WithanoneCAS# 27570-38-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 27570-38-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 21679027 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C28H38O6 | M.Wt | 470.6 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform; sparingly soluble in ethyl acetate and methanol; insoluble in water | ||
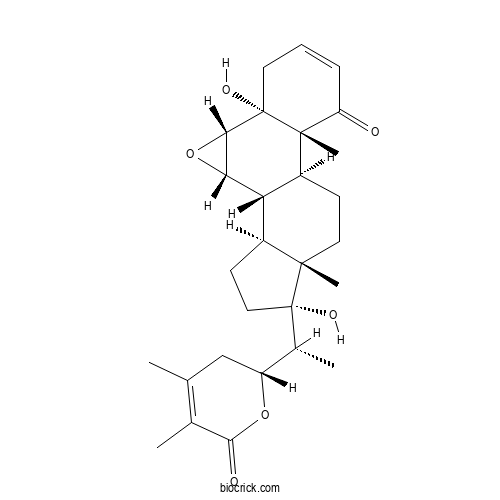
| Chemical Name | (1S,2S,4S,5R,10R,11S,14S,15S,18S)-15-[(1R)-1-[(2R)-4,5-dimethyl-6-oxo-2,3-dihydropyran-2-yl]ethyl]-5,15-dihydroxy-10,14-dimethyl-3-oxapentacyclo[9.7.0.02,4.05,10.014,18]octadec-7-en-9-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=O)OC(C1)C(C)C2(CCC3C2(CCC4C3C5C(O5)C6(C4(C(=O)C=CC6)C)O)C)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FAZIYUIDUNHZRG-PCTWTJKKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H38O6/c1-14-13-19(33-24(30)15(14)2)16(3)27(31)12-9-17-21-18(8-11-25(17,27)4)26(5)20(29)7-6-10-28(26,32)23-22(21)34-23/h6-7,16-19,21-23,31-32H,8-13H2,1-5H3/t16-,17+,18+,19-,21+,22+,23+,25+,26+,27+,28+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Withanone can affords protection against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in neuron-like cells, it may serve as potential neuroprotective agent, it shows promise in Alzheimer's disease treatment because of cognitive benefits. Withanone as a potential candidate molecule in cancer therapy. | |||||

Withanone Dilution Calculator

Withanone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1249 mL | 10.6247 mL | 21.2495 mL | 42.4989 mL | 53.1237 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.425 mL | 2.1249 mL | 4.2499 mL | 8.4998 mL | 10.6247 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2125 mL | 1.0625 mL | 2.1249 mL | 4.2499 mL | 5.3124 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0425 mL | 0.2125 mL | 0.425 mL | 0.85 mL | 1.0625 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0212 mL | 0.1062 mL | 0.2125 mL | 0.425 mL | 0.5312 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Citronellyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9958
CAS No.:150-84-5
- p-Mentha-1,4-diene
Catalog No.:BCN9957
CAS No.:99-85-4
- Isogentisin
Catalog No.:BCN9956
CAS No.:491-64-5
- 4-Methylcatechol
Catalog No.:BCN9955
CAS No.:452-86-8
- Artepillin C
Catalog No.:BCN9954
CAS No.:72944-19-5
- Lapatinib (GW-572016) Ditosylate
Catalog No.:BCN9953
CAS No.:388082-77-7
- 2',5,6',7-Tetrahydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9952
CAS No.:82475-00-1
- 4',5,7-Trihydroxy 3,3',6,8-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9951
CAS No.:58130-91-9
- Manassantin B
Catalog No.:BCN9950
CAS No.:88497-88-5
- Petroselinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9949
CAS No.:593-39-5
- 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9948
CAS No.:89-86-1
- Pipermethystine
Catalog No.:BCN9947
CAS No.:71627-22-0
- 2',6'-Dihydroxy 4'-methoxydihydrochalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9960
CAS No.:35241-55-5
- Oleocanthal
Catalog No.:BCN9961
CAS No.:289030-99-5
- Aegineoside
Catalog No.:BCN9962
CAS No.:752209-48-6
- 4'-Methylchrysoeriol
Catalog No.:BCN9963
CAS No.:4712-12-3
- 2,3-Dehydrosilybin B
Catalog No.:BCN9964
CAS No.:142796-24-5
- Cubebin
Catalog No.:BCN9965
CAS No.:1242843-00-0
- Oxyacanthine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN9966
CAS No.:6183-91-1
- Genistein 7-O-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN9967
CAS No.:38482-81-4
- 4-Ethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9968
CAS No.:35817-27-7
- Psoromic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9969
CAS No.:7299-11-8
- Butyric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9970
CAS No.:107-92-6
- Vescalagin
Catalog No.:BCN9971
CAS No.:36001-47-5
Investigating 11 Withanosides and Withanolides by UHPLC-PDA and Mass Fragmentation Studies from Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera).[Pubmed:33163776]
ACS Omega. 2020 Oct 21;5(43):27933-27943.
