CubebinCAS# 1242843-00-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

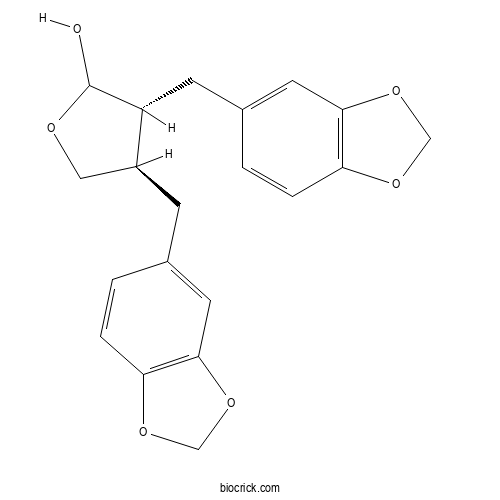
| Cas No. | 1242843-00-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 14137603 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C20H20O6 | M.Wt | 356.4 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3R,4R)-3,4-bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)oxolan-2-ol | ||
| SMILES | C1C(C(C(O1)O)CC2=CC3=C(C=C2)OCO3)CC4=CC5=C(C=C4)OCO5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DIYWRNLYKJKHAM-VKWYCSODSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H20O6/c21-20-15(6-13-2-4-17-19(8-13)26-11-24-17)14(9-22-20)5-12-1-3-16-18(7-12)25-10-23-16/h1-4,7-8,14-15,20-21H,5-6,9-11H2/t14-,15+,20?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Cubebin showes anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities. It also shows neuroprotective effects, this could be attributed to its brain AChE inhibition and antioxidant activity. | |||||

Cubebin Dilution Calculator

Cubebin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8058 mL | 14.0292 mL | 28.0584 mL | 56.1167 mL | 70.1459 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5612 mL | 2.8058 mL | 5.6117 mL | 11.2233 mL | 14.0292 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2806 mL | 1.4029 mL | 2.8058 mL | 5.6117 mL | 7.0146 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0561 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.5612 mL | 1.1223 mL | 1.4029 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1403 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.5612 mL | 0.7015 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2,3-Dehydrosilybin B
Catalog No.:BCN9964
CAS No.:142796-24-5
- 4'-Methylchrysoeriol
Catalog No.:BCN9963
CAS No.:4712-12-3
- Aegineoside
Catalog No.:BCN9962
CAS No.:752209-48-6
- Oleocanthal
Catalog No.:BCN9961
CAS No.:289030-99-5
- 2',6'-Dihydroxy 4'-methoxydihydrochalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9960
CAS No.:35241-55-5
- Withanone
Catalog No.:BCN9959
CAS No.:27570-38-3
- Citronellyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9958
CAS No.:150-84-5
- p-Mentha-1,4-diene
Catalog No.:BCN9957
CAS No.:99-85-4
- Isogentisin
Catalog No.:BCN9956
CAS No.:491-64-5
- 4-Methylcatechol
Catalog No.:BCN9955
CAS No.:452-86-8
- Artepillin C
Catalog No.:BCN9954
CAS No.:72944-19-5
- Lapatinib (GW-572016) Ditosylate
Catalog No.:BCN9953
CAS No.:388082-77-7
- Oxyacanthine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN9966
CAS No.:6183-91-1
- Genistein 7-O-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN9967
CAS No.:38482-81-4
- 4-Ethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9968
CAS No.:35817-27-7
- Psoromic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9969
CAS No.:7299-11-8
- Butyric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9970
CAS No.:107-92-6
- Vescalagin
Catalog No.:BCN9971
CAS No.:36001-47-5
- Terpinyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9972
CAS No.:80-26-2
- Peltatoside
Catalog No.:BCN9973
CAS No.:23284-18-6
- Platycogenin A
Catalog No.:BCN9974
CAS No.:1459719-53-9
- 9-Methyl-9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN9975
CAS No.:552-70-5
- AT101
Catalog No.:BCN9976
CAS No.:866541-93-7
- omega-Benzoyl oxyphloracetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN9977
CAS No.:65982-77-6
Assessment of the In Vitro Antischistosomal Activities of the Extracts and Compounds from Solidago Microglossa DC (Asteraceae) and Aristolochia Cymbifera Mart. & Zucc. (Aristolochiaceae).[Pubmed:33062001]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Sep 29;2020:1726365.
