PeltatosideCAS# 23284-18-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23284-18-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5484066 | Appearance | Powder |
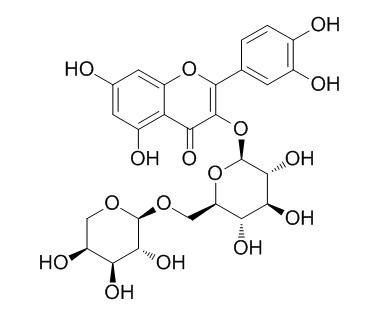
| Formula | C26H28O16 | M.Wt | 596.5 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1C(C(C(C(O1)OCC2C(C(C(C(O2)OC3=C(OC4=CC(=CC(=C4C3=O)O)O)C5=CC(=C(C=C5)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YNMFDPCLPIMRFD-KSPKLRDJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H28O16/c27-9-4-12(30)16-14(5-9)40-23(8-1-2-10(28)11(29)3-8)24(19(16)34)42-26-22(37)20(35)18(33)15(41-26)7-39-25-21(36)17(32)13(31)6-38-25/h1-5,13,15,17-18,20-22,25-33,35-37H,6-7H2/t13-,15+,17-,18+,20-,21+,22+,25-,26-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Peltatoside has antinociceptive and antioxidative effects, it is capable of inducing analgesia through the activation of peripheral CB1 receptors, involving endocannabinoids in this process. | |||||

Peltatoside Dilution Calculator

Peltatoside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6764 mL | 8.3822 mL | 16.7645 mL | 33.5289 mL | 41.9111 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3353 mL | 1.6764 mL | 3.3529 mL | 6.7058 mL | 8.3822 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1676 mL | 0.8382 mL | 1.6764 mL | 3.3529 mL | 4.1911 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0335 mL | 0.1676 mL | 0.3353 mL | 0.6706 mL | 0.8382 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0168 mL | 0.0838 mL | 0.1676 mL | 0.3353 mL | 0.4191 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Terpinyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN9972
CAS No.:80-26-2
- Vescalagin
Catalog No.:BCN9971
CAS No.:36001-47-5
- Butyric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9970
CAS No.:107-92-6
- Psoromic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9969
CAS No.:7299-11-8
- 4-Ethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9968
CAS No.:35817-27-7
- Genistein 7-O-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN9967
CAS No.:38482-81-4
- Oxyacanthine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN9966
CAS No.:6183-91-1
- Cubebin
Catalog No.:BCN9965
CAS No.:1242843-00-0
- 2,3-Dehydrosilybin B
Catalog No.:BCN9964
CAS No.:142796-24-5
- 4'-Methylchrysoeriol
Catalog No.:BCN9963
CAS No.:4712-12-3
- Aegineoside
Catalog No.:BCN9962
CAS No.:752209-48-6
- Oleocanthal
Catalog No.:BCN9961
CAS No.:289030-99-5
- Platycogenin A
Catalog No.:BCN9974
CAS No.:1459719-53-9
- 9-Methyl-9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN9975
CAS No.:552-70-5
- AT101
Catalog No.:BCN9976
CAS No.:866541-93-7
- omega-Benzoyl oxyphloracetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN9977
CAS No.:65982-77-6
- Henricine
Catalog No.:BCN9978
CAS No.:107783-46-0
- Harmol
Catalog No.:BCN9979
CAS No.:487-03-6
- (-)-Verbenone
Catalog No.:BCN9980
CAS No.:1196-01-6
- trans-Beta-Apo-8'-carotenal
Catalog No.:BCN9981
CAS No.:1107-26-2
- 4',6,7-Trimethoxyisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9982
CAS No.:798-61-8
- (R,S)-Equol
Catalog No.:BCN9983
CAS No.:66036-38-2
- Farnesol
Catalog No.:BCN9984
CAS No.:4602-84-0
- 4'-Methoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN9985
CAS No.:97005-76-0
Anti-inflammatory and immune properties of the peltatoside, isolated from the leaves of Annona crassiflora Mart., in a new experimental model zebrafish.[Pubmed:32240748]
Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Jun;101:234-243.