Withania somnifera (WS), also known as ashwagandha or Indian ginseng, is known for its pharmacological significance in neurodegenerative diseases, stress, cancer, immunomodulatory, and antiviral activity. In this study, the WS extract (WSE) from the root was subjected to ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection (UHPLC-PDA) analysis to separate 11 withanoside and withanolide compounds. The quantification validation was carried out as per ICHQ2R1 guidelines in a single methodology. The calibration curves were linear (r (2) > 0.99) for all 11 compounds within the tested concentration ranges. The limits of detection and quantification were in the range of 0.213-0.362 and 0.646-1.098 mug/mL, respectively. The results were precise (relative standard deviation, <5.0%) and accurate (relative error, 0.01-0.76). All compounds showed good recoveries of 84.77-100.11%. For the first time, withanoside VII, 27-hydroxyWithanone, dihydrowithaferin A, and viscosalactone B were quantified and validated along with bioactive compounds withanoside IV, withanoside V, withaferin A, 12-deoxywithastramonolide, withanolide A, Withanone, and withanolide B simultaneously in WS. This UHPLC-PDA method has practical adaptability for ashwagandha raw material, extract, and product manufacturers, along with basic and applied science researchers. The method has been developed on UHPLC for routine analysis. The 11 withanosides and withanolides were confirmed using the fragmentation pattern obtained by the combined use of electrospray ionization and collision-induced dissociation in triple-quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (TQ-MS/MS) in the WSE.
Application of Humanized Zebrafish Model in the Suppression of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induced Pathology by Tri-Herbal Medicine Coronil via Cytokine Modulation.[Pubmed:33147850]
Molecules. 2020 Nov 2;25(21). pii: molecules25215091.
Zebrafish has been a reliable model system for studying human viral pathologies. SARS-CoV-2 viral infection has become a global chaos, affecting millions of people. There is an urgent need to contain the pandemic and develop reliable therapies. We report the use of a humanized zebrafish model, xeno-transplanted with human lung epithelial cells, A549, for studying the protective effects of a tri-herbal medicine Coronil. At human relevant doses of 12 and 58 microg/kg, Coronil inhibited SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, induced humanized zebrafish mortality, and rescued from behavioral fever. Morphological and cellular abnormalities along with granulocyte and macrophage accumulation in the swim bladder were restored to normal. Skin hemorrhage, renal cell degeneration, and necrosis were also significantly attenuated by Coronil treatment. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) analysis identified ursolic acid, betulinic acid, Withanone, withaferine A, withanoside IV-V, cordifolioside A, magnoflorine, rosmarinic acid, and palmatine as phyto-metabolites present in Coronil. In A549 cells, Coronil attenuated the IL-1beta induced IL-6 and TNF-alpha cytokine secretions, and decreased TNF-alpha induced NF-kappaB/AP-1 transcriptional activity. Taken together, we show the disease modifying immunomodulatory properties of Coronil, at human equivalent doses, in rescuing the pathological features induced by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, suggesting its potential use in SARS-CoV-2 infectivity.
