our herein detected pharmacological findings.
Anti-Zika virus activity and chemical characterization by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC-DAD-UV-MS) of ethanol extracts in Tecoma species.[Pubmed:32767975]
BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Aug 7;20(1):246.
BACKGROUND: Plant species from the genus Tecoma are found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. Some of them are grown as ornamental plants and others can be used as medicinal plants. In the present study, ethanolic extracts from trunks and leaves of Tecoma species were tested in vitro using assays against the Zika virus. METHODS: There was a total of 8 extracts obtained from different anatomical parts of three Tecoma species. The Tecoma castaneifolia, T. garrocha, T. stans var. angustata and T. stans var. stans were prepared by percolation with ethanol. The antiviral activity was assayed in vitro against the Zika virus by the MTT colorimetric method (n = 3). The UPLC-DAD-MS analysis of ethanolic extracts was performed from all the studied species. The biofractionation of T. stans var. stans trunk extract using different separation techniques led to the isolation of Crenatoside compound. RESULTS: Ethanolic extract from Tecoma species leaves were more active against the Zika virus (EC(50) 149.90 to 61.25 mug/mL) when compared to the trunk extracts tested (EC(50) 131.0 to 66.79 mug/mL and two were not active). The ethyl acetate and aqueous fractions obtained from T. stans var. stans trunk were active against the Zika virus with EC(50) values of 149.90 and 78.98 mug/mL, respectively. Crenatoside is a phenylethanoid glycoside isolated from the ethyl acetate of T. stans var. stans trunk extract. This compound was tested and exhibited EC(50) 34.78 muM (21.64 mug/mL), thus demonstrating a better result than the original ethanolic extracts as well as others extracts of Tecoma species, and it was more active than the positive control, ribavirin (386.84 muM). Furthermore, its selectivity index was at least 2.5 times higher than the tested ethanolic extracts and 11.1 times more potent than ribavirin. CONCLUSION: The Tecoma species demonstrated interesting in vitro activity against the Zika virus. The Crenatoside, phenylethanoid glycoside that was for the first time isolated from Tecoma stans var. stans, exhibited a potent and relevant anti-Zika virus activity, being more active than ribavirin (positive control). The data show that Crenatoside, was a promising compound with in vitro antiviral activity against the Zika virus.
[Chemome profiling and comparison of three Orobanche medicinal plants].[Pubmed:32726027]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Jul;45(13):3175-3182.
Several Orobanche medicinal plants sometimes served as alternative sources of Cistanches Herba, attributing to the benefits such as tonifying kidney, strengthening tendons and bones. Among them, O. coerulescens, O. cernua and O. pycnostachya have been widely utilized in northern China for treatments of pains in the loins and knees, impotence, and spermatorrhea. However, their chemical profiles haven't been elucidated. In the present study, UHPLC-IT-TOF-MS was implemented to conduct in-depth chemome profiling of O. coerulescens, O. cernua and O. pycnostachya, aiming to achieve a comprehensive chemical characterization and to provide pronounced information for the quality control and clinical applications. An ACE Ultra-Core 2.5 Super C_(18)(3.0 mmx150 mm, 2.5 mum) column was deployed for chromatographic separations, and high-resolution MS~n spectra were recorded by IT-TOF-MS. Forty-eight components, in total, were observed, and thirty-eight ones were structurally annotated according to proposing mass fragmentation patterns, matching with relevant databases. Particularly, nine ones were confirmed by reference compounds. Overall, the chemical compositions of O. coerulescens and O. cernua are quite similar, and differences occur between O. pycnostachya and the prior two ones; primary chemical family is phenylethanoid glycosides, and several lignan glycosides as well as iridoid glycosides are also observed; the primary components include acteoside, isoacteoside, Crenatoside and 2'-acetylacteoside, etc.
Simultaneous Quantification of Four Phenylethanoid Glycosides in Rat Plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study of Acanthus Ilicifolius Herb.[Pubmed:31466218]
Molecules. 2019 Aug 28;24(17):3117.