Schistosomiasis, caused by helminth flatworms of the genus Schistosoma, is a neglected tropical disease that afflicts over 230 million people worldwide. Currently, treatment is achieved with only one drug, praziquantel (PZQ). In this regard, the roots of Solidago microglossa (Asteraceae) and Aristolochia cymbifera (Aristolochiaceae) are popularly used as anthelmintic. Despite their medicinal use against helminthiasis, such as schistosomiasis, A. cymbifera, and S. microglossa have not been evaluated against S. mansoni. Then, in this work, the in vitro antischistosomal activity of the crude extracts of A. cymbifera (Ac) and S. microglossa (Sm) and their isolated compounds were investigated against S. mansoni adult worms. Sm (200 mug/mL) and Ac (100-200 mug/mL) were lethal to all male and female worms at the 24 h incubation. In addition, Sm (10-50 mug/mL) and Ac (10 mug/mL) caused significant reduction in the parasite's movements, showing no significant cytotoxicity to Vero cells at the same range of schistosomicidal concentrations. Confocal laser scanning microscopy revealed that Sm and Ac caused tegumental damages and reduced the numbers of tubercles of male schistosomes. Chromatographic fractionation of Sm leads to isolation of bauerenol, alpha-amirin, and spinasterol, while populifolic acid, Cubebin, 2-oxopopulifolic acid methyl ester, and 2-oxopopulifolic acid were isolated from Ac. At concentrations of 25-100 muM, bauerenol, alpha-amirin, spinasterol, populifolic acid, and Cubebin showed significant impact on motor activity of S. mansoni. 2-oxopopulifolic acid methyl ester and 2-oxopopulifolic acid caused 100% mortality and decreased the motor activity of adult schistosomes at 100 muM. This study has reported, for the first time, the in vitro antischistosomal effects of S. microglossa and A. cymbifera extracts, also showing promising compounds against adult schistosomes.
Prospecting and Identifying Phyllanthus amarus Lignans with Antileishmanial and Antitrypanosomal Activity.[Pubmed:32512613]
Planta Med. 2020 Jul;86(11):782-789.
Ten lignans (1: - 10: ) were isolated from the hexane-ethyl acetate extract of Phyllanthus amarus leaves. Three of them, Cubebin dimethyl ether (3: ), urinatetralin (4: ), and lintetralin (7: ) are described for the first time in this species, while phyllanthin (1: ), niranthin (2: ), 5-demethoxyniranthin (5: ), isolintetralin (6: ), hypophyllanthin (8: ), nirtetralin (9: ), and phyltetralin (10: ) have been already reported from P. amarus. Among the lignans tested against Trypanosoma cruzi intracellular amastigotes, 2: was the most active with an EC50 of 35.28 microM. Lignans 2, 5, 7: , and 9: showed inhibitory effects against Leishmania amazonensis promastigotes with EC50 of 56.34, 51.86, 23.57, and 43.27 microM, respectively. During in vitro infection assays, 5: reduced amastigotes by 91% at 103.68 microM concentration, whereas 7: and 9: reduced amastigotes by approximately 84% at 47.5 and 86.04 microM, respectively. Lignans 5, 7: , and 9: were more potent in intracellular amastigotes with EC50 of 2.76, 8.30, and 15.83 microM, respectively, than in promastigotes. CC50 for all samples was > 100 microg/mL, thus revealing low cytotoxicity against macrophages, and selectivity against the parasite. L. amazonensis promastigotes treated with compounds 2: and 9: showed decreased respiratory control of 38% and 25%, respectively, suggesting a change in mitochondrial membrane potential and lower ATP production.
(-)-O-Methylcubebin from Vitex trifolia Enhanced Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells via the Inhibition of ERK1/2 and p38MAPK Phosphorylation.[Pubmed:31878261]
Molecules. 2019 Dec 24;25(1). pii: molecules25010073.