Effects of moderate high temperature and UV-B on accumulation of withanolides and relative expression of the squalene synthase gene in Physalis peruviana.[Pubmed:33110367]
Turk J Biol. 2020 Oct 13;44(5):295-303.
Physalis peruviana L. (Cape gooseberry) is a source for a variety of phytocompounds such as withanolides, Withanone, withaferin A, and withanolide A. These withanolides are high-value drug candidates due to their various pharmacological properties. To meet the increasing demands for these compounds, plant cell technology offers a reliable alternative. Exogenous addition of elicitors is considered the most effective strategy for enhanced production of secondary metabolites. In this study, we investigated changes in withanolide accumulation and characterized the gene expression level changes of squalene synthase enzyme in P. peruviana shoot cultures exposed to mild nonlethal heat stress (45 degrees C for 2 and 5 h) and UV-B radiation (313 nm for 15 min and 3 h). We demonstrated significant changes in withanolide content with 7.86- and 12.5-fold increases for 2- and 5-hmild high-temperature exposure times, respectively. Exposure to UV-B also changed the withanolide content by 7.22- and 7-fold increases for 15 min and 3 h exposure times, respectively. The relative expression level of squalene synthase gene showed consistent results with1.80- and 10.13-fold increases in withanolide for 2- and 5-h mild high-temperature exposure times, and 1.34- and 2.01-fold increases with 15 min and 3 h UV-B exposure times, respectively.
A Comprehensive Review and Perspective on Anticancer Mechanisms of Withaferin A in Breast Cancer.[Pubmed:32727824]
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2020 Sep;13(9):721-734.
Withaferin A (hereafter abbreviated as WA) is a promising anticancer steroidal lactone abundant in a medicinal plant (Withania somnifera) native to Asia. The root/leaf extract of Withania somnifera, which belongs to the Solanaceae family, continues to be included in the Ayurvedic medicine formulations of alternative medicine practice. Numerous chemicals are detectable in the root/leaf extract of Withania somnifera [e.g., withanolides (WA, Withanone, withanolide A, etc.), alkaloids, sitoindosides, etc.], but the anticancer effect of this medicinal plant is largely attributed to WA. Anticancer effect of WA was initially reported in the early 70s in the Ehrlich ascites tumor cell model in vitro Since then, numerous preclinical studies have been performed using cellular and animal models of different cancers including breast cancer to determine cancer therapeutic and chemopreventive effects of WA. Chemoprevention, a word first introduced by Dr. Michael B. Sporn, was intended to impede, arrest, or reverse carcinogenesis at its earliest stages with pharmacologic agents. This review succinctly summarizes the published findings on anticancer pharmacology of WA in breast cancer focusing on pharmacokinetic behavior, in vivo efficacy data in preclinical models in a therapeutic and chemoprevention settings, and its known effects on cancer-relevant cellular processes (e.g., growth arrest, apoptosis induction, autophagy, metabolic adaptation, immune function, etc.) and molecular targets (e.g., suppression of oncogenes such as estrogen receptor-alpha, STAT3, etc.). Potential gaps in knowledge as well as future research directions essential for clinical development of WA for chemoprevention and/or treatment of breast cancer are also discussed.
Synthesis, in-vitro and in-silico evaluation of Silver Nanoparticles with Root Extract of Withania somnifera for antibacterial activity via binding of penicillin binding protein-4.[Pubmed:32614743]
Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 2. pii: CPB-EPUB-107862.
