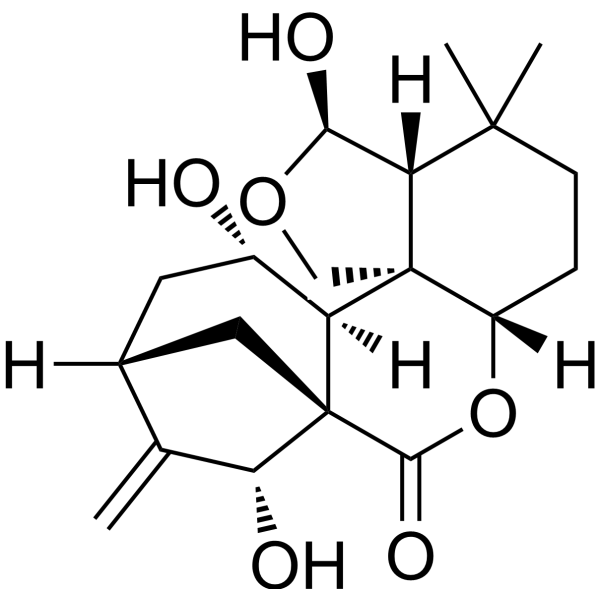
EpinodosinolCAS# 27548-88-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 27548-88-5 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H28O6 | M.Wt | 364.43 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Epinodosinol Dilution Calculator

Epinodosinol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.744 mL | 13.7201 mL | 27.4401 mL | 54.8802 mL | 68.6003 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5488 mL | 2.744 mL | 5.488 mL | 10.976 mL | 13.7201 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2744 mL | 1.372 mL | 2.744 mL | 5.488 mL | 6.86 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0549 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5488 mL | 1.0976 mL | 1.372 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0274 mL | 0.1372 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5488 mL | 0.686 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (1α,2α,6β,8α,9α)-1,2,6,8,12-pentakis(acetyloxy)-9-(benzoyloxy)dihydro-β-agarofuran
Catalog No.:BCX1705
CAS No.:128443-60-7
- Caffeic acid tetramer
Catalog No.:BCX1704
CAS No.:130286-75-8
- Celangulin V
Catalog No.:BCX1703
CAS No.:139979-81-0
- Alismanol M
Catalog No.:BCX1702
CAS No.:2408810-59-1
- Scutellarein-7-O-diglucuronide
Catalog No.:BCX1701
CAS No.:150641-65-9
- Homoveratric acid
Catalog No.:BCX1700
CAS No.:93-40-3
- Ladanetin-6-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1699
CAS No.:89647-63-2
- Pedaliin 6''-acetate
Catalog No.:BCX1698
CAS No.:160789-41-3
- Cirsiliol 4'-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1697
CAS No.:41087-98-3
- Ladanetin-6-O-β-(6''-O- acetyl)glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1696
CAS No.:1256959-27-9
- Complanatin II
Catalog No.:BCX1695
CAS No.:142449-94-3
- Apigenin-7-O-diglucuronoside
Catalog No.:BCX1694
CAS No.:119738-57-7
- Apigenin 4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1707
CAS No.:20486-34-4
- Celangulatin C
Catalog No.:BCX1708
CAS No.:1000784-44-0
- Angulatin G
Catalog No.:BCX1709
CAS No.:1000784-46-2
- Angulatin E
Catalog No.:BCX1710
CAS No.:403613-20-7
- Protoapigenin 4'-O-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1711
CAS No.:163559-04-4
- 2-(trans-1,4-dihydroxy-cyclohexyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-chromone
Catalog No.:BCX1712
CAS No.:1270013-29-0
- Protoapigenin
Catalog No.:BCX1713
CAS No.:879325-07-2
- 2,3-Dihydro-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-1H-indole-3-acetic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1714
CAS No.:57061-17-3
- Wallichoside
Catalog No.:BCX1715
CAS No.:60657-36-5
- Rabdophyllin G
Catalog No.:BCX1716
CAS No.:82460-75-1
- Angulatin K
Catalog No.:BCX1717
CAS No.:1631992-80-7
- (2E,4E)-8-Hydroxy-2,7-dimethyl-decadien-(2,4)-disaeure-(1,10)-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1718
CAS No.:2808401-10-5
Network Pharmacological Screening of the Active Ingredients and Hypoglycemic Effect of Isodon rubescens in the Treatment of Diabetes.[Pubmed:32294788]
Planta Med. 2020 May;86(8):556-564.
