DesonideCAS# 638-94-8 |
- Mozavaptan
Catalog No.:BCC5095
CAS No.:137975-06-5
- Tolvaptan
Catalog No.:BCC5096
CAS No.:150683-30-0
- Conivaptan HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3756
CAS No.:168626-94-6
- Desmopressin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1526
CAS No.:62288-83-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

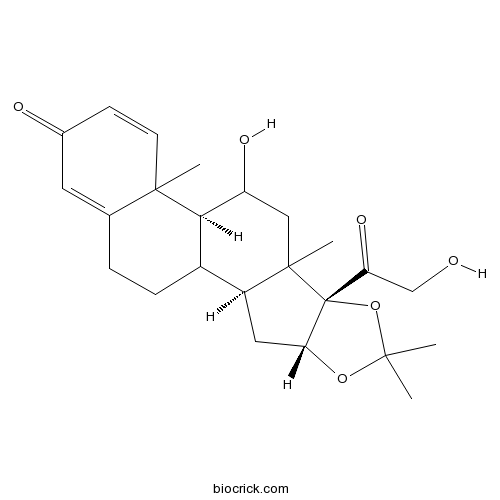
| Cas No. | 638-94-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 12536 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H32O6 | M.Wt | 416.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (240.09 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| SMILES | CC1(OC2CC3C4CCC5=CC(=O)C=CC5(C4C(CC3(C2(O1)C(=O)CO)C)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WBGKWQHBNHJJPZ-YWZQBGSISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H32O6/c1-21(2)29-19-10-16-15-6-5-13-9-14(26)7-8-22(13,3)20(15)17(27)11-23(16,4)24(19,30-21)18(28)12-25/h7-9,15-17,19-20,25,27H,5-6,10-12H2,1-4H3/t15?,16-,17?,19+,20+,22?,23?,24+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Desonide Dilution Calculator

Desonide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4009 mL | 12.0045 mL | 24.009 mL | 48.0181 mL | 60.0226 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4802 mL | 2.4009 mL | 4.8018 mL | 9.6036 mL | 12.0045 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2401 mL | 1.2005 mL | 2.4009 mL | 4.8018 mL | 6.0023 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.048 mL | 0.2401 mL | 0.4802 mL | 0.9604 mL | 1.2005 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.024 mL | 0.12 mL | 0.2401 mL | 0.4802 mL | 0.6002 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Desonide is a nonfluorinated corticosteroid anti-inflammatory agent used topically for dermatoses.
- trans-Methylisoeugenol
Catalog No.:BCN6558
CAS No.:6379-72-2
- Cyclosporin D
Catalog No.:BCC6444
CAS No.:63775-96-2
- 12alpha-Hydroxygrandiflorenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4823
CAS No.:63768-17-2
- 6-Chloromelatonin
Catalog No.:BCC6651
CAS No.:63762-74-3
- 3'-Amino-4'-methoxyacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8611
CAS No.:6375-47-9
- AEG 3482
Catalog No.:BCC8088
CAS No.:63735-71-7
- Pseudoprotogracillin
Catalog No.:BCC8354
CAS No.:637349-03-2
- Paspalinine
Catalog No.:BCN7386
CAS No.:63722-91-8
- Z-Phenylalaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2716
CAS No.:6372-14-1
- (R)-Baclofen hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4123
CAS No.:63701-55-3
- 2-(Dimethylamino)ethanesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1752
CAS No.:637-95-6
- Pramoxine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4705
CAS No.:637-58-1
- alpha-Amyrin
Catalog No.:BCN3341
CAS No.:638-95-9
- beta-Amyrone
Catalog No.:BCN4179
CAS No.:638-97-1
- 2-Amino-3-dodecanol
Catalog No.:BCN4175
CAS No.:
- Erythrinin C
Catalog No.:BCN4176
CAS No.:63807-85-2
- Erythrinin A
Catalog No.:BCN3203
CAS No.:63807-86-3
- Dihydroalpinumisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4177
CAS No.:63807-90-9
- 5-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N-[4-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)phenyl]furan-2-carboxamide
Catalog No.:BCC3636
CAS No.:638156-11-3
- Z-D-Arg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3575
CAS No.:6382-93-0
- Phyllostadimer A
Catalog No.:BCN4178
CAS No.:638203-32-4
- H-Glu-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC2924
CAS No.:6384-08-3
- NMDA (N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid)
Catalog No.:BCC4590
CAS No.:6384-92-5
- Meclofenamate Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5490
CAS No.:6385-02-0
Investigation of the stabilizing effects of antioxidants and benzophenone-3 on desonide photostability.[Pubmed:24871554]
AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014 Oct;15(5):1155-62.