BACKGROUND: Metal nanoparticles (NPs) have been widely used for various applications in biomedical sciences including in drug delivery, and as therapeutic agents, but limited owing to their toxicity towards the healthy tissue. This warrants an alternative method, which can achieve the desired activity with much reduced or no toxicity. Being a biological product, Withania somnifera (W. somnifera) is an environment friendly, besides being less toxic as compared to metal-based NPs. However, the exact mechanism of action of W. somnifera for its antibacterial activities have not been studied so far. OBJECTIVE: To develop "silver nanoparticles with root extract of W. somnifera (AgNPs-REWS)" for antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Further, the analysis of their mechanism of action will be studied. METHOD: Using in-silico approach, the molecular docking study has been performed to evaluate the possible antibacterial mechanism of W. somnifera phytochemicals such as Anaferine, Somniferine, Stigmasterol, Withaferin A, Withanolide- A, G, M, and Withanone by inhibition of penicillin binding protein 4 (PBP4). Next, we utilized bottom-up approach for the green synthesis of AgNPs-REWS, performed an indetail phytochemical analysis, confirmed the AgNPs-REWS by SEM, UV-visible spectroscopy, XRD, FT-IR, and HPLC. Eventually, we examined their antibacterial activity. RESULTS: The result of molecular docking, suggest that WS phytochemical (Somniferine, Withaferin A, Withanolide A, Withanolide G, Withanolide M, and Withanone) possess the higher binding affinity toward the active site of PBP4 as compare to Ampicillin (-6.39 kcal/mol) reference molecule. These phytochemicals predicted as potent inhibitor of PBP4. Next, as a proof-of -concept, AgNPs-REWS showed significant antibacterial effect as compared to crude, and control; against Xanthomonas and Ralstonia species. CONCLUSION: The in-silico and molecular docking analysis showed that active constituents of W. somnifera such as Somniferine, Withaferin A, Withanolide A, Withanolide G, Withanolide M, and Withanone possesses inhibition potential for PBP4 and responsible for the antibacterial property of W. somnifera extract. This study also establishes that AgNPs via the green synthesis with REWS showed enhanced antibacterial activity towards pathogenic bacteria.
Withanone and Withaferin-A are predicted to interact with transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) and block entry of SARS-CoV-2 into cells.[Pubmed:32469279]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Jun 16:1-13.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) initiated in December 2019 in Wuhan, China and became pandemic causing high fatality and disrupted normal life calling world almost to a halt. Causative agent is a novel coronavirus called Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCoV). While new line of drug/vaccine development has been initiated world-wide, in the current scenario of high infected numbers, severity of the disease and high morbidity, repurposing of the existing drugs is heavily explored. Here, we used a homology-based structural model of transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2), a cell surface receptor, required for entry of virus to the target host cell. Using the strengths of molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations, we examined the binding potential of Withaferin-A (Wi-A), Withanone (Wi-N) and caffeic acid phenethyl ester to TPMRSS2 in comparison to its known inhibitor, Camostat mesylate. We found that both Wi-A and Wi-N could bind and stably interact at the catalytic site of TMPRSS2. Wi-N showed stronger interactions with TMPRSS2 catalytic residues than Wi-A and was also able to induce changes in its allosteric site. Furthermore, we investigated the effect of Wi-N on TMPRSS2 expression in MCF7 cells and found remarkable downregulation of TMPRSS2 mRNA in treated cells predicting dual action of Wi-N to block SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cells. Since the natural compounds are easily available/affordable, they may even offer a timely therapeutic/preventive value for the management of SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. We also report that Wi-A/Wi-N content varies in different parts of Ashwagandha and warrants careful attention for their use.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Withanone and caffeic acid phenethyl ester are predicted to interact with main protease (M(pro)) of SARS-CoV-2 and inhibit its activity.[Pubmed:32431217]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Jun 1:1-13.