In this study, for the purpose of elucidation for antidiabetic components, we isolated and identified compounds that could become lead compounds for the development of antidiabetic agents from the herbal medicine Vitex trifolia, which is used for liver protection in Myanmar. Three kinds of lignan, (-)-O-methylCubebin (MC), (-)-hinokinin, and (-)-Cubebin, were isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of the leaves of V. trifolia, using various chromatography. Among the three isolated compounds, MC showed the strongest effects to increase intracellular lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells. From the results of the elucidation of the MC's effects on the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells, the downsizing of adipocytes and the promotion of the expression of adipogenesis-related proteins, as well as adiponectin, were observed. On the other hand, since the activity of MC was inhibited by antagonists of PPARgamma and improved by inhibitors of the classical mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and p38MAPK pathway, MC was considered to be an agonist of PPARgamma, and furthermore promoted adipogenesis via the inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38MAPK phosphorylation. Although MC showed similar effects to those of rosiglitazone (RO) used as a positive control, RO promoted the migration of GLUT4 from the cytoplasm to the cell membrane, whereas MC did not show such an effect. From the abovementioned results, it was considered that MC could be a lead compound for the development of antidiabetic drugs that does not show weight gain, which is a side effect of RO.
In vitro anthelmintic activity of the crude hydroalcoholic extract of Piper cubeba fruits and isolated natural products against gastrointestinal nematodes in sheep.[Pubmed:31600614]
Vet Parasitol. 2019 Nov;275:108932.
This study describes the in vitro anthelmintic activity of a hydroalcoholic extract from the fruit of Piper cubeba and its major isolated components against the eggs and larvae of gastrointestinal nematodes obtained from naturally-infected ovines. In vitro anthelmintic activity was evaluated using the egg hatch test (EHT), larval development test (LDT) and L3 migration inhibition test (LMT). The extract showed ovicidal and larvicidal activity, with an EC50 of 200mug/mL and 83.00mug/mL in the EHT and LDT, respectively. The extract inhibited 100% of larval migration at the lowest tested concentration (95mug/mL). The crude extract was purified using successive silica gel chromatographic columns, which revealed the lignans hinokinin, Cubebin and dihydroCubebin as the major compounds that were present, which were then used in in vitro tests. Cubebin, dihydroCubebin and hinokinin showed higher activity than the crude extract, with an EC50 for ovicidal activity of 150.00mug/mL, 186.70mug/mL and 68.38mug/mL, respectively. In the LDT, Cubebin presented an EC50 of 14.89mug/mL and dihydroCubebin of 30.75mug/mL. Hinokinin inhibited 100% the larval development at all concentrations evaluated. In the LMT, dihydroCubebin inhibited 100% the larval migration in all concentrations evaluated while Cubebin and hinokinin showed EC50 values of 0.89mug/mL and 0.34mug/mL, respectively. P. cubeba extract is rich in several classes of active compounds, but here we demonstrate that the described anthelmintic activity may be related to the presence of these lignans, which are present in larger concentrations than other components of the extract. Our results demonstrate for first time the anthelmintic activity against gastrointestinal nematodes in sheep for this class of special metabolites that are present in P. cubeba fruit. However, future detailed studies are needed to evaluate the effectiveness of P. cubeba fruits extract and active lignans in in vivo tests.
Chemical Constituents and Pharmacology properties of Aristolochia triangularis: a south brazilian highly-consumed botanical with multiple bioactivities.[Pubmed:31411258]
An Acad Bras Cienc. 2019 Aug 12;91(3):e20180621.
Aristolochia triangularis Cham., is one of the most frequently used medicinal plant in Southern Brazil. Preparations containing the leaves and/or stems are traditionally used as anti-inflammatory, diuretic, as well as antidote against snakebites. This study screened A. triangularis extracts, fractions and isolated compounds for different bioactivities. A weak antiproliferative activity against human lung cancer cell line (A549) was observed only for chloroform fraction obtained from stems (CFstems - CC50: 2.93 microg/mL). Also, a moderate antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus was detected just for chloroform fraction obtained from leaves (CFleaves -13-16 mm inhibition zone). Additionally, two semi-purified fractions (CFstems-4 and CFleaves-4) selectively inhibited HSV-1 replication (IC50 values of 0.40 and 2.61 microg/mL, respectively), while only CFleaves showed promising results against Leishmania amazonensis. Fractionation of extracts resulted in the isolation of one neolignan (-) Cubebin and one lignan (+) galbacin. However, these compounds are not responsible for the in vitro bioactivities herein detected. The presence of aristolochic acid I and aristolochic acid II in the crude ethanol extract of stems (CEEstems) and leaves (CEEleaves) was also investigated. The HPLC analysis of these extracts did not display any peak with retention time or UV spectra comparable to aristolochic acids I and II.