Acanthus ilicifolius herb (AIH), the dry plant of Acanthus ilicifolius L., has long been used as a folk medicine for treating acute and chronic hepatitis. Phenylethanoid glycosides (PhGs) are one family of the main components in AIH with hepatoprotective, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities. In this study, the pharmacokinetics of AIH was investigated preliminarily by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). A simultaneously quantitative determination method for four PhGs (acteoside, isoacteoside, martynoside, and Crenatoside) in rat plasma was first established by UPLC-MS/MS. These four PhGs were separated with an ACQUITY UPLC BEH C(18) column (2.1 x 50 mm, 1.7 mum) by gradient elution (mobile phase: MeCN and 0.1% formic acid in water, 0.4 mL/min). The mass spectrometry detection was performed using negative electrospray ionization (ESI(-)) in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. By the established method, the preliminary pharmacokinetics of AIH was elucidated using the kinetic parameters of the four PhGs in rat plasma after intragastric administration of AIH ethanol extract. All four PhGs showed double peaks on concentration-time curves, approximately at 0.5 h and 6 h, respectively. Their elimination half-lives (t(1/2)) were different, ranging from 3.42 h to 8.99 h, although they shared similar molecular structures. This work may provide a basis for the elucidation of the pharmacokinetic characteristics of bioactive components from AIH.
Discovery of Potent Neuraminidase Inhibitors Using a Combination of Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening and Molecular Simulation Approach.[Pubmed:29063410]
Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018 Apr;184(4):1421-1440.
Neuraminidase (NA), a surface protein, facilitates the release of nascent virus and thus spreads infection. It has been renowned as a potential drug target for influenza A virus infection. The drugs such as oseltamivir, zanamivir, peramivir, and laninamivir are approved for the treatment of influenza infection. Additionally, investigational drugs namely MK2206, tamiphosphor, Crenatoside, and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) are also available for the treatment. However, recent outbreaks of highly pathogenic and drug-resistant influenza A strains highlighted the need to discover novel NA inhibitor. Keeping this in mind, in the current investigation, an effort was made to ascertain potent inhibitors using pharmacophore-based virtual screening and docking approach. A 3D pharmacophore model was generated based on the chemical features of approved and investigational NA inhibitors using PHASE module of Schrodinger suite. The model consists of two hydrogen bond acceptors (A), one hydrogen bond donor (D), and one positively charged group (P), AADP. Subsequently, molecules with same pharmacophoric features were screened from among the two million compounds available in the ZINC database using the generated pharmacophore hypothesis. Ligand filtration was also done to obtain an efficient collection of hit molecules by employing Lipinski "rule of five" using Qikprop module. Finally, the screened molecule was subjected to docking and molecular dynamic simulations to examine the inhibiting activity of the compounds. The results of our analysis suggest that "acebutolol hydrochloride" (156792) could be the promising candidates for the treatment of influenza A virus infection.
[Determination of phenylethanoid glycosides in Orobanche coerulescens].[Pubmed:27071260]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Nov;40(21):4218-22.
Orobanche caerulescens is an important medicinal resource in Orobanchaceae. The present study aims to establish methods for determination of acteoside, Crenatoside, and total phenylethanoid glycosides in O. caerulescens, and determine the content in 15 samples to evaluate the resource utilization of this medicinal plant. The content of acteoside and Crenatoside were quantitatively determined by HPLC, while total phenylpropanoid glycosides was estimated by UV-VIS spectrophotometry. According to the results, the content of acteoside was the highest in O. caerulescens, followed by Crenatoside. The contents of acteoside, Crenatoside, and total phenylethanoid glycosides were between 1.15% - 15.60%, 0.83% - 4.47%, and 6.78% - 27.43%, respectively, which had significant differences. The acquisition time has great influence on the content of main components of O. caerulescens. The content of phenylethanoid glycosides is higher in the samples which were collected at the flowering stage. The two determination methods were proved to be simple, accurate and reliable, and can be used to evaluate the quality and resource utilization of O. caerulescens.