This study was firstly to study the relationship of "ingredient-target-pathway" and the pharmacological effects of Isodon rubescens for the treatment of diabetes. Based on a network pharmacology method, 138 active ingredients of Isodon rubescens were screened from the relative literatures, and their targets were confirmed by comparing these with the hypoglycemic targets in the DrugBank database. Results showed that Isodon rubescens contained 25 hypoglycemic ingredients, such as rabdoternin A, rabdoternin B, and Epinodosinol. These ingredients could activate 6 hypoglycemic targets, including 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR), integrin alpha-L (ITGAL), integrin beta-2 (ITGB2), progesterone receptor (PGR), glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1), and nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 2 (NR1I2). These targets were involved in 94 signaling pathways, such as the Rap1, PI3K-Akt, and HIF-1 signaling pathways. The cell viability showed that the human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) treated with alcohol extract (1.00 g/L) and the water extract (0.13 - 0.50 g/L) exhibited high viability compared to the model group (p < 0.05), respectively. 0In animal experiments, the rats treated with water extract of Isodon rubescens showed significant hypoglycemic effects compared to rats in the model group (p < 0.05). Overall, this approach provides an efficient strategy to explore hypoglycemic ingredients of Isodon rubescens and other traditional Chinese medicine.
[Studies on chemical constituents of Isodon henryi].[Pubmed:30989952]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Jan;44(2):319-323.
The chemical constituents of the water extraction of the aerial parts of Isodon henryi were investigated by various chromatographic methods including D-101 macroporous adsorptive resins,silica gel,sephadex LH-20,and semi-preparative HPLC. As a result,ten compounds were separated and purified. By analyses of the UV,IR,MS,NMR spectra,their structures were determined as rabdosinate( 1),lasiokaurin( 2),Epinodosinol( 3),rabdosichuanin C( 4),epinodosin( 5),hebeirubescensin k( 6),rubescensin C( 7),enmenol( 8),oridonin( 9),and enmenol-1-beta-glucoside( 10). Compounds 1-8 and 10 were isolated from I. henryi for the first time. Compounds 2 and 9 showed inhibitory effects against four tumor cells,with IC50 values of 2. 25-9. 32 mumol.L-1.
Molecular structure and vibrational bands and 13C chemical shift assignments of both enmein-type diterpenoids by DFT study.[Pubmed:24013676]
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Jan 3;117:449-58.
We report here theoretical and experimental studies on the molecular structure and vibrational and NMR spectra of both natural enmein type diterpenoids molecule (6, 7-seco-ent-kaurenes enmein type), isolated from the leaves of Isodon japonica (Burm.f.) Hara var. galaucocalyx (maxin) Hara. The optimized geometry, total energy, NMR chemical shifts and vibrational wavenumbers of Epinodosinol and epinodosin have been determined using B3LYP method with 6-311G (d,p) basis set. A complete vibrational assignment is provided for the observed IR spectra of studied compounds. The calculated wavenumbers and 13C c.s. are in an excellent agreement with the experimental values. Quantum chemical calculations at the B3LYP/6-311G (d,p) level of theory have been carried out on studied compounds to obtain a set of molecular electronic properties (MEP,HOMO, LUMO and gap energies DeltaEg). Electrostatic potential surfaces have been mapped over the electron density isosurfaces to obtain information about the size, shape, charge density distribution and chemical reactivity of the molecules.
Chemical constituents of flowers and fruits of Rabdosia excisa.[Pubmed:23302530]
Chin J Nat Med. 2012 Jan;10(1):43-7.
AIM: To study the chemical constituents in the flowers and fruits of Rabdosia excisa. METHODS: The compounds were isolated and purified by silica gel column chromatography and their structures were identified by spectroscopic methods. RESULTS: Sixteen compounds isolated from the flowers and fruits of this plant were identified as: stigm asterol (I), alpha-amyrin palmitate (II), ursolic acid (III), 2alpha, 3alpha, 19-trihydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid (IV), 2alpha-hydroxyursolic acid (V), maslinic acid (VI), isodonal (VII), maoyecrystal E (VIII), kamebakaurin (XI), macrocalyxin G (X), Epinodosinol (XI), rabdosichuanin C (XII), kamebacetal A (XIII), oridonin (XIV), enmenol-glucoside (XV), and lasiononin (XVI). CONCLUSION: All the constituents were found in Rabdosia excisa for the first time, except constituents III, IX, XII and XIV.