Antitrypanosomal activity and effect in plasma membrane permeability of (-)-bornyl p-coumarate isolated from Piper cernuum (Piperaceae).[Pubmed:31129501]
Bioorg Chem. 2019 Aug;89:103001.
This work describes the isolation of six metabolites from leaves and branches of Piper cernuum (Piperaceae): (-)-Cubebin (1), (-)-hinokinin (2), (-)-kusunokinin (3), trans-dehydroagarofuran (4), 11-hydroxi-4,5-secoeudesmane-4,5-dione (5), and (-)-bornyl p-coumarate (6). Antitrypanosomal activity and toxicity of purified compounds were performed in vitro against trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi and NCTC cells, respectively. Compounds 2, 3 and 5 showed moderate activities with IC50 values of 33.1, 31.8 and 45.9muM, respectively, while compounds 1 and 4 were inactive (IC50>100muM). On the other hand, compound 6 displayed an IC50 value of 2.1muM, a selectivity index (SI) of 18 and induced a considerable interference in the plasma membrane permeability (87%) in trypomastigotes of T. cruzi. Additionally, the lethal effect of compound 6 in T. cruzi could be associated to the plasma membrane permeability. Finally, experiments using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) confirmed the obtained results in which was possible to observe total alteration parasites topography after treatment with compound 6 in comparison to untreated parasites. These data indicated that the lethal action of compound 6 is directly related to structural disruption of the membrane.
Development of a Validated High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method and Optimization of the Extraction of Lignans from Piper cubeba.[Pubmed:30583698]
J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Jan 16;67(2):753-759.
Piper cubeba L. f. is a food seasoning, which contains secondary metabolites displaying several biological properties, such as cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, and antiparasitic activities. The lignans (+)-dihydroclusin, (-)-clusin, (-)-Cubebin, (-)-yatein, and (-)-haplomyrfolin were isolated, with (-)-haplomyrfolin reported for the first time in P. cubeba seeds. Chromatographic standards were used to develop a reliable reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography analytical method according to the Agencia Nacional de Vigilancia Sanitaria and International Conference on Harmonization guidelines to quantitate these lignans in both P. cubeba seeds and their extracts. The extraction of the lignans was also optimized, with the best conditions being ultrasound-assisted extraction, with 84% aqueous ethanol for 38 min in a single extraction. This procedure allows for the extraction of more than 80% of the total lignans, which is better in comparison to other techniques, such as maceration and Soxhlet extraction.
Evaluation of Lignans from Piper cubeba against Schistosoma mansoni Adult Worms: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study.[Pubmed:30335227]
Chem Biodivers. 2019 Jan;16(1):e1800305.
Six dibenzylbutyrolactonic lignans ((-)-hinokinin (1), (-)-Cubebin (2), (-)-yatein (3), (-)-5-methoxyyatein (4), dihydroCubebin (5) and dihydroclusin (6)) were isolated from Piper cubeba seed extract and evaluated against Schistosoma mansoni. All lignans, except 5, were able to separate the adult worm pairs and reduce the egg numbers during 24 h of incubation. Lignans 1, 3 and 4 (containing a lactone ring) were the most efficient concerning antiparasitary activity. Comparing structures 3 and 4, the presence of the methoxy group at position 5 appears to be important for this activity. Considering 1 and 3, it is possible to see that the substitution pattern change (methylenedioxy or methoxy groups) in positions 3' and 4' alter the biological response, with 1 being the second most active compound. Computational calculations suggest that the activity of compound 4 can be correlated with the largest lipophilicity value.
Solvent Extraction and Identification of Active Anticariogenic Metabolites in Piper cubeba L. through (1)H-NMR-Based Metabolomics Approach.[Pubmed:30012946]
Molecules. 2018 Jul 16;23(7). pii: molecules23071730.