The recent novel coronavirus, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCoV) has caused a large number of deaths around the globe. There is an urgent need to understand this new virus and develop prophylactic and therapeutic drugs. Since drug development is an expensive, intense and time-consuming path, timely repurposing of the existing drugs is often explored wherein the research avenues including genomics, bioinformatics, molecular modeling approaches offer valuable strengths. Here, we have examined the binding potential of Withaferin-A (Wi-A), Withanone (Wi-N) (active withanolides of Ashwagandha) and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE, bioactive ingredient of propolis) to a highly conserved protein, M(pro) of SARS-CoV-2. We found that Wi-N and CAPE, but not Wi-A, bind to the substrate-binding pocket of SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) with efficacy and binding energies equivalent to an already claimed N3 protease inhibitor. Similar to N3 inhibitor, Wi-N and CAPE were interacting with the highly conserved residues of the proteases of coronaviruses. The binding stability of these molecules was further analyzed using molecular dynamics simulations. The binding free energies calculated using MM/GBSA for N3 inhibitor, CAPE and Wi-N were also comparable. Data presented here predicted that these natural compounds may possess the potential to inhibit the functional activity of SARS-CoV-2 protease (an essential protein for virus survival), and hence (i) may connect to save time and cost required for designing/development, and initial screening for anti-COVID drugs, (ii) may offer some therapeutic value for the management of novel fatal coronavirus disease, (iii) warrants prioritized further validation in the laboratory and clinical tests.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
2, 3-Dihydro-3beta-methoxy Withaferin-A Lacks Anti-Metastasis Potency: Bioinformatics and Experimental Evidences.[Pubmed:31757995]
Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 22;9(1):17344.
Withaferin-A is a withanolide, predominantly present in Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). It has been shown to possess anticancer activity in a variety of human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Molecular mechanism of such cytotoxicity has not yet been completely understood. Withaferin-A and Withanone were earlier shown to activate p53 tumor suppressor and oxidative stress pathways in cancer cells. 2,3-dihydro-3beta-methoxy analogue of Withaferin-A (3betamWi-A) was shown to lack cytotoxicity and well tolerated at higher concentrations. It, on the other hand, protected normal cells against oxidative, chemical and UV stresses through induction of anti-stress and pro-survival signaling. We, in the present study, investigated the effect of Wi-A and 3betamWi-A on cell migration and metastasis signaling. Whereas Wi-A binds to vimentin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP-K) with high efficacy and downregulates its effector proteins, MMPs and VEGF, involved in cancer cell metastasis, 3betamWi-A was ineffective. Consistently, Wi-A, and not 3betamWi-A, caused reduction in cytoskeleton proteins (Vimentin, N-Cadherin) and active protease (u-PA) that are essential for three key steps of cancer cell metastasis (EMT, increase in cell migration and invasion).
A validated HPTLC method for the simultaneous quantifications of three phenolic acids and three withanolides from Withania somnifera plants and its herbal products.[Pubmed:31200247]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019 Aug 15;1124:154-160.
A simple, rapid and selective high-performance thin-layer chromatographic (HPTLC) method has been developed and validated for simultaneous determination of three withanolides (withaferin A, Withanone and withanolide A) and three phenolic acids (caffeic acid, ferulic acid and benzoic acid) from different parts (root, stem and leaf) of Withania somnifera and its two commercially available polyherbal formulations. The extraction efficiency of withanolides and phenolic acids were tested using two solvents, chloroform and methanol, respectively. HPTLC separation was performed on silica coated aluminium plates Si 60F254; using toluene, ethyl acetate and acetic acid (60:40:4). The samples were quantitated at 231nm. The purity and identity of peaks of all the six analytes were confirmed by matching Rf values and UV-spectrum with authentic standards. The identity of three withanolides was further confirmed by positive ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) analyses. The developed method was validated for sensitivity, linearity, reproducibility, accuracy, the limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) following the guidelines of the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). The method was found to be linear (r>0.99) in the range of 50-2000ng/band for benzoic acid and 50-1000ng/band for the other five studied metabolites. This simple and accurate HPTLC method provided enhanced resolution of studied analytes as compared to other phytoconstituents present in W. somnifera extracts. It has also been successfully applied in the analysis and quantification of two polyherbal formulations containing W. somnifera plant parts.