Establishing new animal models for the study of inflammation is very important in the process of discovering new drugs, since the inflammatory event is the basis of many pathological processes. Whereas rodent models have been the primary focus of inflammation research, we defend the zebrafish (Danio rerio) test as a feasible alternative for preclinical studies. Moreover, despite all the technological development already achieved by humanity, nature can still be considered a relevant source of new medicines. In this context, the aim of this work was to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of a substance isolated from the medicinal plant Annona crassilfora Mart, the Peltatoside, in an inflammatory model of zebrafish. It was determined: (i) total leukocyte count in the coelomate exudate; (ii) N-acetyl-beta-d-glucuronidase (NAG); (iii) myeloperoxidase (MPO); (iv) and the histology of liver, intestine and mesentery. Peltotoside (25, 50 and 100 mug) and dexamethasone (25 mug) were administered intracelomatically (i.c.) 30 min before carrageenan (i.c.). Pretreatment with Peltatoside at three doses significantly inhibited leukocyte recruitment in the coelomic cavity, and inhibited NAG and MPO activity against the action of Cg, in a similar manner as dexamethasone. However, some microlesions in the evaluated organs were detected. The dose of 25 mug showed an anti-inflammatory effect with lower undesirable effects in the tissues. Our results suggest that the zebrafish test was satisfactory in performing our analyzes and that the peltotoside has a modulatory action in reducing leukocyte migration.
Peltatoside Isolated from Annona crassiflora Induces Peripheral Antinociception by Activation of the Cannabinoid System.[Pubmed:27574895]
Planta Med. 2017 Feb;83(3-04):261-267.
Peltatoside is a natural compound isolated from leaves of Annona crassiflora Mart., a plant widely used in folk medicine. This substance is an analogue of quercetin, a flavonoid extensively studied because of its diverse biological activities, including analgesic effects. Besides, a previous study suggested, by computer structure analyses, a possible quercetin-CB1 cannabinoid receptor interaction. Thus, the aim of this work was to assess the antinociceptive effect of Peltatoside and analyze the cannabinoid system involvement in this action. The mouse paw pressure test was used and hyperalgesia was induced by intraplantar injection of carrageenan (200 microg/paw). All used drugs were administered by intraplantar administration in Swiss male mice (n = 6). Peltatoside (100 microg/paw) elicited a local inhibition of hyperalgesia. The peripheral antinociceptive action of Peltatoside was antagonized by the CB1 cannabinoid antagonist AM251 (160 microg/paw), but not by CB2 cannabinoid antagonist AM630 (100 microg/paw). In order to assess the role of endocannabinoids in this peripheral antinociceptive effect, we used (i) [5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z]-5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenyl-methyl ester phosphonofluoridic acid, an inhibitor of anandamide amidase; (ii) JZL184, an inhibitor for monoacylglycerol lipase, the primary enzyme responsible for degrading the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol; and (iii) VDM11, an endocannabinoid reuptake inhibitor. MAFP, JZL184, and VDM11 did not induce antinociception, respectively, at the doses 0.5, 3.8, and 2.5 microg/paw, however, these three drugs were able to potentiate the peripheral antinociceptive effect of Peltatoside at an intermediary dose (50 microg/paw). Our results suggest that this natural substance is capable of inducing analgesia through the activation of peripheral CB1 receptors, involving endocannabinoids in this process.
Burdock root extracts limit quorum-sensing-controlled phenotypes and biofilm architecture in major urinary tract pathogens.[Pubmed:25226848]
Urolithiasis. 2015 Feb;43(1):29-40.
Bacterial biofilms are serious concern in patients infected with urinary tract infections, complicated urinary tract infections and other device-associated infections. Microbes within the biofilms are effectively shielded from antibiotics and host immune cells, hence can be treated only with agents which has the potential to disassemble the biofilms. The study is focused on the root extracts of Arctium lappa Linn. as a source for complementary medicine against three major biofilm forming clinical isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Serratia marcescens. Methanol extracts of burdock roots (BR) showed no bactericidal activity (p > 0.05) against the uropathogens, whereas restrained the biofilms (p < 0.05) on polystyrene and glass surfaces at a biofilm inhibitory concentration of 100 microg/mL. The 3D confocal laser scanning microscopy was used to analyze the biofilm architecture which showed significant reduction in the surface area. Z-stack analysis has also revealed substantial reduction in the biofilm thickness (E. coli-50.79%, P. mirabilis-69.49%, and S. marcescens-75.84%). Further, BR extracts also inhibited quorum-sensing (QS)-controlled cellular phenotypes such as violacein, prodigiosin, swarming motility, and cell surface hydrophobicity. LC-MS/MS analysis of BR extracts identified the presence of two major quercetin derivatives (miquelianin and Peltatoside) along with few other constituent components. Exploring such phytocompounds will provide potential agents to treat infections caused by biofilm forming uropathogens. The antibiofilm and anti-QS agents will ultimately serve as armor, facilitating the host immune system to fight infections.
The first report on flavonoid isolation from Annona crassiflora Mart.[Pubmed:24571732]
Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(11):808-11.