The aim of this study was to determine the effects of different solvents for extraction, liquid(-)liquid partition, and concentrations of extracts and fractions of Piper cubeba L. on anticariogenic; antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity against oral bacteria. Furthermore, (1)H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) coupled with multivariate data analysis (MVDA) was applied to discriminate between the extracts and fractions and examine the metabolites that correlate to the bioactivities. All tested bacteria were susceptible to Piper cubeba L. extracts and fractions. Different solvents extraction, liquid(-)liquid partition and concentrations of extracts and fractions have partially influenced the antibacterial activity. MTT assay showed that P. cubeba L. extracts and fractions were not toxic to RAW 264.7 cells at selected concentrations. Anti-inflammatory activity evaluated by nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulated cells showed a reduction in NO production in cells treated with P. cubeba L. extracts and fractions, compared to those without treatment. Twelve putative metabolites have been identified, which are (1) Cubebin, (2) yatein, (3) hinokinin, (4) dihydroCubebin, (5) dihydroclusin, (6) Cubebinin, (7) magnosalin, (8) p-cymene, (9) piperidine, (10) cubebol, (11) d-germacrene and (12) ledol. Different extraction and liquid(-)liquid partition solvents caused separation in principal component analysis (PCA) models. The partial least squares (PLS) models showed that higher anticariogenic activity was related more to the polar solvents, despite some of the active metabolites also present in the non-polar solvents. Hence, P. cubeba L. extracts and fractions exhibited antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity and have potential to be developed as the anticariogenic agent.
Medicinal Attributes of Lignans Extracted from Piper Cubeba: Current Developments.[Pubmed:29435403]
ChemistryOpen. 2018 Feb 2;7(2):180-191.
Lignans are a large class of natural products that have been isolated from many plants. They reveal diverse biological activities, especially antiviral and antitumor properties. From Piper cubeba, lignans of several classes can be isolated from the roots, rhizomes, stems, leaves, seeds, and fruits. Among its various chemical constituents, (-)-Cubebin and (-)-hinokinin are found in significant quantities. Although they have been known for some time, during the last few decades their biological properties have been studied by several research groups. The Cubebins have been identified as a lactol monomer and dimers as a mixture of diastereoisomers. Recently, their structural characterization and the synthesis of the possible structures have led to the correction of some earlier structural proposals. This review describes the more recent developments in the study of the medicinal attributes of Cubebin and hinokinin extracted from Piper cubeba and the synthesis and biological testing of some analogues.
Neuroprotective effect of Cubebin: A dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan on scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice.[Pubmed:29265027]
Indian J Med Res. 2017 Aug;146(2):255-259.
BACKGROUND & OBJECTIVES: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors represent a major class of drugs which provide symptomatic relief and improvement in cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, Cubebin, a dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, was isolated from Piper cubeba and investigated for its AChE inhibitory activity in an attempt to explore its potential for memory-enhancing activities in mice. METHODS: Molecular docking of Cubebin was carried out followed by in vitro AChE activity. Mice were treated with Cubebin (25 & 50 mg/kg; i.p.), for three days and memory impairment was induced by scopolamine (3 mg/kg; i.p.). Memory function was evaluated by Morris water maze (MWM) test. Biochemical parameters of oxidative stress and cholinergic function were estimated in brain. RESULTS: Molecular docking study revealed that Cubebin was well bound within the binding site of the AChE enzyme showing interactions such as pi-pi stacking and hydrogen bonding with residues present therein. Cubebin inhibited AChE enzyme in an in vitro assay with IC50value of 992 muM. Scopolamine administration caused a significant impairment of learning and memory in mice, as indicated by a marked decrease in MWM performance. Scopolamine administration also produced a significant enhancement of brain AChE activity and oxidative stress in mice brain. Pre-treatment of Cubebin (25 and 50 mg/kg; i.p.) significantly prevented scopolamine-induced learning and memory deficits along with attenuation of scopolamine-induced rise in brain AChE activity and oxidative stress level. INTERPRETATION & CONCLUSIONS: Cubebin showed promising protective activity in scopolamine-induced spatial memory impairment in mice. This could be attributed to its brain AChE inhibition and antioxidant activity.
Biotransformation of (-)-cubebin by Aspergillus spp. into (-)-hinokinin and (-)-parabenzlactone, and their evaluation against oral pathogenic bacteria.[Pubmed:28982254]
Nat Prod Res. 2018 Dec;32(23):2803-2816.