Induction of Senescence in Cancer Cells by a Novel Combination of Cucurbitacin B and Withanone: Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential.[Pubmed:31112603]
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020 May 22;75(6):1031-1041.
Cancer, an uncontrolled proliferation syndrome, is treated with synthetic chemotherapeutic drugs that are associated with severe adverse effects. Development and application of new natural compounds is warranted to deal with the exponentially increasing incidence of cancer worldwide. Keeping selective toxicity to cancer cells as a priority criterion, we developed a combination of Cucurbitacin B and Withanone, and analyzed its anticancer potential using non-small cell lung cancer cells. We demonstrate that the selective cytotoxicity of the combination, called CucWi-N, to cancer cells is mediated by induction of cellular senescence that was characterized by decrease in Lamin A/C, CDK2, CDK4, Cyclin D, Cyclin E, phosphorylated RB, mortalin and increase in p53 and CARF proteins. It compromised cancer cell migration that was mediated by decrease in mortalin, hnRNP-K, vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metalloproteinase 2, and fibronectin. We provide in silico, molecular dynamics and experimental data to support that CucWi-N (i) possesses high capability to target mortalin-p53 interaction and hnRNP-K proteins, (ii) triggers replicative senescence and inhibits metastatic potential of the cancer cells, and (iii) inhibits tumor progression and metastasis in vivo. We propose that CucWi-N is a potential natural anticancer drug that warrants further mechanistic and clinical studies.
Anti-Stress and Glial Differentiation Effects of a Novel Combination of Cucurbitacin B and Withanone (CucWi-N): Experimental Evidence.[Pubmed:31000958]
Ann Neurosci. 2018 Dec;25(4):201-209.
Background: Natural extracts and compounds used in traditional home medicine are known for their safety and a variety of health promoting and therapeutic potentials. In contrast to the single molecule mediated targets, the combinational therapies are preferred for their multi-functional and limited toxic regimens and may be useful for disease therapeutics as well as to increase the quality of life during a variety of environmental stresses. Purpose: We aimed to combine the active ingredients of Chinese (Helicteres angustifolia) and Indian (Withania somnifera) ginsengs to develop a natural, efficient, and welfare combinatorial mixture with high anti-stress and glial differentiation potentials. Methods: Using cultured cells as a model system, we developed a combination of active ingredients of Chinese (Cucurbitacin B [Cuc]) and Indian (Withanone [Wi-N]) ginsengs. Eleven chemical models of environmental stresses were used. Cytotoxicity studies were performed using human skin fibroblast for anti-stress and rat glioma cells for glial differentiation effects. Results: We demonstrate that the novel combination of Cuc and Wi-N, CucWi-N, was non-toxic to normal cells. It caused stress protection in assays using normal human fibroblasts subjected to a variety of stresses. Of note, cells showed remarkable protection against oxidative and UV stresses and marked by decrease in DNA damage and reactive oxygen species. We examined and found the glial differentiation potential of CucWi-N in rat glioblastoma cells. CucWi-N clearly induced differentiation phenotype, well-marked with upregulation of GAP43, MAP2, and GFAP, which have been shown to play a key role in glial differentiation. Conclusion: These data demonstrate anti-stress and glial differentiation potential of CucWi-N (a novel combination of Cuc and Wi-N) that could be recruited in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical avenues and hence warrant further evaluation and mechanistic studies.