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of crenatoside analogues as novel influenza neuraminidase inhibitors.[Pubmed:26774928]
Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Feb 15;109:199-205.
Natural products, especially derived from TCMH, have been found to exert antiviral effects against influenza virus. Crenatoside, a phenylethanoid glycoside from Pogostemon cablin Benth, which has been shown as a novel effective NA inhibitor previously, is considered as the leading compound for our further SARs studies. This work presented design, synthesis of novel Crenatoside analogues from readily available d-Glucose and l-rhamnose in a convergent manner. Furthermore, their biological activities and SARs were also investigated. Especially, compound 2 h showed impressive IC50 = 27.77 mug/mL against NAs, which is 3 folds more potent than the leading compound Crenatoside (IC50 = 89.81 mug/mL). These results would promise their therapeutic potential for influenza disease.
[Nonvolatile chemical constituents from Pogostemon cablin].[Pubmed:21246823]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Oct;35(20):2704-7.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the nonvolatile chemical constituents from the ethanol extract of the stems of Pogostemon cablin. METHOD: The constituents were isolated and purified by repeated column chromatography on silica gel and Sephadex LH-20. Their structures were identified by physicochemical properties and spectroscopic analysis. RESULT: Twelve compounds were isolated and identified as tilianin (1), diosmetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2), 3"-O-methylCrenatoside (3), uracil (4), soya-cerebroside I and II (5), agastachoside (6), apigenin-7-O-(3", 6"-di-(E) -p-coumaroyl) -beta-D-galactopyranoside (7), 5-hydroxy-3, 3', 4', 7- tetramethoxy flavone (8), 4', 5-dihydroxy-3, 3', 7-trimethoxyflavone (9), acacetin (10), Crenatoside (11), isoCrenatoside (12). CONCLUSION: Compounds 1, 2, 4-7, 10 were isolated from the genus Pogostemon for the first time.
[Chemical constituents from involatile moiety of Pogostemon cablin].[Pubmed:19459301]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2009 Feb;34(4):410-3.
OBJECTIVE: To study the chemical constituents of involatile moiety of Pogostemon cablin. METHOD: Compounds were isolated and purified by repeated column chromatography, and their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic analysis. RESULT: Nine compounds have been isolated and identified: epifriedelinol (1), 5-hydroxymethol-2-furfural (2), succinic acid (3), beta-sitosterol (4), daucosterol (5), Crenatoside (6), 3'''-O-methylCrenatoside (7), isoCrenatoside (8), and apigenin-7-O-beta-D-(6"-p-coumaryl)-glucoside (9). CONCLUSION: Compounds 2, 3, 6-8 were isolated from Pogostemon genus for the first time.
A new iridoid from Adenosma caeruleum R. Br.[Pubmed:19442709]
Fitoterapia. 2009 Sep;80(6):358-60.
A new iridoid glycoside, adenosmoside, together with five known phenylpropanoids, Crenatoside, verbascoside, cistanoside F, campneoside I, and campneoside II and two known flavonoids, apigenin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside and apigenin 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, were isolated from the aerial parts of Adenosma caeruleum R. Br. Their structures were elucidated by spectral evidence.
Convenient TLC-based Identification Test for the Crude Drug "Pogostemoni Herba".[Pubmed:19043303]
Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008 Dec;128(12):1833-7.
TLC and HPLC were used to identify possible chemical markers for evaluating the quality of the crude drug "Pogostemoni herba" (aerial part of Pogostemon cablin), which is a component of Kampo medicines. In addition to the reported patchouli alcohol and 2-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-(4-methylpentanoyl)-4-pyrone, three phenylethanoids were isolated from this plant material for the first time: acteoside, isoacteoside, and Crenatoside. The usefulness of these compounds as indicators of the crude commercial drug under various TLC conditions was examined, and patchouli alcohol was found to give a definite spot with a reproducible Rf value. Therefore, we propose TLC of the methanol (MeOH) extract using patchouli alcohol as a marker as a convenient method for identifying the crude drug Pogostemoni herba.