The biotransformation of the lignan (-)-Cubebin by filamentous fungi Aspergillus terreus and Aspergillus niger is an efficient bioprocess for obtaining (-)-hinokinin and (-)-parabenzlactone. The relevance of getting (-)-hinokinin is due to its promising effect against oral pathogens, especially S. sanguinis (both MIC and MBC 12.5 mug/mL), and other previous reported effects against Chagas disease and as anti-inflammatory. The advantage of using fungal transformation is the use of non-toxic and/or non-pollutant reagents and/or solvents in comparison with semi-synthesis. Microbial transformation of (-)-Cubebin is also important to evaluate its human metabolism, since Aspergillus species are capable of mimicking P450 reactions, providing possible products of the metabolism, which is important in the assessment of its efficacy and safety. Furthermore, the present study describes a reliable RP-HPLC method to perform quantification of (-)-hinokinin in fungal extracts. It is simple, fast, selective, linear, precise, accurate and robust according to validation guidelines.
Total Synthesis of (-)-Bicubebin A, B, (+)-Bicubebin C and Structural Reassignment of (-)-cis-Cubebin.[Pubmed:28901148]
Org Lett. 2017 Oct 6;19(19):5368-5371.
The first total synthesis of (-)-biCubebin A, and two previously unreported dilignans, (-)-biCubebin B and (+)-biCubebin C has been achieved through the dimerization of (-)-Cubebin, confirming the structure and absolute stereochemistry of (-)-biCubebin A. Analysis of the data for (-)-biCubebin B showed it matched that of reported compound (-)-cis-Cubebin. The NMR data of the subsequently synthesized proposed structure of cis-Cubebin confirmed that its original proposed structure was incorrect.
In vivo and in silico anti-inflammatory mechanism of action of the semisynthetic (-)-cubebin derivatives (-)-hinokinin and (-)-O-benzylcubebin.[Pubmed:27955811]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Jan 15;27(2):176-179.
(-)-Cubebin (CUB), isolated from seeds of Piper cubeba, was used as starting material to obtain the derivatives (-)-hinokinin (HK) and (-)-O-benzyl Cubebin (OBZ). Using paw edema as the experimental model and different chemical mediators (prostaglandin and dextran), it was observed that both derivatives were active in comparison with both negative (5% Tween(R) 80 in saline) and positive (indomethacin) controls. The highest reduction in the prostaglandin-induced edema was achieved by OBZ (66.0%), while HK caused a 59.2% reduction. Nonetheless, the dextran-induced paw edema was not significantly reduced by either of the derivatives (HK or OBZ), which inhibited edema formation by 18.3% and 3.5%, respectively, in contrast with the positive control, cyproheptadine, which reduced the edema by 56.0%. The docking analysis showed that OBZ presented the most stable ligand-receptor (COX-2 - cyclooxygenase-2) interaction in comparison with CUB and HK.
(-)-Hinokinin Induces G2/M Arrest and Contributes to the Antiproliferative Effects of Doxorubicin in Breast Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:27002393]
Planta Med. 2016 Apr;82(6):530-8.
Breast cancer incidence rises worldwide and new chemotherapeutical strategies have been investigated to overcome chemoresistance. (-)-Hinokinin is a dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan derived from the partial synthesis of (-)-Cubebin extracted from Piper cubeba seeds. Biological effects of dibenzylbutyrolactone lignans include antiviral, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and trypanocidal activities. In the present study, we evaluated the ability of (-)-hinokinin to modulate the antiproliferative effects of doxorubicin intumoral (MCF-7 and SKBR-3) and normal (MCF-10 A) breast cell lines. Treatment with (-)-hinokinin did not affect the cellular proliferation or contribute to the antitproliferative effects of doxorubicin in MCF-10 A cells. After 24 and 48 hours of treatment with (-)-hinokinin, MCF-7 and SKBR-3 were accumulated in G2/M and, when combined with doxorubicin, (-)-hinokinin contributed to the antiproliferative effects of this chemotherapic by modulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1. Apoptotic cell death was observed in response to (-)-hinokinin alone in MCF-7, but not in SKBR-3 even 72 hours after treatment. In MCF-7, doxorubicin-induced apoptosis was not increased by (-)-hinokinin. The findings of the present study suggest (-)-hinokinin as an antiproliferative agent that contributes to the effects of doxorubicin. (-)-Hinokinin modulates apoptotic cell death via the molecular regulation of the cell cycle and apoptotic control genes, but the cellular genetic background directly affects the cell fate decision in response to treatment.