Desonide is a topical corticoid used in the treatment of skin diseases and is marketed in different pharmaceutical dosage forms. Recently, the poor photostability of a commercially available hair solution after direct exposure to UVA light was verified. In this study, we investigated the ability of the antioxidants ascorbic acid, butylhydroxyanisole (BHA), butylhydroxytoluene (BHT), alpha-tocopherol, and the UV filter benzophenone-3 (BP-3) to prevent the photodegradation of Desonide in hair solution (Desonide 0.1%) and the stability of the proposed formulation under environmental conditions. The tested antioxidants were not able to prevent the photolysis of Desonide, whereas the addition of 0.3% BP-3 enhanced the photostability of the drug. After 15 h of direct exposure to UVA radiation, the Desonide remaining content in the hair solution with BP-3 was approximately 98%. Higher photostability was also verified under UVC radiation. Additionally, the results indicated that the formulation was stable under accelerated and room temperature conditions for 70 days, corresponding to the total period of the study.
The effect of desonide hydrogel on pruritis associated with atopic dermatitis.[Pubmed:24918564]
J Drugs Dermatol. 2014 Jun;13(6):725-8.
Itch is a common and troubling symptom of atopic dermatitis. It is not mediated by histamine, and standard anti-itch therapies, therefore, have limited benefit for most AD patients. Instead, anti-inflammatory agents are used to reduce inflammation and therefore improve associated itch. Studies confirm that long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to a reduction in pruritus. A pilot study was designed to assess the effects of one week of twice-daily application of Desonide hydrogel 0.05% for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Active treatment was associated with significant improvements in IGA scores at day 3 and day 7 (mean score 0.55, 75.83% improvement from Baseline; P <.0001) and pruritus VAS scores at day 3 and day 7 (mean 6.35-point, 86.61% reduction in VAS scores; P <.0001). Treatment with the convenient, hydrating hydrogel formulation is effective and associated with an improvement in subjects' quality of life.
Topical niacinamide 4% and desonide 0.05% for treatment of axillary hyperpigmentation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.[Pubmed:23355788]
Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:29-36.
BACKGROUND: Axillary hyperpigmentation is a frequent cause of cosmetic consultations in dark-skinned women from tropical areas, including Latin America. Currently, there is no widely accepted treatment for the disorder, but it is usually treated with bleaching agents because it is considered a variant of inflammatory hyperpigmentation. The purpose of this study was to assess the efficacy of niacinamide 4% and Desonide 0.05% emulsions compared with placebo in the treatment of axillary hyperpigmentation. METHODS: Twenty-four women aged 19-27 years with hyperpigmented axillae (phototype III-V) were randomly assigned to receive the study treatments in the axillary region. Improvement was assessed at baseline, then clinically and by colorimetry 9 weeks later. Quantitative evaluation including melanin, inflammatory infiltrates, NKI/Beteb, CD1a, CD68, and collagen type IV content was performed by histochemistry and immunohistochemistry, assisted by computerized morphometric analysis. RESULTS: Both niacinamide and Desonide induced significant colorimetric improvement compared with placebo; however, Desonide showed a better depigmenting effect than niacinamide. A good to excellent response was achieved in 24% of cases for niacinamide, 30% for Desonide, and 6% for placebo. We observed a marked disruption of the basal membrane in axillary hyperpigmentation and an inflammatory infiltrate that improved after treatment. Decreased pigmentation in the Desonide-treated axillae was associated with recovery of disruption at the basal membrane. CONCLUSION: Niacinamide and Desonide showed depigmenting properties in women with axillary hyperpigmentation. These findings may be explained by their antimelanogenic and anti-inflammatory properties, respectively.
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a desonide gel-cream photostabilized with benzophenone-3.[Pubmed:25775013]
Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016 Jan;42(1):19-27.
CONTEXT: Our group previously reported the photoinstability of some Desonide topical commercial formulations under direct exposure to UVA radiation. OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to prepare and characterize a gel-cream containing Desonide, with greater photostability than the commercial gel-cream (C-GC). Benzophenone-3 (BP-3) was used as a photostabilizing agent. METHODS: The gel-cream developed (D-GC) containing BP-3 at 0.1% was prepared and characterized regarding its pH, drug content, spreadability, viscosity, in vitro drug release and in vitro permeation. The in vivo anti-inflammatory effect was assessed by ear edema measurement, croton oil-induced acute skin inflammation and myeloperoxidase assay. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: D-GC presented characteristics compatible with topical application, appropriate drug content and good spreadability, and non-Newtonian behavior with pseudoplastic flow. D-GC showed a good photostability profile, presenting a Desonide content of 95.70% after 48 h of exposure to UVA radiation, and stability under room conditions during 60 days. The amount of Desonide released from D-GC and C-GC was 57.8 and 51.7 microg/cm(2), respectively, measured using the vertical Franz cell. The in vitro skin permeation showed that Desonide reached the site of action of the topical corticosteroids, from both formulations; however, the Desonide amount retained in the dermis was lower with D-GC. The in vivo evaluation of topical anti-inflammatory activity indicated that D-GC presented the same biological effect as C-GC. CONCLUSION: D-GC represents a promising approach to treat dermatological disorders, since it presented satisfactory physicochemical characteristics, the same biological activity as C-GC and superior photostability, conferred by the addition of BP-3 at 0.1%.


