CyclanolineCAS# 18556-27-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18556-27-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3082134.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H24NO4 | M.Wt | 342.41 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (7S,13aS)-3,10-dimethoxy-7-methyl-6,8,13,13a-tetrahydro-5H-isoquinolino[2,1-b]isoquinolin-7-ium-2,9-diol | ||
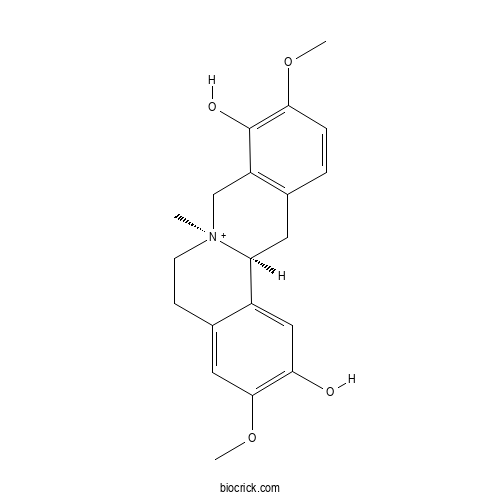
| SMILES | C[N+]12CCC3=CC(=C(C=C3C1CC4=C(C2)C(=C(C=C4)OC)O)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LKLWVKCEYSPQHL-KKSFZXQISA-O | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H23NO4/c1-21-7-6-13-9-19(25-3)17(22)10-14(13)16(21)8-12-4-5-18(24-2)20(23)15(12)11-21/h4-5,9-10,16H,6-8,11H2,1-3H3,(H-,22,23)/p+1/t16-,21-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Cyclanoline Dilution Calculator

Cyclanoline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9205 mL | 14.6024 mL | 29.2048 mL | 58.4095 mL | 73.0119 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5841 mL | 2.9205 mL | 5.841 mL | 11.6819 mL | 14.6024 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.292 mL | 1.4602 mL | 2.9205 mL | 5.841 mL | 7.3012 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0584 mL | 0.292 mL | 0.5841 mL | 1.1682 mL | 1.4602 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0292 mL | 0.146 mL | 0.292 mL | 0.5841 mL | 0.7301 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Myricetin 3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCX0698
CAS No.:41093-68-9
- Desacylsenegasaponin B
Catalog No.:BCX0697
CAS No.:163589-51-3
- Quercetin 3-O-[beta-D-xylosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside]
Catalog No.:BCX0696
CAS No.:83048-35-5
- Cavidine
Catalog No.:BCX0695
CAS No.:32728-75-9
- Polygalasaponin XXVIII
Catalog No.:BCX0694
CAS No.:176182-01-7
- N-benzyl-heptadecanamide
Catalog No.:BCX0693
CAS No.:883715-19-3
- N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-octadecanamide
Catalog No.:BCX0692
CAS No.:1429659-99-3
- 8,9-epoxy-3,10-diisobutyryloxythymol
Catalog No.:BCX0691
CAS No.:22518-06-5
- Farnesene
Catalog No.:BCX0690
CAS No.:502-61-4
- Koumidine
Catalog No.:BCX0689
CAS No.:1358-75-4
- Gentianose
Catalog No.:BCX0688
CAS No.:25954-44-3
- 3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethoxy-anthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCX0687
CAS No.:10383-62-7
- Cauloside D
Catalog No.:BCX0700
CAS No.:12672-45-6
- Methylcantharidinimide
Catalog No.:BCX0701
CAS No.:76970-78-0
- Mussaenosidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0702
CAS No.:82451-22-7
- Epirosmanol
Catalog No.:BCX0703
CAS No.:93380-12-2
- Endothalic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0704
CAS No.:145-73-3
- Ginsenoside Ra6
Catalog No.:BCX0705
CAS No.:1346522-89-1
- Methyl jasmonate
Catalog No.:BCX0706
CAS No.:1211-29-6
- 5-Hydroxy-2′,3,4′,7-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX0707
CAS No.:19056-75-8
- Oroxylin A-7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0708
CAS No.:36948-77-3
- Oleandrigenin
Catalog No.:BCX0709
CAS No.:465-15-6
- Digitoxigenin
Catalog No.:BCX0710
CAS No.:143-62-4
- Pinolenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0711
CAS No.:16833-54-8
Dissection of transcriptome and metabolome insights into the isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis during stem development in Phellodendron amurense (Rupr.).[Pubmed:36122814]
Plant Sci. 2022 Dec;325:111461.