A sensitive analysis method for 7 diterpenoids in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and its application to pharmacokinetic study of Isodon serra extract.[Pubmed:21930275]
J Chromatogr A. 2011 Oct 28;1218(43):7771-80.
A simple and sensitive LC-MS/MS method has been developed and validated for the identification and quantification of epinodosin, Epinodosinol, nodosin, oridonin, lasiokariurinol, lasiokaurin and rabdoternin A in rat plasma using sulfamethoxazole as the internal standard. The plasma sample pre-treatment consisted of a liquid-liquid extraction. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a C18 column with linear gradient elution using water and methanol, which were both acidified with 0.1% formic acid, at a flow rate of 0.7 mL/min. A tandem mass spectrometric detection was conducted using multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) via an electrospray ionization (ESI) source. A novel multi-determination-periods program was executed to achieve a higher sensitivity by setting five scanning periods. The method presented here utilizes a novel determination strategy, enabling the application of positive and negative ESI-MS in a single run. The optimized mass transition ion-pairs (m/z) for quantitation were 361.2/287.1 for epinodosin, 382.3/347.3 for Epinodosinol, 363.3/281.2 for nodosin, 365.3/347.3 for oridonin, 407.3/329.1 for lasiokariurinol, 405.2/59.0 for lasiokaurin, 363.2/283.1 for rabdoternin A and 254.1/156.0 for IS. The total run time was 20.50 min (including 5 min equilibration time) between injections. The specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery, matrix effect and several validation results demonstrate that this method is sensitive, specific and reliable. The proposed method was further applied to investigate the pharmacokinetics of all analytes after a single oral administration of Isodon serra extract to rats.
Comparison of cytotoxicity and DNA damage potential induced by ent-kaurene diterpenoids from Isodon plant.[Pubmed:19606380]
Nat Prod Res. 2011 Sep;25(15):1402-11.
The cytotoxicity of six ent-kaurene diterpenoids isolated from the leaves of Isodon japonica (Burm.f.) Hara var. galaucocalyx (maxin) Hara was evaluated against three human tumour HepG2, GLC-82 and HL-60 cell lines through SRB assay, and their DNA damage potential (against HepG2 cell line) was assessed by comet assay. Among the six ent-kaurene diterpenoids, Rabdosin B was most cytotoxic, followed by Oridonin, Epinodosin, Rabdosinate, Lasiokaurin and Epinodosinol. All of the six ent-kaurene diterpenoids induced significant DNA damage (p < 0.05) to HepG2 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner except Lasiokaurin and Eponodosinol at 6 micromol L(-)(1) for 24 h. The structure-activity relationships (SARs) were discussed and it was found that exo-methylene cyclopentanone in the molecular structure was important for maintaining the cytotoxicity and DNA damage potential of the compounds.-OAc group at site C-1 in Lasiokaurin had a higher stereospecific blockade, which made the compound have less cytotoxicity and DNA damage potential than Oridonin (-OH at C-1).
Two novel ent-kauranoid diterpenoids from Isodon japonica leaves.[Pubmed:16142643]
Planta Med. 2005 Aug;71(8):764-9.
Two novel ent-kaurane diterpenoids, taihangjaponicain A (1), and taihangjaponicain B ( 2), and nine known diterpenoids, epinodosin (3), oridonin (4), Epinodosinol (5), lasiokaurin ( 6), 1alpha- O-beta- D-glucopyranosylenmenol (7), lasiodonin (8), rabdosichuanin D ( 9), shikokianin (10) and rabdoternin A (11) were isolated from I. japonica leaves. The structures of the two new compounds were elucidated using 1-D and 2-D NMR spectroscopy. Compounds 1 and 3 - 11 were tested against HL-60, HO-8910 and A-549 human tumor cells. Compounds 4, 6 and 10 showed significant cytotoxicity against HL-60 cells with IC (50) values of 4.6, 2.0 and 3.4 microM, respectively, and against A-549 cells with IC (50) values of 17.5, 11.4 and 18.8 microM, respectively. Compound 6 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against HO-8910 cells with an IC (50) value of 17.9 microM.
[Chemical constituents of Isodon parvifolia (Batalin) Hara].[Pubmed:2390167]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 1990 Feb;15(2):101-3, 127.
Twelve compounds were isolated from the leaves and stems of Isodon parvifolia. This paper deals with the isolation and identification of two diterpenes Epinodosinol (I), lasiodonin (II) and two triterpenes alpha-amyrin (XI a) and beta-amyrin (XI b).