Understanding ligands driven mechanism of wild and mutant aryl hydrocarbon receptor in presence of phytochemicals combating Parkinson's disease: an in silico and in vivo study.[Pubmed:30836878]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Feb;38(3):807-826.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) is a key player to regulate the expression of a group of enzymes known as cytochrome P450s (CYPs) super family (CYP1A1, CYP1B1, CYP2B6, and CYP2E1) which metabolites diverse endogenous as well as toxic compounds such as Benzo[a] Pyrene (B[a] P) and TCDD. B[a] P induces oxidative stress and causes degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain, may leads to Parkinson's disease (PD). The metabolism of B[a] P through the expression of CYPs is mainly triggered after binding of B[a] P within ligand binding domain of AhR. But, the molecular mechanism of AhR mediated xenobiotic metabolism in presence of diverse phytochemicals is yet to be studied. The solved AhR (PDB ID: 5NJ8, 23-273aa) structure lacks information for ligand binding domain therefore both wild type and mutant models were predicted and screened virtually against sixty one natural compounds. The result proposed withaferin A, withanolide A, withanolide B, withanolide D and Withanone of plant Withania Somnifera as efficient ligand against both wild type and mutants (V381A and V381D) AhR models. However, in silico studies hypothesised withanolide A as a potent phytochemical to trigger the AhR mediated gene regulation activity of CYPs. The in vivo study in zebra fish model proposed about the neuro protective role of W. Somnifera leaf extract in presence of B[a]P. The present study would throw lights on the molecular mechanism of phytochemicals mediated AhR activity which may be useful in treatment of PD. [Formula: see text] Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Wild type p53 function in p53(Y220C) mutant harboring cells by treatment with Ashwagandha derived anticancer withanolides: bioinformatics and experimental evidence.[Pubmed:30808373]
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 26;38(1):103.
BACKGROUND: Tumor suppressor p53 protein is frequently mutated in a large majority of cancers. These mutations induce local or global changes in protein structure thereby affecting its binding to DNA. The structural differences between the wild type and mutant p53 thus provide an opportunity to selectively target mutated p53 harboring cancer cells. Restoration of wild type p53 activity in mutants using small molecules that can revert the structural changes have been considered for cancer therapeutics. METHODS: We used bioinformatics and molecular docking tools to investigate the structural changes between the wild type and mutant p53 proteins (p53(V143A), p53(R249S), p53(R273H) and p53(Y220C)) and explored the therapeutic potential of Withaferin A and Withanone for restoration of wild type p53 function in cancer cells. Cancer cells harboring the specific mutant p53 proteins were used for molecular assays to determine the mutant or wild type p53 functions. RESULTS: We found that p53(V143A) mutation does not show any significant structural changes and was also refractory to the binding of withanolides. p53(R249S) mutation critically disturbed the H-bond network and destabilized the DNA binding site. However, withanolides did not show any selective binding to either this mutant or other similar variants. p53(Y220C) mutation created a cavity near the site of mutation with local loss of hydrophobicity and water network, leading to functionally inactive conformation. Mutated structure could accommodate withanolides suggesting their conformational selectivity to target p53(Y220C) mutant. Using human cell lines containing specific p53 mutant proteins, we demonstrated that Withaferin A, Withanone and the extract rich in these withanolides caused restoration of wild type p53 function in mutant p53(Y220C) cells. This was associated with induction of p21(WAF-1)-mediated growth arrest/apoptosis. CONCLUSION: The study suggested that withanolides may serve as highly potent anticancer compounds for treatment of cancers harboring a p53(Y220C) mutation.
Cytotoxic Withanolides from the Roots of Indian Ginseng ( Withania somnifera).[Pubmed:30776236]
J Nat Prod. 2019 Apr 26;82(4):765-773.
Withania somnifera, commonly known as "Indian ginseng" or "ashwagandha", is popular as a functional food because of its diverse purported therapeutic efficacies including invigorating, improvement of cognitive ability, and stress release activities. Chemical investigation of the MeOH extract of W. somnifera roots combined with LC/MS-based analysis resulted in the identification of six new withanolides, withasilolides A-F (1-6), as well as seven known compounds (7-13). The structures of the new compounds were established by application of spectroscopic methods, including 1D and 2D NMR, HRMS, and ECD measurements. The cytotoxicity of the isolated compounds was evaluated against four human cancer cell lines (A549, SK-OV-3, SK-MEL-2, and HCT-15). Compounds 1, 2, 4, 6, and Withanone (11) each showed cytotoxicity for one or more of the four cancer cell lines used.