Phellodendron amurense (Rupr.) is a well-known medicinal plant with high medicinal value, and its various tissues are enriched in various active pharmaceutical ingredients. Isoquinoline alkaloids are the primary medicinal component of P. amurense and have multiple effects, such as anti-inflammation, antihypertension, and antitumor effects. However, the potential regulatory mechanism of isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis during stem development in P. amurense is still poorly understood. In the present study, a total of eight plant hormones for each stem development stage were detected; of those, auxin, gibberellins and brassinosteroids were significantly highly increased in perennial stems and played key roles during stem development in P. amurense. We also investigated the content and change pattern of secondary metabolites and comprehensively identified some key structural genes involved in the isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis pathway by combining the transcriptome and metabolomics. A total of 39,978 DEGs were identified in the present study, and six of those had candidate structural genes (NCS, GOT2, TYNA, CODM, TYR, TAT and PSOMT1) that were specifically related to isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in P. amurense. Corydalmine, Cyclanoline, dehydroyanhunine, (S)-canadine and corybulbine were the most significantly upregulated metabolites among the different comparative groups. Three differentially expressed metabolites, dopamine, (S)-corytuberine and (S)-canadine, were enriched in the isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis pathway. Furthermore, bHLH and WRKY transcription factors play key roles in the isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis pathway in P. amurense. The results not only provide comprehensive genetic information for understanding the molecular mechanisms of isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis but also lay a foundation for the combinatory usage of the medicinal active ingredient of P. amurense.
Binding interaction of protoberberine alkaloids against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) using molecular dynamics simulations and QM/MM calculations.[Pubmed:34033838]
Chem Biol Interact. 2021 Aug 1;344:109523.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) plays a vital role in Alzheimer's disease (AD), which is one of the most common causes of dementia. Discovering new effective inhibitors against AChE activity is seen to be one of the effective approaches to reduce the suffering from AD. Protoberberine alkaloids isolated from natural resources have previously been reported as potent AChE inhibitors. In order to gain insights into how these alkaloids could inhibit AChE, berberine, palmatine, and Cyclanoline were selected to investigate in terms of binding orientation and their key interactions with AChE using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations and quantum chemical calculations. The results revealed that the molecular dynamics structures of palmatine and berberine indicated that their equilibrated structures did not occupy the gorge but they slightly moved away from the catalytic site (CAS). For Cyclanoline, the binding mode was quite different from those of donepezil and the other protoberberine alkaloids: it preferred to stay deeper in the CAS site. Interaction energies and residual interaction energies confirmed that the key interactions for palmatine and berberine were pi-pi interactions with Trp286 and Tyr341 and H-bond interactions with Tyr124. Cyclanoline formed pi-pi interactions with Trp86 and H-bonds to the amino acids in the CAS site. The results suggested the importance of aromaticity in the core structure and the flexibility of the core structure or the substituents in order to fit into the narrow gorge. The HOMO, LUMO, bioavailability, drug-likeness and pharmacokinetics were also predicted. The results obtained will be useful for further AD drug development.
The Cholinesterase Inhibitory Properties of Stephaniae Tetrandrae Radix.[Pubmed:33327436]
Molecules. 2020 Dec 14;25(24):5914.