Annona crassiflora, a native tree from Brazilian Cerrado, is reported to possess several ethnomedical uses. Here, we report the isolation and unambiguous characterisation of the flavonoids quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosil(1 --> 6)-O-alpha-L-arabinoside (1), known as Peltatoside, kaempferol-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside (2), quercetin-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside (3), quercetin-3-O-beta-L-arabinopiranoside (4) and the ( - )-epicatechin (5) from the hydroalcoholic portion of the leaf ethanolic extract. Their structures were elucidated by using 1D and 2D NMR, ESI-MS, UV/Vis spectroscopy, optical rotation analysis and literature data comparison. The leaf ethanolic extract and its isolated compounds were evaluated by using antimicrobial, antioxidant and larvicidal assays, expressing antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. This is the first report on flavonoid isolation from A. crassiflora.
Isolation and structure elucidaton of polyphenols from Loranthus micranthus Linn. parasitic on Hevea brasiliensis with antiinflammatory property.[Pubmed:26417309]
EXCLI J. 2014 Aug 20;13:859-68. eCollection 2014.
The present study was carried out to evaluate the anti-inflammatory activities of polyphenols isolated from the leaves of mistletoe (Loranthus micranthus Linn.) parasitic on Hevea brasiliensis. The anti-inflammatory properties of the isolated compounds were evaluated on the basis of their ability to inhibit the production of nitric oxide (NO) and tumuor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activated RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages. Semi-preparative HPLC separation of the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) and butanol (n-BuOH) fractions of the leaves of mistletoe (Loranthus micranthus Linn) parasitic on Hevea brasiliensis led to the isolation of four polyphenols: 3-O-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)-(-)-epicatechin (TMECG) (1); (-)-epicatechin-3-O-(3''-O-methyl)-gallate (ECG3''Me) (2); rutin (3) and Peltatoside (4). Compounds 1-4 were isolated for the first time from this plant while 1 was isolated for the first time in nature. These compounds (1-4) were readily identified by comparison of their spectroscopic data with those reported in the literature. The polyphenols proved to have anti-inflammatory activity as evidenced by the suppression of inducible nitric oxide (iNO) and cytokine (TNF-alpha) levels in the culture supernatant of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophages. However, the study showed that the quercetin diglycosides showed stronger inhibition of proinflammatory mediators than the epicatechin derivates. These data provide evidence that polyphenolic compounds isolated from the mistletoe parasitic on Hevea brasiliensis may contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the expression of inducible nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor-alpha.
Antioxidative polyphenols from Nigerian mistletoe Loranthus micranthus (Linn.) parasitizing on Hevea brasiliensis.[Pubmed:23422225]
Fitoterapia. 2013 Apr;86:78-83.
Two new phenolic glycosides, linamarin gallate (1) and walsuraside B (2), together with nine known compounds, catechin (3), epicatechin (4), epicatechin 3-O-gallate (5), epicatechin 3-O-(3-O-methyl)gallate (6), epicatechin 3-O-(3,5-O-dimethyl)gallate (7), epicatechin 3-O-(3,4,5-O-trimethyl)gallate (8), quercetin 3-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside (9), rutin (10), and Peltatoside (11), were isolated from the leafy twigs of Nigerian mistletoe Loranthus micranthus (Linn.) parasitic on Hevea brasiliensis. Compound 1 was characterized as an unusual cyanogenic glycoside, while compound 8 was isolated for the first time from a natural source. This is the first report of a cyanogenic glycoside from mistletoes. The structures of the new compounds were unambiguously elucidated by 1D ((1)H, (13)C), 2D NMR (COSY, HSQC, and HMBC) and by mass spectroscopy. The antioxidant activities of the isolated compounds (1-11) were evaluated using the 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay.
Fungitoxic phenols from carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus) effective against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. dianthi.[Pubmed:12597250]
Phytochem Anal. 2003 Jan-Feb;14(1):8-12.
The phenol compositions of two cultivars of carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus) namely "Gloriana" and "Roland", which are partially and highly resistant, respectively, to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. dianthi have been investigated with the aim of determining if endogenous phenols could have an anti-fungal effect against the pathogen. Analyses were performed on healthy and F. oxysporum-inoculated in vitro tissues, and on in vivo plants. Two benzoic acid derivatives, protocatechuic acid (3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid) and vanillic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid), were found within healthy and inoculated tissues of both cultivars, together with the flavonol glycoside Peltatoside (3-[6-O-(alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl] quercetin). These molecules proved to be only slightly inhibitory towards the pathogen. 2,6-Dimethoxybenzoic acid was detected in small amounts only in the inoculated cultivar "Gloriana", while the highly resistant cultivar "Roland" showed the presence of the flavone datiscetin (3,5,7,2'-tetrahydroxyflavone). The latter compound exhibited an appreciable fungitoxic activity towards F. oxysporum f. sp. dianthi.