Stephaniae tetrandrae radix (STR) is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine in alleviating edema by inducing diuresis. In the clinic, STR extracts or its components are widely used in the treatment of edema, dysuria, and rheumatism for the regulation of water metabolism. Furthermore, STR has been used in treating emotional problems for years by combining with other Chinese herbs. However, the material basis and mechanism of STR on the nervous system have not been revealed. Here, the main components of STR extracts with different extracting solvents were identified, including three major alkaloids, i.e., Cyclanoline, fangchinoline, and tetrandrine. The cholinesterase inhibitory activity of STR extracts and its alkaloids was determined using the Ellman assay. Both Cyclanoline and fangchinoline showed acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory activity, demonstrating noncompetitive enzyme inhibition. In contrast, tetrandrine did not show enzymatic inhibition. The synergism of STR alkaloids with huperzine A or donepezil was calculated by the median-effect principle. The drug combination of fangchinoline-huperzine A or donepezil synergistically inhibited AChE, having a combination index (CI) < 1 at F(a) = 0.5. Furthermore, the molecular docking results showed that fangchinoline bound with AChE residues in the peripheral anionic site, and Cyclanoline bound with AChE residues in the peripheral anionic site, anionic site, and catalytic site. In parallel, Cyclanoline bound with butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) residues in the anionic site, catalytic site, and aromatic site. The results support that fangchinoline and Cyclanoline, alkaloids derived from STR, could account for the anti-AChE function of STR. Thus, STR extract or its alkaloids may potentially be developed as a therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's patients.
Differentiation between wild and artificial cultivated Stephaniae tetrandrae radix using chromatographic and flow-injection mass spectrometric fingerprints with the aid of principal component analysis.[Pubmed:32884703]
Food Sci Nutr. 2020 Jun 23;8(8):4223-4231.
High-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) and flow-injection mass spectrometric (FIMS) fingerprinting profiles were used to differentiate between wild and artificial cultivated Stephaniae tetrandrae Radix samples. HPLC and FIMS fingerprints of 15 wild S. tetrandrae Radix samples and 12 artificial cultivated S. tetrandrae Radix samples were obtained and analyzed with the aid of principal component analysis (PCA). PCA of the fingerprints showed that the chemical differences between wild and artificial cultivated S. tetrandrae Radix samples could be differentiated by either HPLC or FIMS fingerprints. The HPLC fingerprints provided more chemical information but required longer analytical time compared with FIMS fingerprints. This study indicated that the wild samples contained higher concentrations of almost all of the major compounds than the cultivated samples. Three characteristic compounds which were responsible for the differences between the samples were tentatively identified with the aid of MS data. Furthermore, these three compounds, tetrandrine (TET), fangchinoline (FAN), and Cyclanoline (CYC), were quantified. The HPLC and FIMS fingerprints combined with PCA could be used for quality assessment of wild and artificial cultivated S. tetrandrae Radix samples.
A new pyrrole alkaloid from the roots of Cissampelos pareira.[Pubmed:31135214]
Nat Prod Res. 2021 Jan;35(1):80-87.
Phytochemical investigation of the roots of Cissampelos pareira Linn. led to the isolation of one new pyrrole alkaloid, cissampeline (1), together with ten known alkaloids, (-)-curine (2), (-)-Cyclanoline (3), (+)-tetrandrine (4), (+)-obaberine (5), (+)-obamegine (6), (-)-oblongine (7), (+)-homoaromoline (8), (-)-nor-N׳-chondrocurine (9), trans-N-feruloyltyramine (10) and (+)-coclaurine (11). Their structures were elucidated by extensive NMR and MS spectroscopic analyses. Interestingly, compound 1 represents the first example of pyrrole alkaloid found in the genus Cissampelos. Moreover, compounds 5-11 were isolated for the first time from this genus. Among them, compound 6 showed the highest anti-acetylcholinesterase activity with an IC(50) value of 3.26 microM, whereas compound 8 displayed the most potent cytotoxicity against human colon cancer (HT29) cells with an IC(50) value of 7.89 microM.
Direct analysis of quaternary alkaloids by in situ reactive desorption corona beam ionization MS.[Pubmed:25118336]
Analyst. 2014 Oct 21;139(20):5185-91.
The direct detection of quaternary alkaloids by atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI)-base ambient MS is difficult because of their poor volatility. In this study, a reactive protocol was developed for the in situ determination of quaternary alkaloids using desorption corona beam ionization (DCBI) mass spectrometry (MS). The model compounds of 8 quaternary alkaloids including sanguinarine, chelerythrine, Cyclanoline, nitidine, coptisine, jatrorrhizine, berberine, palmatine and 2 tertiary alkaloids including protopine and allocryptopine were investigated in different states such as on a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) plate, in raw herbal materials, and in silica gel. After various reactive reagents were studied, the mixture of saturated aqueous NaOH solution and CH3OH solvent (3 : 7, v/v) was selected as the optimized reactive reagent for the reactive DCBI-MS detection. All the target molecules can be detected with high sensitivity. On a PTFE plate the limits of detection were 0.0795, 0.1060, 0.4860, 0.9665, 0.8879, 0.3987, 0.5557, 0.4591, 0.0889, and 0.1929 mg L(-1) for sanguinarine, chelerythrine, Cyclanoline, nitidine, coptisine, jatrorrhizine, berberine, palmatine, protopine, and allocryptopine, respectively. The reactive protocol was also applied to the direct detection of raw herbal materials and thin layer chromatography successfully.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Stephania venosa tuber.[Pubmed:16640839]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2006 May;58(5):695-700.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors have lately gained interest as potential drugs in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Three AChE inhibitors were isolated from tubers of a Thai medicinal plant, Stephania venosa (Bl) Spreng. They were identified as quaternary protoberberine alkaloids, stepharanine, Cyclanoline and N-methyl stepholidine. They expressed inhibitory activity on AChE with IC50 values (concentration that caused 50% inhibition of activity) of 14.10 +/- 0.81, 9.23 +/- 3.47 and 31.30 +/- 3.67 microM, respectively. The AChE inhibitory activity of these compounds was compared with those of the related compounds, palmatine, jatrorrhizine and berberine, as well as tertiary protoberberine alkaloids isolated from the same plant, stepholidine and corydalmine. The results suggest that the positive charge at the nitrogen of the tetrahydroisoquinoline portion, steric substitution at the nitrogen, planarity of the molecule or substitutions at C-2, -3, -9, and -10 affect the AChE inhibitory activity of protoberberine alkaloids.
Inhibitory effects of Stephania tetrandra S. Moore on free radical-induced lysis of rat red blood cells.[Pubmed:15802807]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Apr;28(4):667-70.
Crude preparations of Stephania tetrandra S. MOORE (ST), a traditional herbal medicine, have been used safely for arthritis and silicosis in China. In this study, we demonstrated that ST in vitro protects red blood cells from 2,2-azo-bis (2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH)-induced hemolysis. The inhibitory effect was dose-dependent at concentrations of 10 to 1000 microg/ml. Moreover, tests were carried out to identify the main ingredient of ST that exerts a scavenging effect on free-radicals. Three representative alkaloids, tetrandrine, fangchinoline, and Cyclanoline, isolated from ST, were found to have inhibitory activities against AAPH-induced lysis of red blood cells (RBC). Furthermore, the ingestion of 200 mg of ST extract was associated with a significant increase in free-radical scavenging effect of plasma in rats. These results suggest that ST as antioxidant inhibits AAPH-induced hemolysis of RBC both in vitro and in vivo.
Quaternary isoquinoline alkaloids from Stephania cepharantha.[Pubmed:10726860]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2000 Mar;48(3):370-3.
From the quaternary alkaloidal fraction of the dried tubers of Stephania cepharantha, two new isoquinoline alkaloids, stecepharine and tetradehydroreticuline have been isolated along with the known compounds, magnoflorine, menisperine, steponine, Cyclanoline, oblongine, cis-N-methylcapaurine and 2'-N-methylisotetrandrine. cis-N-Methylcapaurine (=9-O-methylstecepharine) was isolated as a natural product for the first time. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic evidence.


